Difference between revisions of "Burroughs Crater"
m (→See also) |
(added image) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
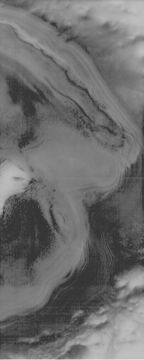
File:Burroughsthemis.jpg|Picture of part of Burroughs Crater, as seen by THEMIS | File:Burroughsthemis.jpg|Picture of part of Burroughs Crater, as seen by THEMIS | ||
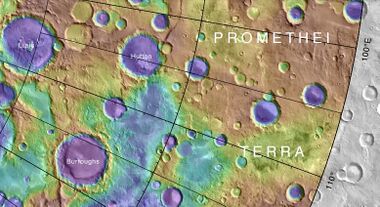
File:Burroughscratertopo.jpg|Topo map showing Burroughs Crater and other nearby features. | File:Burroughscratertopo.jpg|Topo map showing Burroughs Crater and other nearby features. | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:Burroughsctx2.jpg|Picture of eastern part of Burroughs Crater, as seen by CTX | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | An ice deposit in Burroughs Crater contains strong evidence that recent Martian climate is influenced by changes in the planet's orbit and axial tilt.<ref>https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2021GL097450</ref> <ref>Sori, M., et al. 2022. Orbital Forcing of Martian Climate Revealed in a South Polar Outlier Ice Deposit. Geophysical Research Letters. 49:6. e2021GL097450</ref> <ref>https://phys.org/news/2022-03-mounds-ice-craters-insight-mars.html?fbclid=IwAR3NCXL54r5BWWevZhY1fusERFiIElBOpKmNxByP0auxi_ecPjF6oLHbBv0</ref> | + | An ice deposit in Burroughs Crater contains strong evidence that recent Martian climate is influenced by changes in the planet's orbit and axial tilt.<ref>https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2021GL097450</ref> <ref>Sori, M., et al. 2022. Orbital Forcing of Martian Climate Revealed in a South Polar Outlier Ice Deposit. Geophysical Research Letters. 49:6. e2021GL097450</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | <ref>https://phys.org/news/2022-03-mounds-ice-craters-insight-mars.html?fbclid=IwAR3NCXL54r5BWWevZhY1fusERFiIElBOpKmNxByP0auxi_ecPjF6oLHbBv0</ref> | ||
<gallery class="center" widths="380px" heights="360px"> | <gallery class="center" widths="380px" heights="360px"> | ||
| − | File:Burroughslayers.jpg|Layers in Burroughs Crater. These have been shown to be controlled by changes in the tilt of axis. This image is an enlarged part of the above THEMIS image. | + | File:Burroughslayers.jpg|Layers in Burroughs Crater. These have been shown to be controlled by changes in the tilt of axis. This image is an enlarged part of the above THEMIS image and the CTX image. |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 17:02, 4 April 2022
Burroughs Crater lies at latitude 72.5S and longitude 243.1W. It is in the Mare Australe quadrangle and is 104.0 kilometres (64.6 mi) in diameter.[1] It is named after Edgar Rice Burroughs, an American science fiction novelist who wrote a series of fantasy novels Mars Science Fiction set on Mars.
An ice deposit in Burroughs Crater contains strong evidence that recent Martian climate is influenced by changes in the planet's orbit and axial tilt.[2] [3]
References
- ↑ https://dbpedia.org/page/Burroughs_(crater)
- ↑ https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2021GL097450
- ↑ Sori, M., et al. 2022. Orbital Forcing of Martian Climate Revealed in a South Polar Outlier Ice Deposit. Geophysical Research Letters. 49:6. e2021GL097450
- ↑ https://phys.org/news/2022-03-mounds-ice-craters-insight-mars.html?fbclid=IwAR3NCXL54r5BWWevZhY1fusERFiIElBOpKmNxByP0auxi_ecPjF6oLHbBv0