Difference between revisions of "Artificial cave"
(wall stabilization methods) |
(img+) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Drilling an '''artificial cave''' is a concept to create room for an artificial [[habitat]]. If no usable natural [[caves]] are found an [[mining|artificial tunnel]] can be drilled into a rock mountain. The walls of the tunnel must be stabilized. For automated construction, the usage of segmented rings or [[arch segments]] can be considered, made from [[sintered regolith]] or [[concrete]]. Sprayed [[foam]] could also be used to stabilize the walls. | Drilling an '''artificial cave''' is a concept to create room for an artificial [[habitat]]. If no usable natural [[caves]] are found an [[mining|artificial tunnel]] can be drilled into a rock mountain. The walls of the tunnel must be stabilized. For automated construction, the usage of segmented rings or [[arch segments]] can be considered, made from [[sintered regolith]] or [[concrete]]. Sprayed [[foam]] could also be used to stabilize the walls. | ||
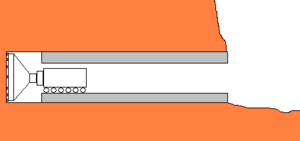
| + | [[Image:tunnelgreenhouse.png|thumb|left|100px|sectional view of a tunnel, used as a greenhouse]] | ||
For example, a tunnel with a diameter of 5 meters is drilled. The stabilization reduces the diameter to 4 meters. Thermal [[insulation]] leads to another reduction to approx. 3 meters. With such a tunnel of 1 km length it should be possible to build an underground [[greenhouse]] to feed 10 people. | For example, a tunnel with a diameter of 5 meters is drilled. The stabilization reduces the diameter to 4 meters. Thermal [[insulation]] leads to another reduction to approx. 3 meters. With such a tunnel of 1 km length it should be possible to build an underground [[greenhouse]] to feed 10 people. | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 16 January 2009
Drilling an artificial cave is a concept to create room for an artificial habitat. If no usable natural caves are found an artificial tunnel can be drilled into a rock mountain. The walls of the tunnel must be stabilized. For automated construction, the usage of segmented rings or arch segments can be considered, made from sintered regolith or concrete. Sprayed foam could also be used to stabilize the walls.
For example, a tunnel with a diameter of 5 meters is drilled. The stabilization reduces the diameter to 4 meters. Thermal insulation leads to another reduction to approx. 3 meters. With such a tunnel of 1 km length it should be possible to build an underground greenhouse to feed 10 people.
Though the drilling requires a high sophisticated digging machine this concept allows the creation of virtually unlimited room with best protection against radiation and meteorites. Once the drill is in place the process is continual and easy to be remote controlled and is, therefore, considered to be part of the unmanned setup of a whole settlement.
| Concepts: | Greenhouse · Settlements · Locations · General |
| Hazards: | Space Weather · Climate · General |
| Technology: | Hi-Tech · Lo-Tech · Energy · Spaceflight science · Communication · General |
| Human Considerations: | Economics · Health · Governance · Trade · Law · Social |