Difference between revisions of "Mars Global Surveyor"
m |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | NASA's '''Mars Global Surveyor''' was launched on November 7, 1996 from [[Cape Canaveral Air Station]] (Florida) on a McDonnell Douglas-built [[Delta II]]-7925 rocket. ''Mars Global Surveyor'' was the first successful US mission launched to Mars in 20 years since the [[Viking]] mission in 1976. On November 2, 2006 it was lost due to loss of power (through incorrect alignment of the solar panels). On arriving into Mars orbit, the [[Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter]] made attempts to image the lost ''Mars Global Surveyor'' so mission control could diagnose the problem, but the spacecraft could not be found. | + | [[Image:Mgs_orbiter.jpg|thumb|right|200px|An artists impression of the '''Mars Global Surveyor''' in orbit above Mars.]] |
| + | |||
| + | NASA's '''Mars Global Surveyor''' was launched on November 7, 1996 from [[Cape Canaveral Air Force Station]] (Florida) on a McDonnell Douglas-built [[Delta II]]-7925 rocket. ''Mars Global Surveyor'' was the first successful US mission launched to Mars in 20 years since the [[:category:Viking Program|Viking]] mission in 1976. On November 2, 2006 it was lost due to loss of power (through incorrect alignment of the solar panels). On arriving into Mars orbit, the [[Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter]] made attempts to image the lost ''Mars Global Surveyor'' so mission control could diagnose the problem, but the spacecraft could not be found. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Observations from the Mars Global Surveyor orbiter are used on the interactive [[Google Mars]] website. | ||
==Mission Overview== | ==Mission Overview== | ||
In its highly successful decade of operations, the ''Mars Global Surveyor'' orbiter became the longest-lasting Mars mission collecting a massive quantity of data about the Martian environment. | In its highly successful decade of operations, the ''Mars Global Surveyor'' orbiter became the longest-lasting Mars mission collecting a massive quantity of data about the Martian environment. | ||
| + | [[Image:moc_mgs.jpg|thumb|center|200px|The Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) onboard the Mars Global Surveyor: Global views of Mars in the late northern summer (2002).]] | ||
| + | |||
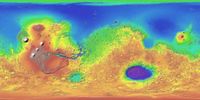
| + | [[File:Mars MGS colorhillshade mola 1024.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Topographic map produced with data from a laser altitmeter onboard the Mars Global Surveyor Colors show relative elevations.]] | ||
| + | |||
===Primary mission=== | ===Primary mission=== | ||
| + | |||
The ''Mars Global Surveyor'' completed its primary mission to: | The ''Mars Global Surveyor'' completed its primary mission to: | ||
* Characterize the surface features and geological processes on Mars. | * Characterize the surface features and geological processes on Mars. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 22: | ||
* Monitor global weather and the thermal structure of the atmosphere. | * Monitor global weather and the thermal structure of the atmosphere. | ||
* Study interactions between Mars' surface and the atmosphere by monitoring surface features, polar caps that expand and recede, the polar energy balance, and dust and clouds as they migrate over a seasonal cycle. | * Study interactions between Mars' surface and the atmosphere by monitoring surface features, polar caps that expand and recede, the polar energy balance, and dust and clouds as they migrate over a seasonal cycle. | ||
| + | |||
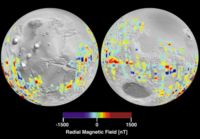
| + | [[Image:mag_mgs.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Magnetometer data from the Electron Reflectometer onboard the Mars Global Surveyor.]] | ||
===Instrumentation=== | ===Instrumentation=== | ||
To achieve this primary objectives, the mission consisted of five principal instruments: | To achieve this primary objectives, the mission consisted of five principal instruments: | ||
* Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) - to produce daily wide-angle and narrow-angle images of Mars. | * Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) - to produce daily wide-angle and narrow-angle images of Mars. | ||
| − | |||
* Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) - to measure the height of Martian surface features such as mountains and depth of valleys. | * Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) - to measure the height of Martian surface features such as mountains and depth of valleys. | ||
* Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) - analysis of infrared radiation by scanning the heat emitted from the surface of Mars to gain insight into the mineral composition of the surface. | * Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) - analysis of infrared radiation by scanning the heat emitted from the surface of Mars to gain insight into the mineral composition of the surface. | ||
* Electron Reflectometer (magnetometer) - to understand the magnetic properties of Mars to probe the interior of the planet. | * Electron Reflectometer (magnetometer) - to understand the magnetic properties of Mars to probe the interior of the planet. | ||
| − | |||
* Gravity Field Experiment (Radio Science) - mapping the gravity variations in Mars' gravitation. | * Gravity Field Experiment (Radio Science) - mapping the gravity variations in Mars' gravitation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pictures from Mars Orbital Camera== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="380px" heights="360px"> | ||
| + | |||
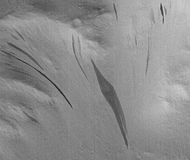
| + | File:Dust devil tracks in Eridania.jpg|Pattern of large and small tracks made by giant dust devils as seen under the MOC Public Targeting Program. Image is located in Eridania quadrangle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:800px-Coprates layers.jpg|Layers in the canyon wall in Coprates quadrangle | ||
| + | |||
| + | Image:Water_deposit.jpg|Evidence from the [[Mars Global Surveyor]] MOC instrument that spurts of liquid water may sporadically flow on the Martian surface]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:Phaethontis surface.jpg|Brain terrain in Phaethontis quadrangle | ||
| + | File:Mantle on Cliff.jpg|Latitude dependent mantle on a cliff face. The circled part shows the edge of the mantle. Mantle falls from the sky and is ice-rich. | ||
| + | File:Tikonravev Crater Floor.JPG|Layers, dark slope streaks, and pedestal crater on floor of Tikonravev Crater | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:Dark streaks in Diacria.JPG|Dark slope streaks | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | *[[MGS Oblique Views]]. | ||
| + | *[[Water]]. | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | [http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/mgs/science/objectives.html MGS mission objectives] | + | *[http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/mgs/science/objectives.html MGS mission objectives] |
| − | [[Category:Missions]] | + | {{Featured_red_ring}} |
| + | [[Category:Orbital Missions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:48, 21 March 2020
NASA's Mars Global Surveyor was launched on November 7, 1996 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (Florida) on a McDonnell Douglas-built Delta II-7925 rocket. Mars Global Surveyor was the first successful US mission launched to Mars in 20 years since the Viking mission in 1976. On November 2, 2006 it was lost due to loss of power (through incorrect alignment of the solar panels). On arriving into Mars orbit, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter made attempts to image the lost Mars Global Surveyor so mission control could diagnose the problem, but the spacecraft could not be found.
Observations from the Mars Global Surveyor orbiter are used on the interactive Google Mars website.
Contents
Mission Overview
In its highly successful decade of operations, the Mars Global Surveyor orbiter became the longest-lasting Mars mission collecting a massive quantity of data about the Martian environment.
Primary mission
The Mars Global Surveyor completed its primary mission to:
- Characterize the surface features and geological processes on Mars.
- Determine the composition, distribution and physical properties of surface minerals, rocks and ice.
- Determine the global topography, planet shape, and gravitational field.
- Establish the nature of the magnetic field and map the crustal remnant field (a crustal remnant field is evidence of magnetism within the planet's crust or rocks, produced by the planet's own magnetic field at the time of formation).
- Monitor global weather and the thermal structure of the atmosphere.
- Study interactions between Mars' surface and the atmosphere by monitoring surface features, polar caps that expand and recede, the polar energy balance, and dust and clouds as they migrate over a seasonal cycle.
Instrumentation
To achieve this primary objectives, the mission consisted of five principal instruments:
- Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) - to produce daily wide-angle and narrow-angle images of Mars.
- Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) - to measure the height of Martian surface features such as mountains and depth of valleys.
- Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) - analysis of infrared radiation by scanning the heat emitted from the surface of Mars to gain insight into the mineral composition of the surface.
- Electron Reflectometer (magnetometer) - to understand the magnetic properties of Mars to probe the interior of the planet.
- Gravity Field Experiment (Radio Science) - mapping the gravity variations in Mars' gravitation.
Pictures from Mars Orbital Camera
Evidence from the Mars Global Surveyor MOC instrument that spurts of liquid water may sporadically flow on the Martian surface]]