Difference between revisions of "Silicon"
m (→Open issues) |
|||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Silicon''' (''periodic table symbol:'' Si<sup>14</sup>) is a chemical element that can be found in several [[ | + | {{element|elementSymbol=Si|elementName=Silicon|protons=14|abundance=27,7% ([[regolith]])}} |
| + | '''Silicon''' (''[[Elements on Mars|periodic table]] symbol:'' Si<sup>14</sup>) is a chemical element<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silicon</ref> that can be found in several [[minerals]] on [[Mars]]. It is the second most common element on Mars, after oxygen. | ||
| − | == | + | __NOTOC__ |
| − | + | ==Chemistry== | |
| + | [[File:Cyclohexasilane_cyclohexane_cyclohexasiloxane.png|frame|right|Structure of cyclohexasilane (top), cyclohexasiloxane (bottom right) and the [[hydrocarbon]] cyclohexane (bottom left).]] | ||
| + | As a group 14 element, silicon has a chemistry similar to that of [[tin]] and [[lead]], and especially that of [[carbon]] and [[germanium]].<br /> | ||
| + | As we go down from carbon at the top of group 14, the reactivity (and electropositivity) of the elements increases. At the same time, the bond [[enthalpy]] decreases for chains of the element<ref name="Housecroft_Sharpe">C.E. Housecroft & A.G. Sharpe - ''Inorganic chemistry'' 2012. ISBN 978-0-273-74275-3 pp. 433, 444-446.</ref>. That is, C-C bonds are more stable than Si-Si bonds, which are more stable than Ge-Ge bonds, etc. The strength of their bonds with hydrogen similarly decreases. This is why, for example, [[methane]] is more stable than [[Silicon#Silanes|silane]].<br /> | ||
| + | Despite the instability of silicon chains relative to their carbon analogues, they are industrially significant. | ||
| − | == | + | ===Silanes=== |
| − | + | The silanes are acyclic chains of singly-bonded silicon atoms analogous to the [[alkanes]]. The cyclosilanes are (highly unstable) cyclic silanes. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Silenes=== | |
| − | + | The silenes are acyclic chains of doubly-bonded silicon atoms, analogous to the [[alkenes]]. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| + | ===Siloxanes=== | ||
| + | Due to the instability of Si-Si bonds, longer chains of silicon atoms are often constructed with some other atom between the silicon atoms, which bonds more strongly to them. In the case of the siloxanes, this results in Si-O-Si chains. For comparison, the enthalpy of a Si-O bond is in higher than that of a C-C single bond but lower than that of a C=C double bond, and more than twice that of a Si-Si bond. | ||
| − | {{ | + | Silicones are made of polymers of siloxane. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Silicates=== | ||
| + | Silica, SIO<sub>2</sub> ,is the most common compound found in the Martian crust. Other silicates exist as well, in the general SiOx form. Quartz is pure SiO<sub>2</sub> in crystalline form. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Occurrence== | ||
| + | [[File:Mars resources Silicon.jpg|thumb|600x600px|Mars Odyssey MOLA data of Silicon]] | ||
| + | Analysis of Martian soil<ref name="Pathfinder">NASA JPL - [http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/MPF/science/apxs_elemental.html ''Mars Pathfinder: Analysis of Martian Samples by the Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer: Preliminary Results''] Access 2013-04-28.</ref> shows a composition broadly similar to that of Earth, with oxygen and silicon also taking the first and second respective positions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Silicon is the second most common element in the earth's crust (after [[oxygen]]); in fact their compound [[silica]] makes up about 60% of the crust, as on Mars. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Silica production== | ||
| + | Silica can be obtained [[In-situ resource utilization|in-situ]] directly from the Martian regolith. However is is usually mixed with contaminants and will require a separation process before it can be used for Martian industry. There may have been geological processes that have concentrated silica into easily usable forms. Silica production for glass has an [[embodied energy]] of 6-15 MJ/kg. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Silica dust is a known cancer causing agent. Dust collectors and atmospheric treatment systems will be required in production areas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Silicon production== | ||
| + | Silicon production is usually a by product of steel production.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silicon#Production</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Embodied energy]] of silicon depends on its purity<ref>https://greenchemuoft.wordpress.com/2017/12/12/embodied-energy-and-solar-cells/</ref>. Solar cell grade silicon crystals have 1656 MJ/kg of embodied energy. Transforming these into solar cells adds 432 MJ/kg for a total of 2088 MJ/kg. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Clean rooms can be extremely expensive to build for production of electronic products. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Uses== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Silicate (or Quartz) is the main components of glass | ||
| + | *Sand, usually composed of a large parts of silicates, is an essential construction material | ||
| + | *Stone, concrete and bricks are largely composed of silicates. Therefore silica is a prime construction material for a martian settlement | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Silicon is the main material for monocrystalline wafers, used for [[solar panel]]s and for electronics.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wafer_(electronics)</ref> | ||
| + | *Silicon can be used to produce [[phosphorus]] through neutron capture. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Silicon is needed for [[silicone synthesis]] to produce [[synthetic materials]].<br /> High-purity silicon (produced by deposition from silanes) is used as a semiconductor in electronics (after being suitably doped). There are alternatives, such as germanium, though their exact performance characteristics vary and silicon is the obvious choice due to its abundance. | ||
| + | *Silicon Carbide, SiC, is used in metallurgy and is an extremely hard ceramic. | ||
| + | *Silicon is used in the production of iron. | ||
| + | {{science question|How pure does silicon need to be? - [[User:PeterBrett|Peter]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:26, 4 December 2020
Silicon (periodic table symbol: Si14) is a chemical element[1] that can be found in several minerals on Mars. It is the second most common element on Mars, after oxygen.
Chemistry
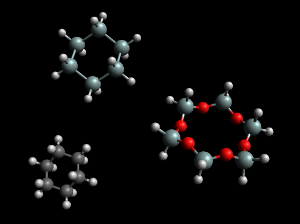
As a group 14 element, silicon has a chemistry similar to that of tin and lead, and especially that of carbon and germanium.
As we go down from carbon at the top of group 14, the reactivity (and electropositivity) of the elements increases. At the same time, the bond enthalpy decreases for chains of the element[2]. That is, C-C bonds are more stable than Si-Si bonds, which are more stable than Ge-Ge bonds, etc. The strength of their bonds with hydrogen similarly decreases. This is why, for example, methane is more stable than silane.
Despite the instability of silicon chains relative to their carbon analogues, they are industrially significant.
Silanes
The silanes are acyclic chains of singly-bonded silicon atoms analogous to the alkanes. The cyclosilanes are (highly unstable) cyclic silanes.
Silenes
The silenes are acyclic chains of doubly-bonded silicon atoms, analogous to the alkenes.
Siloxanes
Due to the instability of Si-Si bonds, longer chains of silicon atoms are often constructed with some other atom between the silicon atoms, which bonds more strongly to them. In the case of the siloxanes, this results in Si-O-Si chains. For comparison, the enthalpy of a Si-O bond is in higher than that of a C-C single bond but lower than that of a C=C double bond, and more than twice that of a Si-Si bond.
Silicones are made of polymers of siloxane.
Silicates
Silica, SIO2 ,is the most common compound found in the Martian crust. Other silicates exist as well, in the general SiOx form. Quartz is pure SiO2 in crystalline form.
Occurrence
Analysis of Martian soil[3] shows a composition broadly similar to that of Earth, with oxygen and silicon also taking the first and second respective positions.
Silicon is the second most common element in the earth's crust (after oxygen); in fact their compound silica makes up about 60% of the crust, as on Mars.
Silica production
Silica can be obtained in-situ directly from the Martian regolith. However is is usually mixed with contaminants and will require a separation process before it can be used for Martian industry. There may have been geological processes that have concentrated silica into easily usable forms. Silica production for glass has an embodied energy of 6-15 MJ/kg.
Silica dust is a known cancer causing agent. Dust collectors and atmospheric treatment systems will be required in production areas.
Silicon production
Silicon production is usually a by product of steel production.[4]
Embodied energy of silicon depends on its purity[5]. Solar cell grade silicon crystals have 1656 MJ/kg of embodied energy. Transforming these into solar cells adds 432 MJ/kg for a total of 2088 MJ/kg.
Clean rooms can be extremely expensive to build for production of electronic products.
Uses
- Silicate (or Quartz) is the main components of glass
- Sand, usually composed of a large parts of silicates, is an essential construction material
- Stone, concrete and bricks are largely composed of silicates. Therefore silica is a prime construction material for a martian settlement
- Silicon is the main material for monocrystalline wafers, used for solar panels and for electronics.[6]
- Silicon can be used to produce phosphorus through neutron capture.
- Silicon is needed for silicone synthesis to produce synthetic materials.
High-purity silicon (produced by deposition from silanes) is used as a semiconductor in electronics (after being suitably doped). There are alternatives, such as germanium, though their exact performance characteristics vary and silicon is the obvious choice due to its abundance. - Silicon Carbide, SiC, is used in metallurgy and is an extremely hard ceramic.
- Silicon is used in the production of iron.
References
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silicon
- ↑ C.E. Housecroft & A.G. Sharpe - Inorganic chemistry 2012. ISBN 978-0-273-74275-3 pp. 433, 444-446.
- ↑ NASA JPL - Mars Pathfinder: Analysis of Martian Samples by the Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer: Preliminary Results Access 2013-04-28.
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silicon#Production
- ↑ https://greenchemuoft.wordpress.com/2017/12/12/embodied-energy-and-solar-cells/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wafer_(electronics)






