Difference between revisions of "Acetic acid"
| (14 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Acetic acid''' is a weak [[acid]], and the defining ingredient in vinegar. Aside from its common use in [[food]], acetic acid is an important industrial chemical. | + | [[File:Acetic acid 2.svg|thumb|Acetic acid molecule]] |
| + | '''Acetic acid''' is a weak [[acid]], and the defining ingredient in vinegar. Aside from its common use in [[food]], acetic acid is an important industrial chemical. Its formulae is C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub>O<sub>2.</sub> | ||
| − | ==Production== | + | __NOTOC__ |
| − | + | ==[[In-situ resource utilization|In Situ Production]]== | |
| + | ===Biological Synthesis=== | ||
| + | Since prehistoric times, humans have produced acetic acid by exposing [[alcohol|alcoholic]] beverages to aerobic [[bacteria]] usually of the ''acetobacter'' genus. The bacteria convert the alcohol to acetic acid. [[Distillation]] of the vinegar concentrates the acid. | ||
===Artificial Synthesis=== | ===Artificial Synthesis=== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 12: | ||
[[Methanol]] and [[carbon monoxide]] are combined under pressure, in the presence of a [[catalyst]]. | [[Methanol]] and [[carbon monoxide]] are combined under pressure, in the presence of a [[catalyst]]. | ||
=====Ethylene Oxidation===== | =====Ethylene Oxidation===== | ||
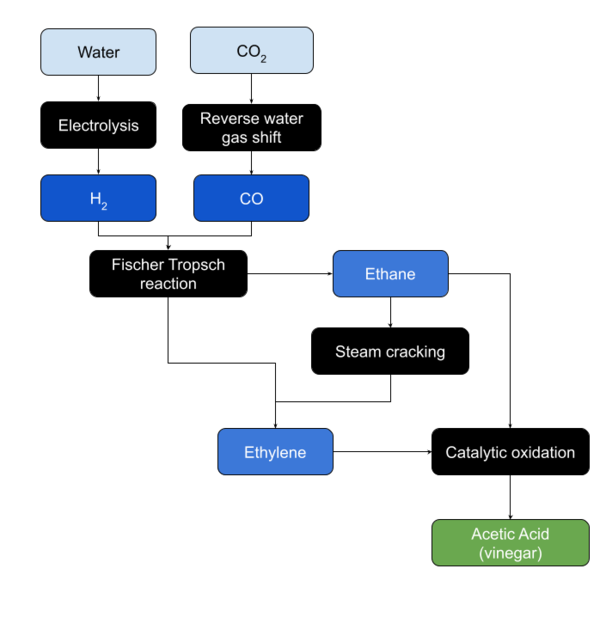
| − | [[Ethylene]] is [[oxidized| | + | [[File:Process-Acetic acid.png|thumb|642x642px|Acetic Acid production process]] |
| + | [[Ethylene]] is [[oxidized|oxidized]] in the presence of a [[palladium]] based catalyst. | ||
| + | =====Ethane Oxidation===== | ||
| + | [[Ethane]] is [[oxidized|oxidized]] in the presence of a catalyst. | ||
==Use== | ==Use== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 22: | ||
===Chemical Production=== | ===Chemical Production=== | ||
| − | Acetic acid is used in the production of [[ | + | Acetic acid has the formula CH3COOH, and is used in the production of [[adhesives]], inks, paints, acetic anhydride (used in synthetic textiles, photographic film, and flexible plastic type materials), it is an excellent polar protic solvent, and (its largest use on Earth) vinyl acetate monomer. |
| − | [[ | + | ===Medical Use=== |
| − | + | Since ancient times, it has been used as a medicine to reduce headaches and act is a weak blood thinner. See [[Aspirin]]. | |
| − | [[ | + | |
| + | [[Category:Materials]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:56, 26 May 2021
Acetic acid is a weak acid, and the defining ingredient in vinegar. Aside from its common use in food, acetic acid is an important industrial chemical. Its formulae is C2H4O2.
In Situ Production
Biological Synthesis
Since prehistoric times, humans have produced acetic acid by exposing alcoholic beverages to aerobic bacteria usually of the acetobacter genus. The bacteria convert the alcohol to acetic acid. Distillation of the vinegar concentrates the acid.
Artificial Synthesis
There are several techniques used to produce acetic acid on an industrial scale.
Methanol Carbonylation
Methanol and carbon monoxide are combined under pressure, in the presence of a catalyst.
Ethylene Oxidation
Ethylene is oxidized in the presence of a palladium based catalyst.
Ethane Oxidation
Ethane is oxidized in the presence of a catalyst.
Use
Food Preservation
Though acetic acid is commonly generated by certain microbes, in high enough concentrations it preserves food.
Chemical Production
Acetic acid has the formula CH3COOH, and is used in the production of adhesives, inks, paints, acetic anhydride (used in synthetic textiles, photographic film, and flexible plastic type materials), it is an excellent polar protic solvent, and (its largest use on Earth) vinyl acetate monomer.
Medical Use
Since ancient times, it has been used as a medicine to reduce headaches and act is a weak blood thinner. See Aspirin.