Difference between revisions of "Starship"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
The fundamental enabling technology of the Starship is retro propulsive landing on Mars. The use of retro propulsion in a critical phase of the Mars entry path allows the vehicle to land heavier payloads that previously thought possible. Although the exact details are not public, the current SpaceX Falcon 9 booster rocket has done flight tests that would confirm the flight path. <ref>[https://elib.dlr.de/120072/1/00040_ECKER.pdf]</ref> | The fundamental enabling technology of the Starship is retro propulsive landing on Mars. The use of retro propulsion in a critical phase of the Mars entry path allows the vehicle to land heavier payloads that previously thought possible. Although the exact details are not public, the current SpaceX Falcon 9 booster rocket has done flight tests that would confirm the flight path. <ref>[https://elib.dlr.de/120072/1/00040_ECKER.pdf]</ref> | ||
| + | <references />AEROTHERMAL ANALYSIS OF REUSABLE LAUNCHER SYSTEMS DURING RETRO-PROPULSION REENTRY AND LANDING | ||
Revision as of 10:10, 6 April 2019
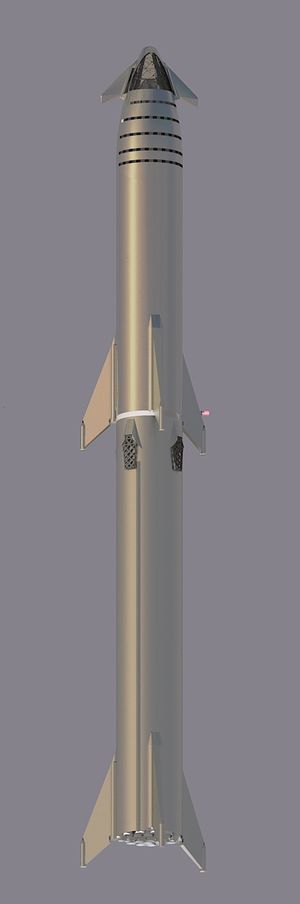
Starship is the name of the 2019 version of the second stage of the SpaceX super heavy lift vehicle.
It was presented by Elon Musk during the announcement of Yusaku Maezawa' Dear Moon project, as an evolution of the BFR/BFS concept.
Originally planned to be constructed of carbon fiber composite, it was changed to a Stainless Steel design.
9m diameter, 100 tonnes to LEO, 100 tonnes to Mars
120 day transportation time
Raptor engine
The fundamental enabling technology of the Starship is retro propulsive landing on Mars. The use of retro propulsion in a critical phase of the Mars entry path allows the vehicle to land heavier payloads that previously thought possible. Although the exact details are not public, the current SpaceX Falcon 9 booster rocket has done flight tests that would confirm the flight path. [1]
AEROTHERMAL ANALYSIS OF REUSABLE LAUNCHER SYSTEMS DURING RETRO-PROPULSION REENTRY AND LANDING