Difference between revisions of "Mars Express"
| (24 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Mars Express''' was launched on June 2, 2003 from [[Baikonur Cosmodrome]] on a [[Soyuz-Fregat]] | + | [[Image:Mars Express X orbit 2a-new.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Artists impression of the Mars Express orbiter]] |
| + | |||
| + | '''Mars Express''' was launched on June 2, 2003 from [[Baikonur Cosmodrome]] (Kazakhstan) on a [[Soyuz-Fregat rocket]] to search for water and the possibility of Martian life. Consisting of a low-cost orbiter and lander, ''Mars Express'' is a [[European Space Agency]] (ESA) mission to the Red Planet involving a consortium of countries (primarily France, Germany, Great Britain, Ireland, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Norway, Russia, Sweden, Spain, and the United States). In February 2007, ''Mars Express'' was granted a second mission extension until May 2009. | ||
==Mission Overview== | ==Mission Overview== | ||
| − | ''Mars Express'' was a two-component mission consisting of the ''Mars Express Orbiter'' and [[Beagle 2]] lander. Unfortunately, the ''Beagle 2'' lander failed on entry into the Martian atmosphere and was lost on Christmas Day, 2003. The crash site of ''Beagle 2'' was later imaged by [[NASA]]'s [[Mars Global Surveyor]] in a | + | [[Image:Mars express logo.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Official [[ESA]] Mars Express mission logo.]] |
| + | ''Mars Express'' was a two-component mission consisting of the ''Mars Express Orbiter'' and [[Beagle 2]] lander. Unfortunately, the ''Beagle 2'' lander failed on entry into the Martian atmosphere and was lost on Christmas Day, 2003. The crash site of ''Beagle 2'' was later imaged by [[NASA]]'s [[Mars Global Surveyor]] in a crater near the planned landing site of the equatorial region known as [[Isidis Planitia]]. Despite this early loss, the ''Mars Express orbiter'' continues on its mission to explore the Martian surface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mars Express will be providing support for the [[NASA]] [[Phoenix]] lander when it arrives on Mars in mid-2008. | ||
| + | ===Instrumentation=== | ||
The ''Mars Express'' mission is now dedicated to the orbital study of the interior, | The ''Mars Express'' mission is now dedicated to the orbital study of the interior, | ||
| − | subsurface, surface, atmosphere, and environment of Mars. The technology for ''Mars Express'' was developed from cancelled Russian Mars-96 mission and the small ESA ''Rosetta'' mission to small solar system bodies (i.e. comets and asteroids). The orbiter carried eight instruments at launch: | + | subsurface, surface, atmosphere, and environment of Mars. The technology for ''Mars Express'' was developed from cancelled [[Russian Mars-96]] mission and the small ESA ''Rosetta'' mission to small solar system bodies (i.e. comets and asteroids). The orbiter carried eight instruments at launch: |
* The ''High Resolution Stereo Camera'' (HRSC) for high resolution surface imaging. | * The ''High Resolution Stereo Camera'' (HRSC) for high resolution surface imaging. | ||
* ''Energetic Neutron Atoms Analyser'' (ASPERA) to analyse how the [[solar wind]] erodes the Martian atmosphere. | * ''Energetic Neutron Atoms Analyser'' (ASPERA) to analyse how the [[solar wind]] erodes the Martian atmosphere. | ||
* ''Planetary Fourier Spectrometer'' (PFS) to study of the atmospheric composition and circulation. | * ''Planetary Fourier Spectrometer'' (PFS) to study of the atmospheric composition and circulation. | ||
| − | * ''Visible and Infrared Mineralogical Mapping Spectrometer'' (OMEGA) to determine the surface composition and evolution processes. | + | * ''Visible and Infrared Mineralogical Mapping Spectrometer'' (OMEGA) to determine the [[surface composition]] and evolution processes. |
* ''Sub-Surface Sounding Radar Altimeter'' (MARSIS) intended for the search for water in the subsurface. | * ''Sub-Surface Sounding Radar Altimeter'' (MARSIS) intended for the search for water in the subsurface. | ||
* ''The Radio Science Experiment'' (MaRS) for sounding of the internal structure, atmosphere and environment. | * ''The Radio Science Experiment'' (MaRS) for sounding of the internal structure, atmosphere and environment. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 21: | ||
* ''Beagle 2'' lander intended for [[geochemistry]] and [[exobiology]]. | * ''Beagle 2'' lander intended for [[geochemistry]] and [[exobiology]]. | ||
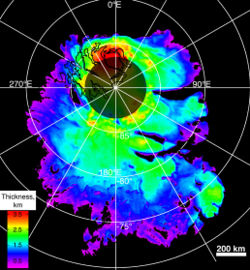
| + | [[Image:MARSIS.jpg|thumb|250px|right|A MARSIS map of Mars' south pole ice deposits.]] | ||
| + | == Scientific Discoveries == | ||
| + | Mars Express has made several important discoveries during its mission: | ||
| + | * Detection of [[water]] in the southern polar icecap using OMEGA (2004) | ||
| + | * Detection of [[methane]] & [[ammonia]] in the Martian atmosphere using PFS (2004) | ||
| + | * Location of an area of water ice near the north pole using HRSC (2005) | ||
| + | * Mapping the [[water|location and thickness of water ice]] in the south pole with the MARSIS instrument (2007) | ||
| + | It has also carried out a wide variety of other important observations which have increased understanding of the Martian atmosphere and geology. | ||
| + | == External links == | ||
| + | * [http://www.esa.int/SPECIALS/Mars_Express/index.html ESA's Mars Express pages] | ||
| + | * [http://www.esa.int/esa-mmg/mmg.pl?mission=Mars+Express Recent Mars Express images] | ||
| + | * [http://marsprogram.jpl.nasa.gov/express/ NASA's Mars Express pages] | ||
| + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mars_Express Wikipedia page on Mars Express] | ||
| − | + | [[category:Orbital Missions]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[category:Missions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:23, 17 December 2018
Mars Express was launched on June 2, 2003 from Baikonur Cosmodrome (Kazakhstan) on a Soyuz-Fregat rocket to search for water and the possibility of Martian life. Consisting of a low-cost orbiter and lander, Mars Express is a European Space Agency (ESA) mission to the Red Planet involving a consortium of countries (primarily France, Germany, Great Britain, Ireland, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Norway, Russia, Sweden, Spain, and the United States). In February 2007, Mars Express was granted a second mission extension until May 2009.
Mission Overview

Mars Express was a two-component mission consisting of the Mars Express Orbiter and Beagle 2 lander. Unfortunately, the Beagle 2 lander failed on entry into the Martian atmosphere and was lost on Christmas Day, 2003. The crash site of Beagle 2 was later imaged by NASA's Mars Global Surveyor in a crater near the planned landing site of the equatorial region known as Isidis Planitia. Despite this early loss, the Mars Express orbiter continues on its mission to explore the Martian surface.
Mars Express will be providing support for the NASA Phoenix lander when it arrives on Mars in mid-2008.
Instrumentation
The Mars Express mission is now dedicated to the orbital study of the interior, subsurface, surface, atmosphere, and environment of Mars. The technology for Mars Express was developed from cancelled Russian Mars-96 mission and the small ESA Rosetta mission to small solar system bodies (i.e. comets and asteroids). The orbiter carried eight instruments at launch:
- The High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) for high resolution surface imaging.
- Energetic Neutron Atoms Analyser (ASPERA) to analyse how the solar wind erodes the Martian atmosphere.
- Planetary Fourier Spectrometer (PFS) to study of the atmospheric composition and circulation.
- Visible and Infrared Mineralogical Mapping Spectrometer (OMEGA) to determine the surface composition and evolution processes.
- Sub-Surface Sounding Radar Altimeter (MARSIS) intended for the search for water in the subsurface.
- The Radio Science Experiment (MaRS) for sounding of the internal structure, atmosphere and environment.
- Ultraviolet and Infrared Mars Atmospheric Spectrometer (SPICAM) for the determination of the composition of the atmosphere of Mars.
- Beagle 2 lander intended for geochemistry and exobiology.
Scientific Discoveries
Mars Express has made several important discoveries during its mission:
- Detection of water in the southern polar icecap using OMEGA (2004)
- Detection of methane & ammonia in the Martian atmosphere using PFS (2004)
- Location of an area of water ice near the north pole using HRSC (2005)
- Mapping the location and thickness of water ice in the south pole with the MARSIS instrument (2007)
It has also carried out a wide variety of other important observations which have increased understanding of the Martian atmosphere and geology.