Difference between revisions of "Photovoltaics"
(Fixed error, solar power at Mars is 43%, not 48%.) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | '''Photovoltaics''' (or PV) is the generation of electric currents from electromagnetic radiation using the [[photovoltaic effect]] (compare [[solar_concentrator#Thermoelectric_Generators|solar-thermal electricity]]). | + | '''[[w:Photovoltaics|Photovoltaics]]''' (or PV) is the generation of electric currents from electromagnetic radiation using the [[photovoltaic effect]] (compare [[solar_concentrator#Thermoelectric_Generators|solar-thermal electricity]]). |
| + | [[File:Solar cell tile.JPG|right|frameless|50x50px|alt=|link=Create a settlement]] | ||
A PV cell is the basic unit of a PV array. It is usually made of a [[silicon]] substrate coated with a thin film. These are mounted together with supporting structure to form [[solar_panel|PV panel]].<ref>G.D.J. Harper - ''Domestic solar energy: a guide for the home owner'' 2009. ISBN 978-1-84797-060-2 p. 140</ref> A number of technologies are available, but costs vary widely and increase sharply with high efficiencies. | A PV cell is the basic unit of a PV array. It is usually made of a [[silicon]] substrate coated with a thin film. These are mounted together with supporting structure to form [[solar_panel|PV panel]].<ref>G.D.J. Harper - ''Domestic solar energy: a guide for the home owner'' 2009. ISBN 978-1-84797-060-2 p. 140</ref> A number of technologies are available, but costs vary widely and increase sharply with high efficiencies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mars is further from the sun and the average insolation is 43% of Earth. In addition, solar panels lose about 0.2% power per Sol from dust settling on them <ref>https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032063321001768</ref> which will require dangerous EVA's to clean them, or some sort of automated cleaner (which itself must be maintained). During dust storms energy losses of 25 to 50% are typical, tho 95% power losses have happened historically. <ref>https://www.researchgate.net/publication/24390796_Resource_Utilization_and_Site_Selection_for_a_Self-Sufficient_Martian_Outpost</ref> | ||
==Technologies== | ==Technologies== | ||
Thin film technologies are generally less expensive than the others, as well as being lighter. Some versions have reached 23% efficiency | Thin film technologies are generally less expensive than the others, as well as being lighter. Some versions have reached 23% efficiency | ||
| − | Single junction gallium arsenide up to 28% | + | Single junction gallium arsenide are up to 28% efficiency. |
Multijunction cells, three and four junction cells have reached about 36% efficiency without concentrators and up to 46% with concentrators. | Multijunction cells, three and four junction cells have reached about 36% efficiency without concentrators and up to 46% with concentrators. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 18: | ||
Emerging technologies: Perovskite cells may reach over 30% efficiency for very low costs. Still in development. | Emerging technologies: Perovskite cells may reach over 30% efficiency for very low costs. Still in development. | ||
| − | Multijunction cells | + | Multijunction cells can be over 100 times more expensive than less efficient crystalline silicon cells or thin film cells. |
==Use on Mars== | ==Use on Mars== | ||
===Roll out films=== | ===Roll out films=== | ||
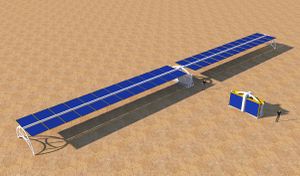
| − | Flexible solar cells can be attached to a flexible backing and packed into large rolls. These can be unrolled directly onto the martian surface for a very simple deployment method. Flexible film cells are less efficient and the variations in the sun's angle during the days reduce the available energy. | + | [[File:Rolls of solar cells.jpg|thumb|Roll out film solar arrays]] |
| + | Flexible solar cells can be attached to a flexible backing and packed into large rolls. These can be unrolled directly onto the martian surface for a very simple deployment method (assuming the surface is level with no large rocks). Flexible film cells are less efficient and the variations in the sun's angle during the days reduce the available energy. This might be the best technology for automated deployment in the early stages of the settlement. An example are the [http://www.renovagen.com/ Renovagen] rapid roll products | ||
| + | [[File:Solar array.jpg|thumb|A power station made with sun tracking solar array. The central battery has a charging station for vehicles.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Sun tracking panels=== | ||
| + | [[w:Solar_tracker|Sun tracking]] can increase the input energy over a year by up to 40% for the same installed capacity. However the tracking mechanisms can be heavy and are moving parts that can fail over time. Might best be used after crews have arrived and there are maintenance facilities set up. Sun tracking may be less useful during dusty seasons, when a large part of the incident light is diffuse light. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Back-up power for rovers=== |
| − | + | Rovers can be partly covered with solar cells for emergency back-up power. This is a feature of the NASA MMSEV design.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_Exploration_Vehicle</ref> Alternatively, rovers can carry fold out or roll out solar arrays for emergency charging. | |
| − | === | + | ===Power stations=== |
| − | + | Solar panels and batteries can be combined into local charging power stations allowing for operating rovers and other equipment in remote locations. A series of power stations could be built along a long road between two remote locations and provide extended operational range. Solar power stations orbiting the planet would avoid dust accumulation and dust storms, but a significant amount of energy (~20%) would be lost beaming the power down to the surface with microwaves. | |
| − | === Power | + | ===Power for landed ships=== |
| − | + | Ships landing on Mars will require power. Do to the heat or re entry, solar cells on the exterior of ships may not be possible, and solar panels designed to be deployed in space may not be capable of being deployed under Martian gravity. Although an established Mars settlement may be able to provide power to landed ships, the first ships on Mars could be required to rapidly deploy solar panels to provide the power needed for their operation. | |
| − | + | This article <ref>https://medium.com/swlh/solar-power-is-never-going-to-work-on-mars-and-everybody-knows-it-b2fb221722b1</ref> discussed the amount of area it would take to refuel a SpaceX Starship landing on Mars. It concludes that 2.83 hectares (28,300 square meters, or about 13 football fields), would be needed assuming no dust storms and not accounting for the mass of any batteries. Setting up this many solar panels on Earth is a giant job, on Mars such an attempt would be much more difficult. Likely two full cargo missions would be required just to bring these solar panels to Mars. | |
==Maintenance== | ==Maintenance== | ||
| + | Photovoltaic arrays will be subject to damage from dust, as well as a reduction capacity from dust deposits. Some form of cleaning mechanism is required. For a settlement, this work may be done by the colonists themselves, or be automated in various ways. Solar tracking systems require even more maintenance. (Mars has very fine dusts (fines), blown by the wind. These are very damaging to moving parts which must be carefully sealed and lubricated to protect them.) | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:20, 29 October 2024
Photovoltaics (or PV) is the generation of electric currents from electromagnetic radiation using the photovoltaic effect (compare solar-thermal electricity).
A PV cell is the basic unit of a PV array. It is usually made of a silicon substrate coated with a thin film. These are mounted together with supporting structure to form PV panel.[1] A number of technologies are available, but costs vary widely and increase sharply with high efficiencies.
Mars is further from the sun and the average insolation is 43% of Earth. In addition, solar panels lose about 0.2% power per Sol from dust settling on them [2] which will require dangerous EVA's to clean them, or some sort of automated cleaner (which itself must be maintained). During dust storms energy losses of 25 to 50% are typical, tho 95% power losses have happened historically. [3]
Contents
Technologies
Thin film technologies are generally less expensive than the others, as well as being lighter. Some versions have reached 23% efficiency
Single junction gallium arsenide are up to 28% efficiency.
Multijunction cells, three and four junction cells have reached about 36% efficiency without concentrators and up to 46% with concentrators.
Crystalline silicon cells, 25-26 %, 22% for commercially available products (2019).
Emerging technologies: Perovskite cells may reach over 30% efficiency for very low costs. Still in development.
Multijunction cells can be over 100 times more expensive than less efficient crystalline silicon cells or thin film cells.
Use on Mars
Roll out films
Flexible solar cells can be attached to a flexible backing and packed into large rolls. These can be unrolled directly onto the martian surface for a very simple deployment method (assuming the surface is level with no large rocks). Flexible film cells are less efficient and the variations in the sun's angle during the days reduce the available energy. This might be the best technology for automated deployment in the early stages of the settlement. An example are the Renovagen rapid roll products
Sun tracking panels
Sun tracking can increase the input energy over a year by up to 40% for the same installed capacity. However the tracking mechanisms can be heavy and are moving parts that can fail over time. Might best be used after crews have arrived and there are maintenance facilities set up. Sun tracking may be less useful during dusty seasons, when a large part of the incident light is diffuse light.
Back-up power for rovers
Rovers can be partly covered with solar cells for emergency back-up power. This is a feature of the NASA MMSEV design.[4] Alternatively, rovers can carry fold out or roll out solar arrays for emergency charging.
Power stations
Solar panels and batteries can be combined into local charging power stations allowing for operating rovers and other equipment in remote locations. A series of power stations could be built along a long road between two remote locations and provide extended operational range. Solar power stations orbiting the planet would avoid dust accumulation and dust storms, but a significant amount of energy (~20%) would be lost beaming the power down to the surface with microwaves.
Power for landed ships
Ships landing on Mars will require power. Do to the heat or re entry, solar cells on the exterior of ships may not be possible, and solar panels designed to be deployed in space may not be capable of being deployed under Martian gravity. Although an established Mars settlement may be able to provide power to landed ships, the first ships on Mars could be required to rapidly deploy solar panels to provide the power needed for their operation.
This article [5] discussed the amount of area it would take to refuel a SpaceX Starship landing on Mars. It concludes that 2.83 hectares (28,300 square meters, or about 13 football fields), would be needed assuming no dust storms and not accounting for the mass of any batteries. Setting up this many solar panels on Earth is a giant job, on Mars such an attempt would be much more difficult. Likely two full cargo missions would be required just to bring these solar panels to Mars.
Maintenance
Photovoltaic arrays will be subject to damage from dust, as well as a reduction capacity from dust deposits. Some form of cleaning mechanism is required. For a settlement, this work may be done by the colonists themselves, or be automated in various ways. Solar tracking systems require even more maintenance. (Mars has very fine dusts (fines), blown by the wind. These are very damaging to moving parts which must be carefully sealed and lubricated to protect them.)
References
- ↑ G.D.J. Harper - Domestic solar energy: a guide for the home owner 2009. ISBN 978-1-84797-060-2 p. 140
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032063321001768
- ↑ https://www.researchgate.net/publication/24390796_Resource_Utilization_and_Site_Selection_for_a_Self-Sufficient_Martian_Outpost
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_Exploration_Vehicle
- ↑ https://medium.com/swlh/solar-power-is-never-going-to-work-on-mars-and-everybody-knows-it-b2fb221722b1