Difference between revisions of "Jezero Crater"
(→External links: added to list) |
(added new info and ref) |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
The Mars 2020 rover mission will be able to examine at least 5 types of rock, including clays and carbonates.<ref>https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7539&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily-20191112-1</ref> These can preserve signs of ancient life. Additional materials probably washed in from the surroundings; therefore, we will be able to determine mineral information about the area around the crater. | The Mars 2020 rover mission will be able to examine at least 5 types of rock, including clays and carbonates.<ref>https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7539&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily-20191112-1</ref> These can preserve signs of ancient life. Additional materials probably washed in from the surroundings; therefore, we will be able to determine mineral information about the area around the crater. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On September 6, 2021 NASA announced that Perseverance rover collected its first sample of Martian rock. Perseverance’s rotary-percussive drill on its robotic arm cored into a flat, briefcase-size rock. It has been called “Rochette.” | ||
| + | The sample was slightly thicker than a pencil. It is now enclosed in an airtight titanium sample tube, making it available for retrieval in the future. NASA and ESA (European Space Agency) are planning future missions to return the rover’s sample tubes to Earth. This first sample was placed in sample tube serial number 266.<ref>https://mars.nasa.gov/news/9029/nasas-perseverance-rover-collects-first-mars-rock-sample/</ref> | ||
| + | |||
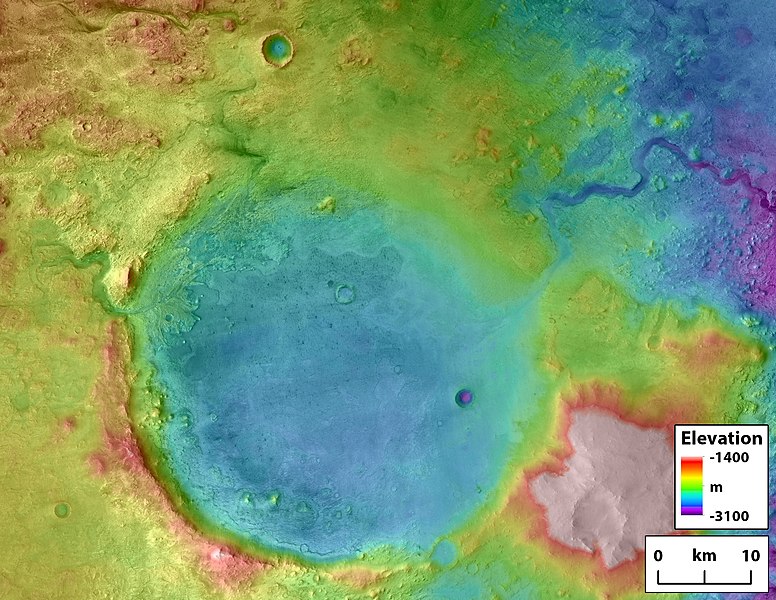
[[File:NASA-Mars-JezeroCrater-20181116.jpg|600pxr|Rivers on the left side of Jezero carried water into the crater, while the overflow went out at the upper right.]] | [[File:NASA-Mars-JezeroCrater-20181116.jpg|600pxr|Rivers on the left side of Jezero carried water into the crater, while the overflow went out at the upper right.]] | ||
Revision as of 08:07, 21 September 2021
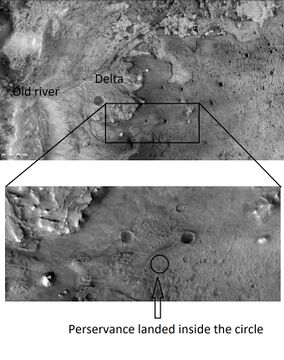
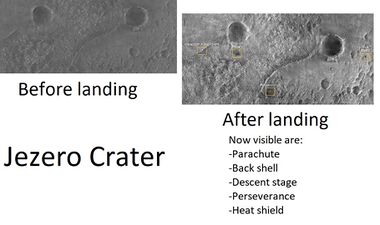
Jezero crater was chosen as the landing site for the Mars 2020 rover mission.[1] [2] [3] Perseverance was the name picked for the rover; it landed right on target near the delta on February 18, 2021.[4]
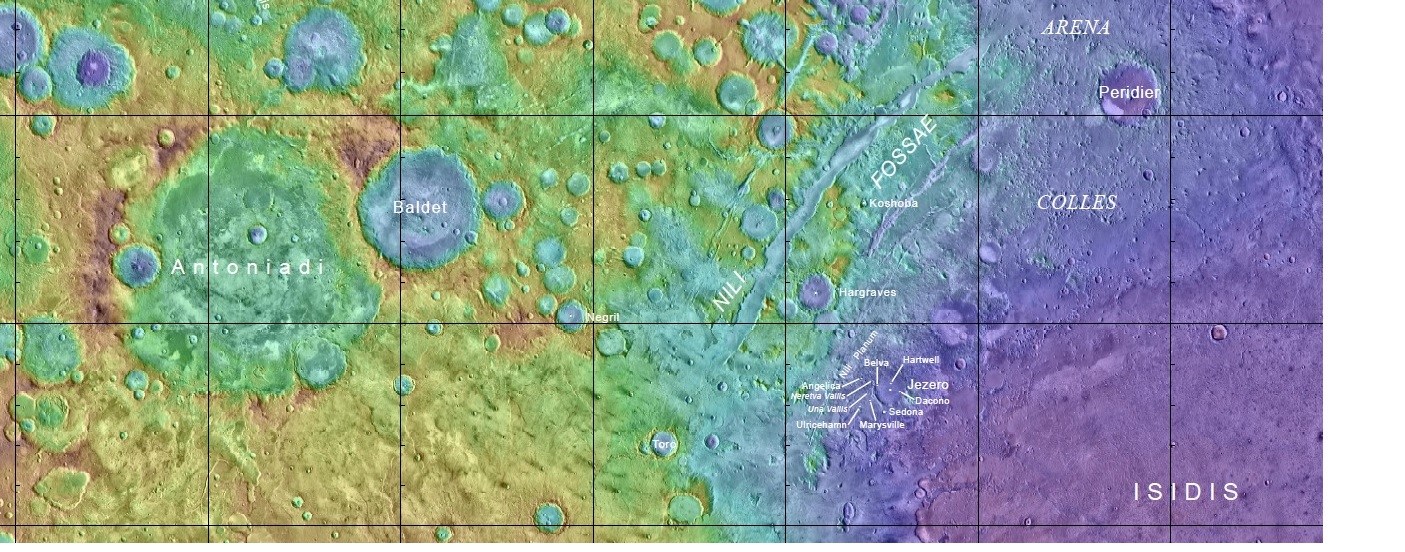
Jezero is an impact crater located at 18.855 N and 77.519 E (282.481 W) in the Syrtis Major quadrangle.[5] [6] It is 47.52 Km in diameter.[7] The crater was named after one of the towns with this name in Bosnia and Herzegovina.[8]
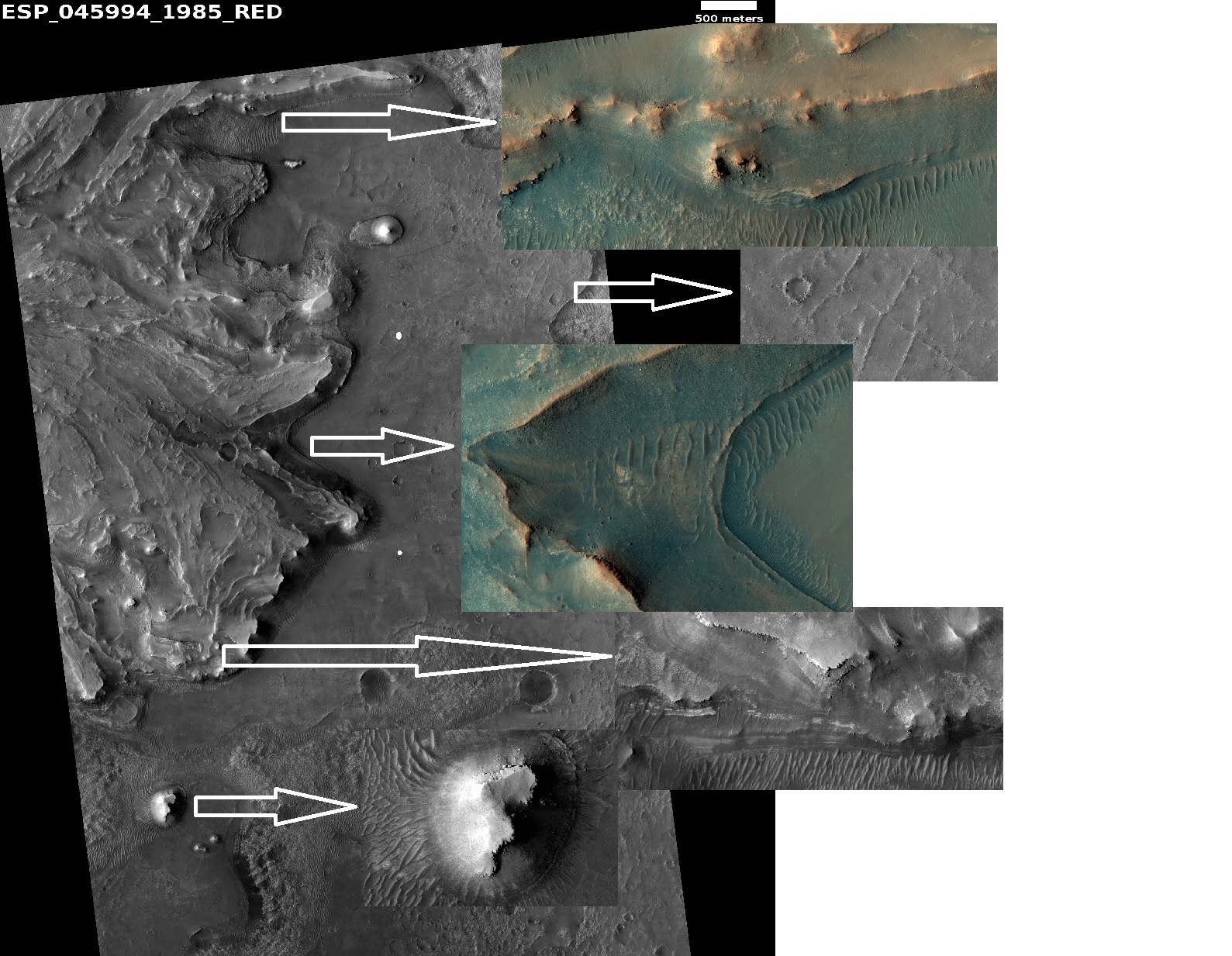
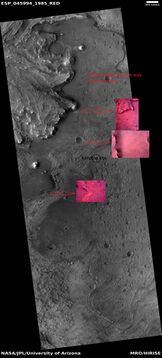
Features near Jezero Crater
Close view of features in and around Jezero Crater
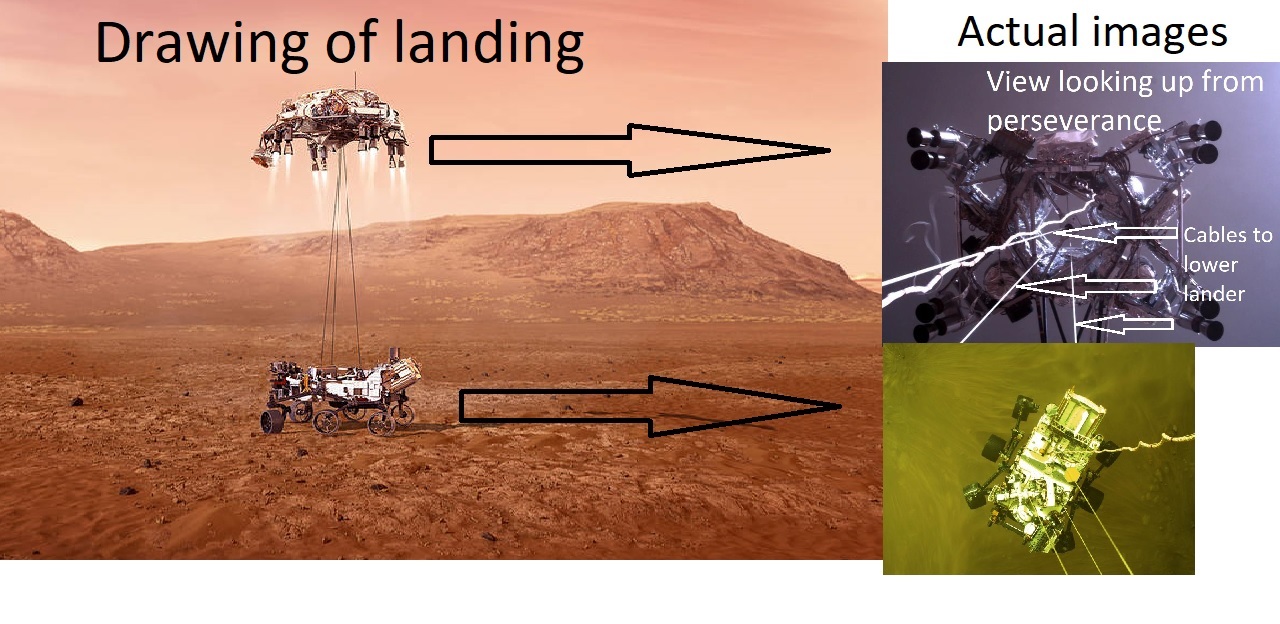
Drawing and actual pictures of Perseverance actual landing on Mars
This is the first 360-degree panorama taken by Mastcam-Z, a zoomable pair of cameras aboard NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover.
Rocket Scour and Wheel Prints https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24488 Taken on March 5, 2021, this color-calibrated image from a Navigation Camera aboard NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover shows tracks from the rover's first drive (darker marks in the foreground) and an area scoured by the Mars 2020 mission's descent stage rockets (lighter-colored area in the middle ground).
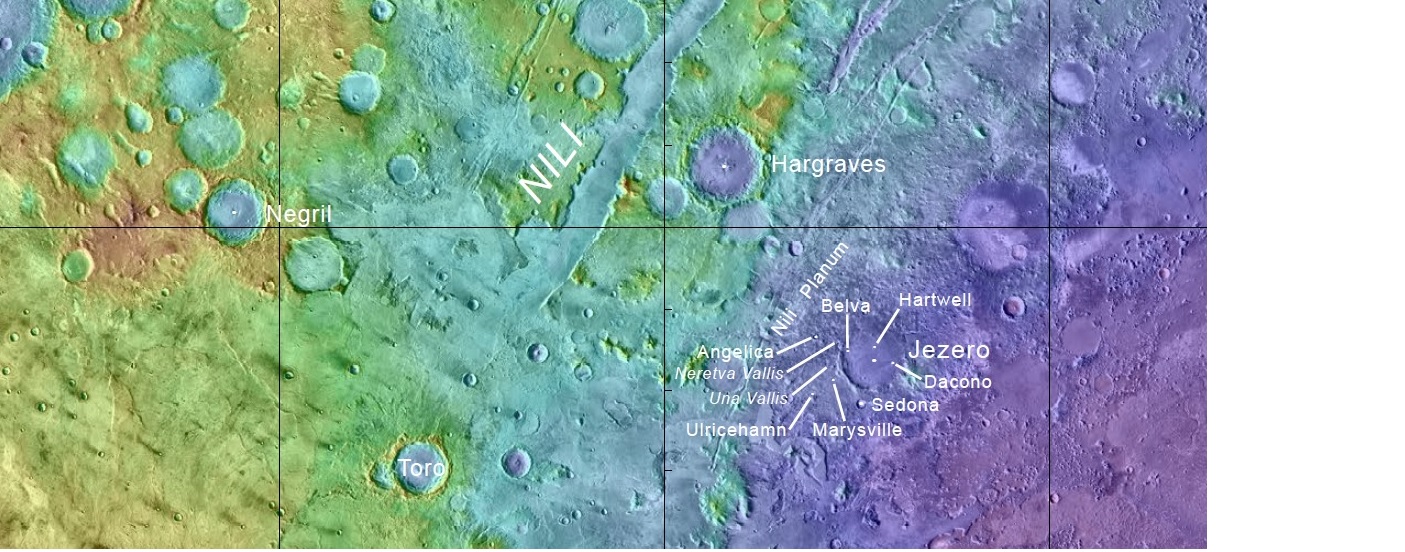
Features in Jezero Crater near delta
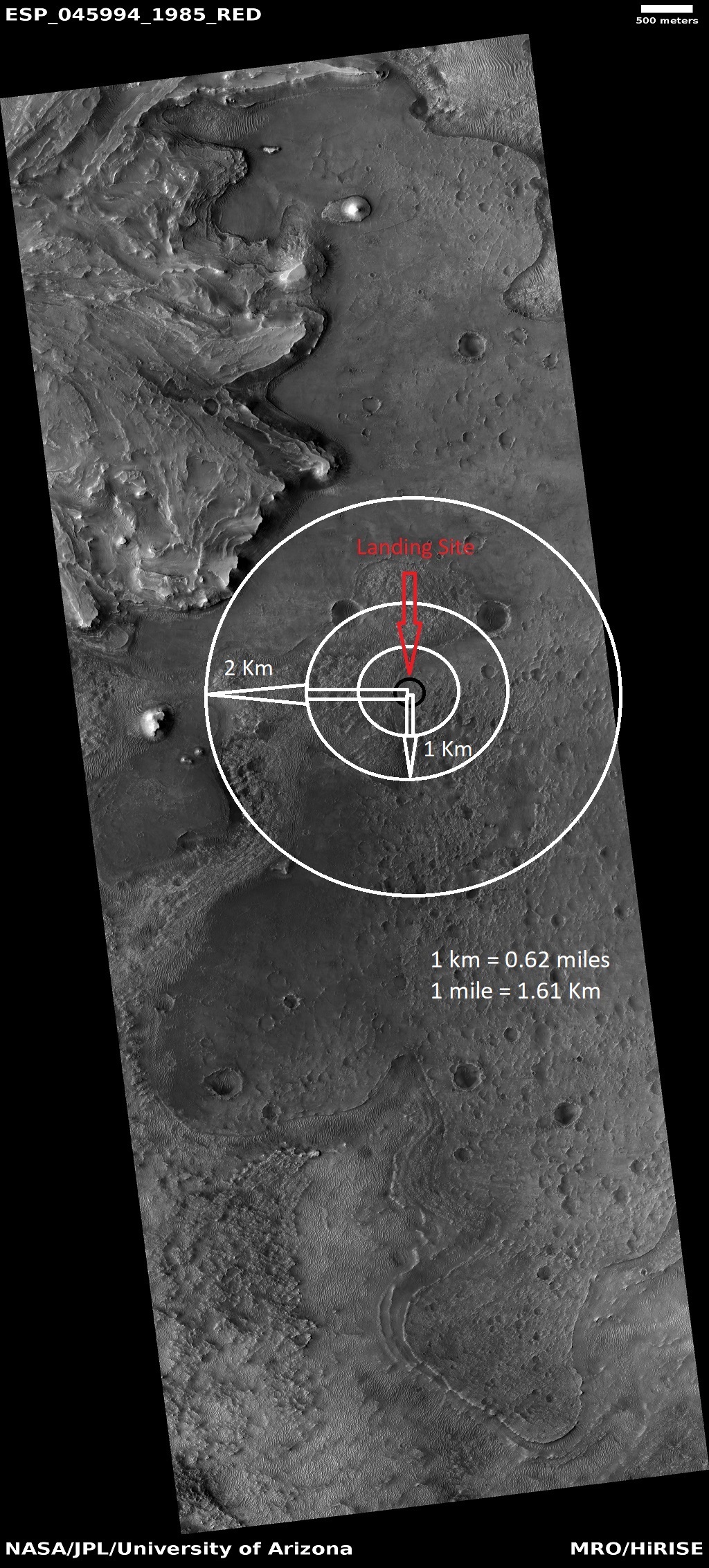
Distances from landing site to various features in Jezero Crater
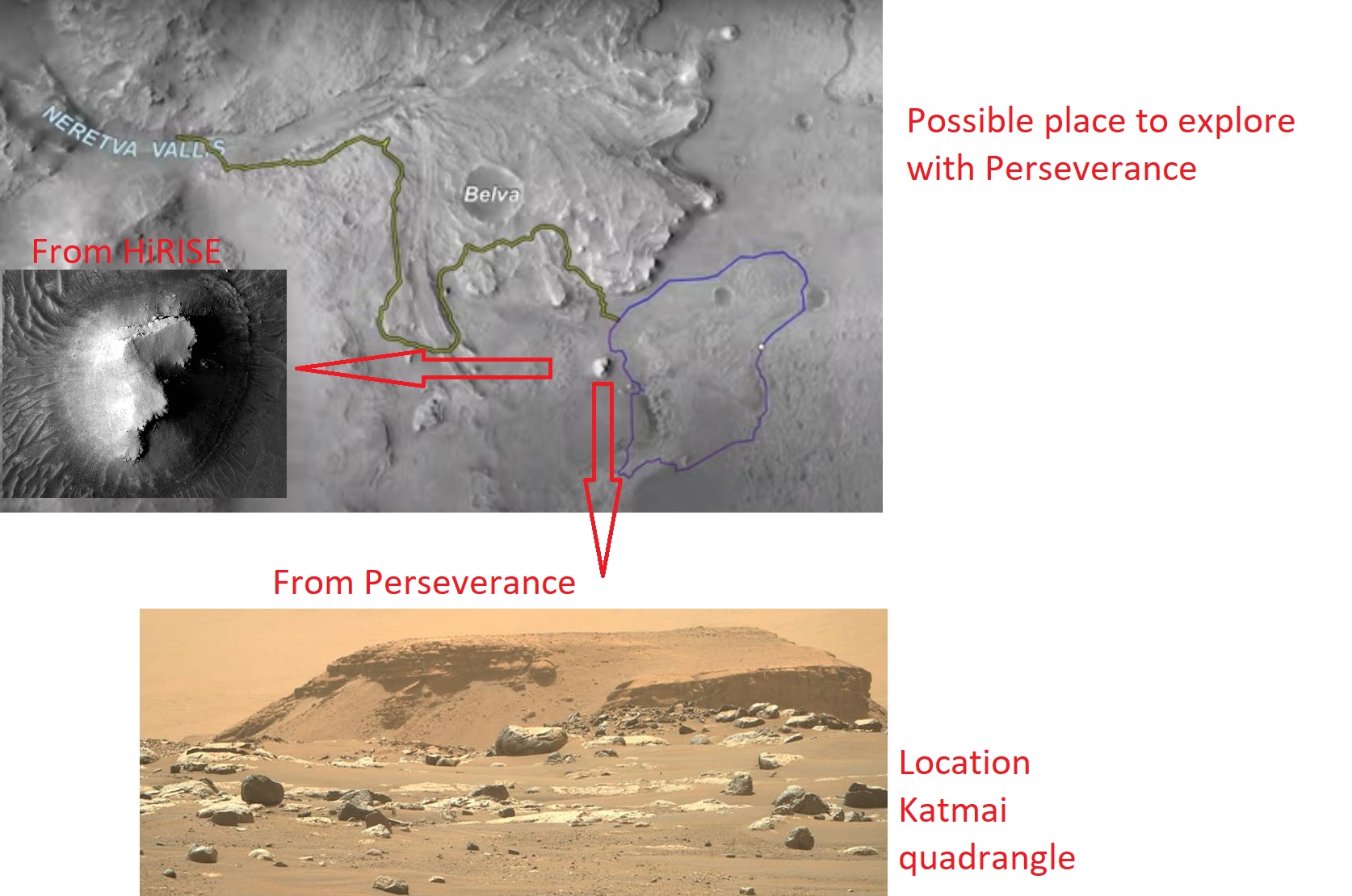 Possible paths for Perseverance in Jezero Crater Mesa is shown from the ground and from orbit.
Possible paths for Perseverance in Jezero Crater Mesa is shown from the ground and from orbit.
Thought to have once been flooded with water, the crater contains a fan-delta deposit rich in clays.[9] The lake in the crater was present when valley networks were forming on Mars.[10] [11] Besides having a delta, the crater shows point bars and inverted channels. From a study of the delta and channels, it was concluded that water stayed in the lake for a time; it did not experience times when the water went down. It probably formed when there was continual surface runoff.[12] Jezero Crater is found on the western edge of Isidis Planitia, which is a giant impact basin just north of the Martian equator. This location contains some of the oldest and most scientifically interesting landscapes of Mars. It is thought that Jezero may hold ancient organic molecules and other signs of microbial life because water and sediments collected in the crater billions of years ago when conditions were much more favorable for life.
A team, lead by Briony Horgan used the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM), high resolution imagery, and digital elevation models, to discover places in Jezero Crater that contain carbonates. These minerals they named “Marginal Carbonates” are found along the inside margin of the crater, near the largest valley and in a delta in the west. The authors of the paper believe they were formed in an old lake in Jezero. Evidence of life could be found in these deposits by the 2020 Rover. Even large fossils of strmatolites could be present.[13] [14]
The Mars 2020 rover mission will be able to examine at least 5 types of rock, including clays and carbonates.[15] These can preserve signs of ancient life. Additional materials probably washed in from the surroundings; therefore, we will be able to determine mineral information about the area around the crater.
On September 6, 2021 NASA announced that Perseverance rover collected its first sample of Martian rock. Perseverance’s rotary-percussive drill on its robotic arm cored into a flat, briefcase-size rock. It has been called “Rochette.”
The sample was slightly thicker than a pencil. It is now enclosed in an airtight titanium sample tube, making it available for retrieval in the future. NASA and ESA (European Space Agency) are planning future missions to return the rover’s sample tubes to Earth. This first sample was placed in sample tube serial number 266.[16]
Rivers on the left side of Jezero carried water into the crater, while the overflow went out at the upper right.
References
- ↑ https://www.space.com/42486-mars-2020-rover-jezero-crater-landing-site.html
- ↑ https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7286&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily20181119-2
- ↑ https://www.sciencenews.org/article/nasa-mars-2020-rover-landing-site-ancient-alien-life-river-delta?utm_source=email&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=latest-newsletter-v2
- ↑ https://mars.nasa.gov/news/8865/touchdown-nasas-mars-perseverance-rover-safely-lands-on-red-planet/
- ↑ https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007925_1990
- ↑ https://www.space.com/mars-2020-alien-life-hunt-microfossils.html?utm_source=Selligent&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=10118&utm_content=20191116_SDC_Newsletter+-+adhoc+&utm_term=2946561&m_i=LKHS2VBMPdPBKbRsJssJ6HqkTujMa1rGRCQddp5zz8Ss3OSL%2Bdjwc5LY%2BNjlmSR30MzcdNIUCuC1q%2Bfn0ySWT1TcOiknL7DjLx
- ↑ https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14300
- ↑ https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14300
- ↑ https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007925_1990
- ↑ Fassett and Head Iii, 2005 C.I. Fassett, J.W. Head Iii Fluvial sedimentary deposits on Mars: ancient deltas in a crater lake in the Nili Fossae region Geophys. Res. Lett., 32 (14) (2005), 10.1029/2005GL023456 n/a–n/a
- ↑ Fassett and Head Iii, 2008 C.I. Fassett, J.W. Head Iii. Valley network-fed, open-basin lakes on Mars: distribution and implications for Noachian surface and subsurface hydrology Icarus, 198 (1) (2008), pp. 37-56, 10.1016/j.icarus.2008.06.016
- ↑ Goudge, T., et al. 2017. STRATIGRAPHY AND EVOLUTION OF DELTA CHANNEL DEPOSITS, JEZERO CRATER, MARS. Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII (2017). 1195.pdf.
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0019103518306067
- ↑ Horgan, B., et al. 2019. The mineral diversity of Jezero crater: Evidence for possible lacustrine carbonates on Mars. Icarus. In press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2019.113526
- ↑ https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7539&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily-20191112-1
- ↑ https://mars.nasa.gov/news/9029/nasas-perseverance-rover-collects-first-mars-rock-sample/
See Also
- Columbus Crater
- Curiosity
- Gale Crater
- Holden Crater
- Mars Perseverance Rover
- Ritchey Crater
- Rivers on Mars
- Syrtis Major quadrangle
- Water
External links
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uzeQ1aha5D4 NASA's Mars 2020 Crater Will Land in Jezero Crater https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uzeQ1aha5D4 NASA's Mars 2020 Crater Will Land in Jezero Crater
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=63PWQeQGfhc Layered Material Cut by a Valley Connected to East Jezero Crater https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=63PWQeQGfhc Layered Material Cut by a Valley Connected to East Jezero Crater
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jev51W_j_5w HiClip mini 4K: In Praise of Jezero Crater https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jev51W_j_5w HiClip mini 4K: In Praise of Jezero Crater
- The Evolution of Water on Mars
- Photogeologic Map of the Perseverance Rover Field Site in Jezero Crater Constructed by the Mars 2020 Science Team