Difference between revisions of "Jezero Crater"
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Jezero crater was chosen as the landing site for the Mars 2020 rover mission.<ref> https://www.space.com/42486-mars-2020-rover-jezero-crater-landing-site.html</ref> <ref> https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7286&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily20181119-2</ref> <ref> https://www.sciencenews.org/article/nasa-mars-2020-rover-landing-site-ancient-alien-life-river-delta?utm_source=email&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=latest-newsletter-v2</ref> | Jezero crater was chosen as the landing site for the Mars 2020 rover mission.<ref> https://www.space.com/42486-mars-2020-rover-jezero-crater-landing-site.html</ref> <ref> https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7286&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily20181119-2</ref> <ref> https://www.sciencenews.org/article/nasa-mars-2020-rover-landing-site-ancient-alien-life-river-delta?utm_source=email&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=latest-newsletter-v2</ref> | ||
| − | Jezero is an impact crater located at 18.855 N and 77.519E in the Syrtis Major quadrangle. <ref> https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007925_1990</ref> It is 47.52 Km in diameter.<ref>https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14300<ref> The crater was named after one of the towns with this name in Bosnia and Herzegovina.<ref>https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14300<ref> | + | Jezero is an impact crater located at 18.855 N and 77.519E in the Syrtis Major quadrangle.<ref> https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007925_1990</ref> It is 47.52 Km in diameter.<ref>https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14300</ref> The crater was named after one of the towns with this name in Bosnia and Herzegovina.<ref>https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14300</ref> |
| + | |||
<gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
File:IMAGE2-MOLAmapjezero.jpg|Jezero Crater is in northern hemisphere. | File:IMAGE2-MOLAmapjezero.jpg|Jezero Crater is in northern hemisphere. | ||
File:JezeroCraterdelta.jpg|A stream carried water into Jezero Crater forming a lake and a delta. | File:JezeroCraterdelta.jpg|A stream carried water into Jezero Crater forming a lake and a delta. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
Thought to have once been flooded with water, the crater contains a fan-delta deposit rich in clays.<ref> https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007925_1990</ref> The lake in the crater was present when valley networks were forming on Mars. Besides having a delta, the crater shows point bars and inverted channels. From a study of the delta and channels, it was concluded that water stayed in the lake for a time; it did not experience times when the water went down. It probably formed when there was continual surface runoff.<ref>Goudge, T., et al. 2017. STRATIGRAPHY AND EVOLUTION OF DELTA CHANNEL DEPOSITS, JEZERO CRATER, MARS. Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII (2017). 1195.pdf. </ref> | Thought to have once been flooded with water, the crater contains a fan-delta deposit rich in clays.<ref> https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007925_1990</ref> The lake in the crater was present when valley networks were forming on Mars. Besides having a delta, the crater shows point bars and inverted channels. From a study of the delta and channels, it was concluded that water stayed in the lake for a time; it did not experience times when the water went down. It probably formed when there was continual surface runoff.<ref>Goudge, T., et al. 2017. STRATIGRAPHY AND EVOLUTION OF DELTA CHANNEL DEPOSITS, JEZERO CRATER, MARS. Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII (2017). 1195.pdf. </ref> | ||
Jezero Crater is found on the western edge of Isidis Planitia, a giant impact basin just north of the Martian equator. This location contains some of the oldest and most scientifically interesting landscapes of Mars. It is thought that Jezero may hold ancient organic molecules and other signs of microbial life because water and sediments collected in the crater billions of years ago when conditions were much more favorable for life. | Jezero Crater is found on the western edge of Isidis Planitia, a giant impact basin just north of the Martian equator. This location contains some of the oldest and most scientifically interesting landscapes of Mars. It is thought that Jezero may hold ancient organic molecules and other signs of microbial life because water and sediments collected in the crater billions of years ago when conditions were much more favorable for life. | ||
Revision as of 11:45, 21 November 2018
Jezero crater was chosen as the landing site for the Mars 2020 rover mission.[1] [2] [3] Jezero is an impact crater located at 18.855 N and 77.519E in the Syrtis Major quadrangle.[4] It is 47.52 Km in diameter.[5] The crater was named after one of the towns with this name in Bosnia and Herzegovina.[6]
Thought to have once been flooded with water, the crater contains a fan-delta deposit rich in clays.[7] The lake in the crater was present when valley networks were forming on Mars. Besides having a delta, the crater shows point bars and inverted channels. From a study of the delta and channels, it was concluded that water stayed in the lake for a time; it did not experience times when the water went down. It probably formed when there was continual surface runoff.[8]
Jezero Crater is found on the western edge of Isidis Planitia, a giant impact basin just north of the Martian equator. This location contains some of the oldest and most scientifically interesting landscapes of Mars. It is thought that Jezero may hold ancient organic molecules and other signs of microbial life because water and sediments collected in the crater billions of years ago when conditions were much more favorable for life.
The Mars 2020 rover mission will be able to examine at least 5 types of rock, including clays and carbonates. These can preserve signs of ancient life. Additional materials probably washed in from the surroundings; therefore, we will be able to determine mineral information about the area around the crater.
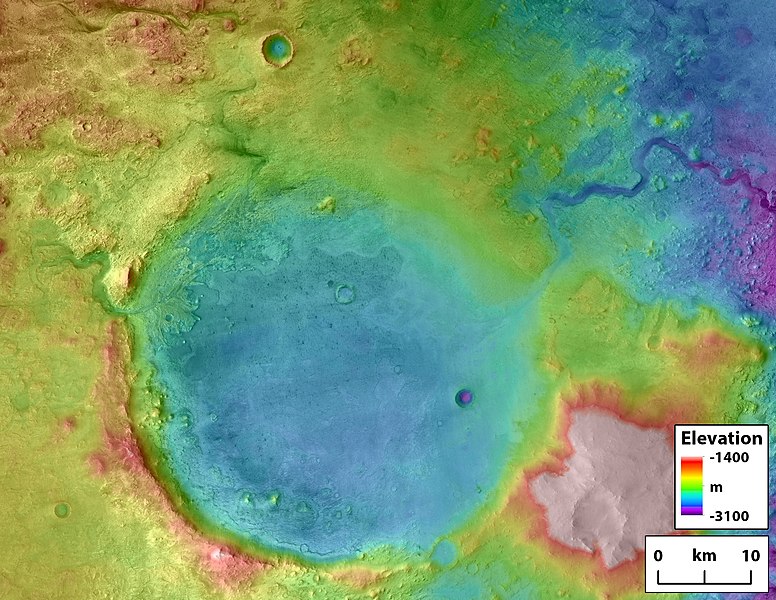
Rivers on the left side of Jezero carried water into the crater, while the overflow went out at the upper right.
References
- ↑ https://www.space.com/42486-mars-2020-rover-jezero-crater-landing-site.html
- ↑ https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7286&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily20181119-2
- ↑ https://www.sciencenews.org/article/nasa-mars-2020-rover-landing-site-ancient-alien-life-river-delta?utm_source=email&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=latest-newsletter-v2
- ↑ https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007925_1990
- ↑ https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14300
- ↑ https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/14300
- ↑ https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007925_1990
- ↑ Goudge, T., et al. 2017. STRATIGRAPHY AND EVOLUTION OF DELTA CHANNEL DEPOSITS, JEZERO CRATER, MARS. Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII (2017). 1195.pdf.
See Also
External links
- [[ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uzeQ1aha5D4 NASA's Mars 2020 Crater Will Land in Jezero Crater]]
- [[ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=63PWQeQGfhc Layered Material Cut by a Valley Connected to East Jezero Crater]]
- [[ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jev51W_j_5w HiClip mini 4K: In Praise of Jezero Crater]]
- [[ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9a79p_Ff1sw Carl Sagan on the Mariner 9 Mars Orbiter: "The Search Begins" 1974 NASA-JPL]]








