Difference between revisions of "Cosmic rays"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Cosmic rays are high energy particles that are part of the background radiation in space. Most cosmic rays are | + | Cosmic rays are high energy particles that are part of the background radiation in space. Most cosmic rays are absorbed in the Earth's atmosphere and do not reach the planet's surface. On Mars, cosmic rays are not absorbed as the atmosphere is too thin, and [[radiation shielding]] is required for the habitats. |
| − | == Composition == | + | ==Composition== |
Cosmic radiation comprises 85% protons, 14% alpha particles, and 1% heavy ions.<ref>Schimmerling W. (2011, Feb 5). The Space Radiation Environment: An Introduction. <nowiki>https://three.jsc.nasa.gov/concepts/SpaceRadiationEnviron.pdf</nowiki></ref> | Cosmic radiation comprises 85% protons, 14% alpha particles, and 1% heavy ions.<ref>Schimmerling W. (2011, Feb 5). The Space Radiation Environment: An Introduction. <nowiki>https://three.jsc.nasa.gov/concepts/SpaceRadiationEnviron.pdf</nowiki></ref> | ||
| − | == Energy == | + | ==Energy== |
[[File:GCR spectra.png|alt=|frame|Energy distribution of cosmic radiation, as measured during the 1977 solar minimum.<ref>Kim MY, Thibeault SA, Simonsen LC, Wilson JW. (1998). Comparison of Martian Meteorites and Martian Regolith as Shield Materials for Galactic Cosmic Rays. NASA TP-1998-208724. <nowiki>http://hdl.handle.net/2060/19980237030</nowiki></ref>|none]] | [[File:GCR spectra.png|alt=|frame|Energy distribution of cosmic radiation, as measured during the 1977 solar minimum.<ref>Kim MY, Thibeault SA, Simonsen LC, Wilson JW. (1998). Comparison of Martian Meteorites and Martian Regolith as Shield Materials for Galactic Cosmic Rays. NASA TP-1998-208724. <nowiki>http://hdl.handle.net/2060/19980237030</nowiki></ref>|none]] | ||
Revision as of 09:09, 5 August 2019
Cosmic rays are high energy particles that are part of the background radiation in space. Most cosmic rays are absorbed in the Earth's atmosphere and do not reach the planet's surface. On Mars, cosmic rays are not absorbed as the atmosphere is too thin, and radiation shielding is required for the habitats.
Composition
Cosmic radiation comprises 85% protons, 14% alpha particles, and 1% heavy ions.[1]
Energy
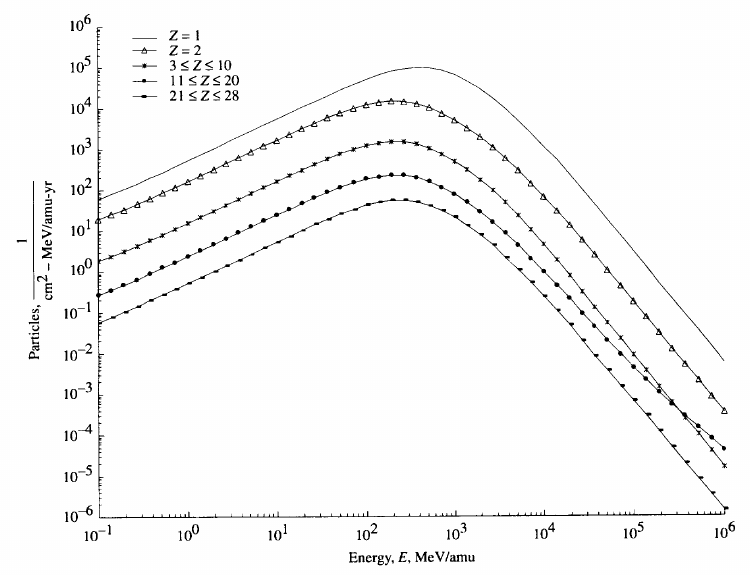
Energy distribution of cosmic radiation, as measured during the 1977 solar minimum.[2]
References
- ↑ Schimmerling W. (2011, Feb 5). The Space Radiation Environment: An Introduction. https://three.jsc.nasa.gov/concepts/SpaceRadiationEnviron.pdf
- ↑ Kim MY, Thibeault SA, Simonsen LC, Wilson JW. (1998). Comparison of Martian Meteorites and Martian Regolith as Shield Materials for Galactic Cosmic Rays. NASA TP-1998-208724. http://hdl.handle.net/2060/19980237030






