Difference between revisions of "Hecates Tholus"
(added info and ref) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Image:Hecates_Tholus.jpg|thumb|right|px|Hecates Tholus with [[cloud|clouds]]]]'''Hecates Tholus''' is a [[volcano]] in the [[Elysium Volcanic Region]]. | + | [[Image:Hecates_Tholus.jpg|thumb|right|px|Hecates Tholus with [[cloud|clouds]]]]'''Hecates Tholus''' is a [[volcano]] in the [[Elysium Volcanic Region]]. |
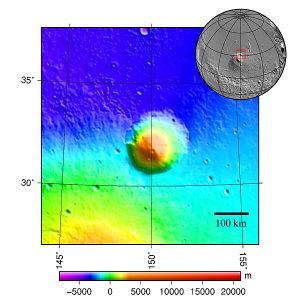
[[Image:MOLA hecates tholus.jpg |thumb|left|px|Tographic map of area around Hecates Tholus]] | [[Image:MOLA hecates tholus.jpg |thumb|left|px|Tographic map of area around Hecates Tholus]] | ||
| + | Hecates is in the Cebrenia quadrangle. It is thought that the [[caldera]] may have had [[glacier|glaciers]] in the past.<ref>http://www.msnbc.msn/id/7209308</ref> Some valleys on Hecates show a parallel drainage pattern.<ref>Hugh H. Kieffer 1992. Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7.</ref> Using the High Resolution Stereo Camera onboard ESA's Mars Express that is orbiting Mars, a team of researchers discovered evidence of a large explosive eruption and recent glaciers on the volcano. Although some of the ice has sublimated into the atmosphere, the authors believe there ice still exists under a cover of debris. They state the ice could be "accessible for automated or human exploration."<ref>Hauber, E., et al. 2005. Discovery of flank caldera and very young glacial activity at Hecates Tholus, Mars. Nature: 434, 356-361.</ref> On Earth 8 million year old ice is still present in the Antarctic dry valleys under a layer of dirt.<ref>Marchant, D., et al. 2002. Formation of patterned ground and sublimation till over Miocene glacial ice in Beacon Valley, southern Victoria Land, Antarctia. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 114, 718-730.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:27108hecatechannels.jpg |thumb|right|px|Lava channels on Hecates Tholus]] | [[Image:27108hecatechannels.jpg |thumb|right|px|Lava channels on Hecates Tholus]] | ||
Revision as of 09:32, 15 February 2018

Hecates Tholus with clouds
Hecates Tholus is a volcano in the Elysium Volcanic Region.
Hecates is in the Cebrenia quadrangle. It is thought that the caldera may have had glaciers in the past.[1] Some valleys on Hecates show a parallel drainage pattern.[2] Using the High Resolution Stereo Camera onboard ESA's Mars Express that is orbiting Mars, a team of researchers discovered evidence of a large explosive eruption and recent glaciers on the volcano. Although some of the ice has sublimated into the atmosphere, the authors believe there ice still exists under a cover of debris. They state the ice could be "accessible for automated or human exploration."[3] On Earth 8 million year old ice is still present in the Antarctic dry valleys under a layer of dirt.[4]
References:
- ↑ http://www.msnbc.msn/id/7209308
- ↑ Hugh H. Kieffer 1992. Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7.
- ↑ Hauber, E., et al. 2005. Discovery of flank caldera and very young glacial activity at Hecates Tholus, Mars. Nature: 434, 356-361.
- ↑ Marchant, D., et al. 2002. Formation of patterned ground and sublimation till over Miocene glacial ice in Beacon Valley, southern Victoria Land, Antarctia. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 114, 718-730.