Nuclear fusion
Modern nuclear power generates energy by splitting apart rare, huge atoms releasing the binding energy. This is called nuclear fission.
However, stars generate energy by joining small atoms into larger ones. This is called fusion. Fusion power plants have not been built on Earth yet. But if such a power source is created, it might be a good source of power on Mars.
Currently several countries and private firms are working to build a profitable fusion reactor.
Contents
Advantages on Mars
- Fusion may use Deuterium, an Isotope of hydrogen with one proton and one neutron. Deuterium is rare, and expensive to concentrate. However, Deuterium on Mars is 5 times more common than on Earth, so this concentration step would be 5 times cheaper. (In fact, deuterium is so expensive, it might be worth exporting concentrated deuterium to Earth.) If Fusion Propulsion space craft are built, Mars may be a spot to inexpensively refuel them. (Mars' low gravity makes getting fuel into space cheaper than on Earth.)
- Fusion powered ship should be faster than chemical ones, making the transit to Mars faster and easier.
This is a stub. Help Marspedia by expanding this article.
Fusion propulsion
General Physical Characteristics of Fusion Propulsion Systems
Fusion rockets use a propellant, which in most systems is comprised of the reaction products, unspent fuel, and other material directly involved in the underlying fusion reaction. These materials are contained within a reaction chamber and ejected via a magnetic nozzle. The nozzle typically includes an energy recovery system that is used to power the ignition system, called the ‘‘driver’’. A secondary energy production system is usually required to enable start-up of the propulsion system.
In some variations, the driver may be powered by an external source.
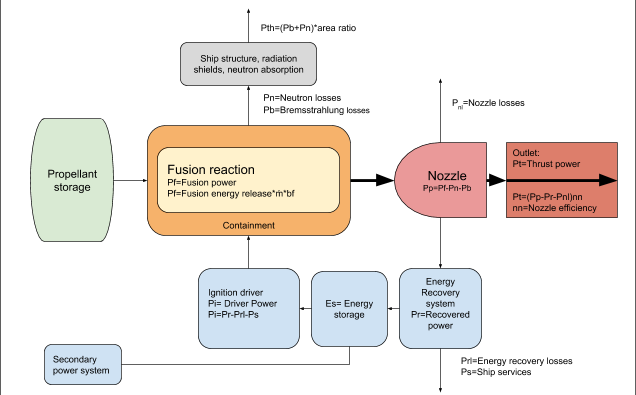
The power flow within a fusion propulsion system is shown in the following graph. The graph also shows the physical systems that are required to produce fusion propulsion system.
Fusion drive example
Pf= Fusion power, Pf=Fe*ṁ*bf
Pp= Plasma power, Pp=Pf-Pn-Pb
Pn= Neutron losse s
Pb= Bremsstrahlung losses
Pt= Thrust power, Pt=(Pp-Pr-Pnl)*ηn
Pnl= Nozzle (reaction chamber) power losses
Pr= Recovered power, Pr=Prl-Ps
Prl= Energy recovery system power losses
Ps= Power to ship services
Pi= Driver power (ignition power)
Es= Energy stored in energy recovery system
Pth= Thermal power loads from radiation losses, Pth=(Pn+Pb)*area ratio
ηn= Nozzle efficiency
bf= Burnup fraction
ṁ= Mass flow of propellant
G= Gain, G=Pf/Pi
Fusion power = fusion energy release*mass flow*burnup fraction, Pf=Ef*ṁ*bf
Plasma power = Fusion power-Neutron losses-bremsstrahlung losses, Pp=(Pf-Pn-Pb)ηn
Thrust power = (Plasma power-Recovered power-Nozzle power losses)*nozzle efficiency, Pt=(Pp-Pr-Pnl)ηn
Ignition power = Power recovery-Power recovery system losses- Ship services, Pi=Pr-Prl-Ps
Recovered power may be replaced by an external source. Project Longshot() used a separate nuclear reactor to power ignition.
Fusion gain = Fusion power/ Recovered power, G=Pf / Pr
According to Newton’s laws of motion the vehicle thrust (F) is equal to the mass flow rate (ṁ) times the exhaust velocity(ve) and the efficiency of the nozzle (ηn):
F=ṁ*ve*ηn
Since for a rocket the power (P) can be related to the thrust by the following equation:
Pt=1/2ṁve2 or
ve =√(2Pt/ṁ)
It follows that the thrust is related to the power by:
F=ṁ*√(2Pt/ṁ)*ηn or
F=√(ṁ*2Pt)*ηn
The rocket equation uses the exhaust velocity Ve to find the mass ratio of the vehicle and the final rocket velocity:
Rocket equation:
Vf=Ve*ln(mo/mf)
If the mass flow is constant (as per most of these fusion designs) the distance crossed while under power is:
s=Ve*(t-(m0/ṁ))*ln(m0/mf)+t(Vo-Ve)
where (t) is the time under power and Vo the initial velocity.
Using our earlier mass flow (ṁ) of 1 kg/s and power (P) of 35 300 GW, and supposing an overall efficiency of 0,8, including fusion losses, the thrust from the fusion drive will be F=√(1kg/s*35300GW*2)*0,8= 8 403 000 N or 857 tonnes. This is about ¼ of the thrust of the Saturn 5 rocket.