Difference between revisions of "Cosmic rays"
m (Minor format changes.) |
m (Added information on particle types.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Composition == | ||
| + | Cosmic radiation comprises 85% protons, 14% alpha particles, and 1% heavy ions.<ref>Schimmerling W. (2011, Feb 5). The Space Radiation Environment: An Introduction. <nowiki>https://three.jsc.nasa.gov/concepts/SpaceRadiationEnviron.pdf</nowiki></ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Energy == | ||
[[File:GCR spectra.png|alt=|frame|Energy distribution of cosmic radiation, as measured during the 1977 solar minimum.<ref>Kim MY, Thibeault SA, Simonsen LC, Wilson JW. (1998). Comparison of Martian Meteorites and Martian Regolith as Shield Materials for Galactic Cosmic Rays. NASA TP-1998-208724. <nowiki>http://hdl.handle.net/2060/19980237030</nowiki></ref>|none]] | [[File:GCR spectra.png|alt=|frame|Energy distribution of cosmic radiation, as measured during the 1977 solar minimum.<ref>Kim MY, Thibeault SA, Simonsen LC, Wilson JW. (1998). Comparison of Martian Meteorites and Martian Regolith as Shield Materials for Galactic Cosmic Rays. NASA TP-1998-208724. <nowiki>http://hdl.handle.net/2060/19980237030</nowiki></ref>|none]] | ||
| − | == References == | + | ==References== |
[[Category:Medicine]] | [[Category:Medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Radiation Protection]] | [[Category:Radiation Protection]] | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 11:21, 3 March 2019
Composition
Cosmic radiation comprises 85% protons, 14% alpha particles, and 1% heavy ions.[1]
Energy
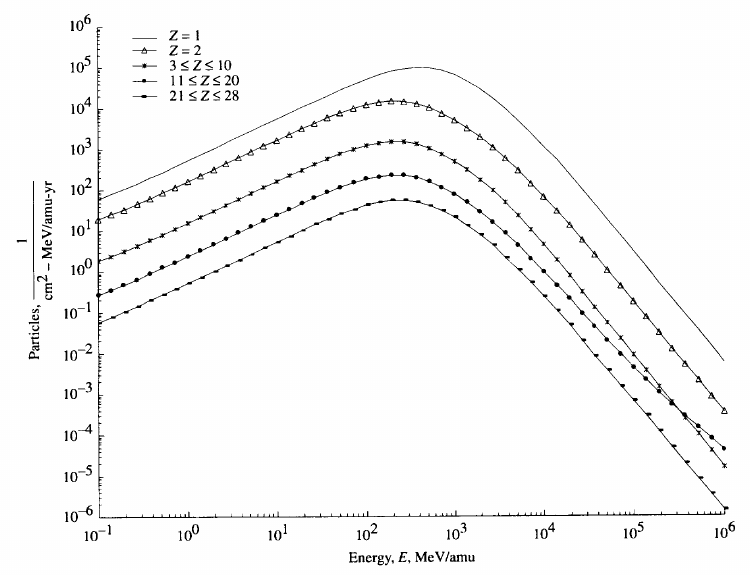
Energy distribution of cosmic radiation, as measured during the 1977 solar minimum.[2]
References
- ↑ Schimmerling W. (2011, Feb 5). The Space Radiation Environment: An Introduction. https://three.jsc.nasa.gov/concepts/SpaceRadiationEnviron.pdf
- ↑ Kim MY, Thibeault SA, Simonsen LC, Wilson JW. (1998). Comparison of Martian Meteorites and Martian Regolith as Shield Materials for Galactic Cosmic Rays. NASA TP-1998-208724. http://hdl.handle.net/2060/19980237030






