Difference between revisions of "Hellas quadrangle"
(added pictures, info, and ref) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
File:PIA00188-MC-28-HellasRegion-19980605.jpg | File:PIA00188-MC-28-HellasRegion-19980605.jpg | ||
</gallery>The most famous feature of this area is the [[Hellas Basin|Hellas]] basin, a impact crater 2300 km in diameter. | </gallery>The most famous feature of this area is the [[Hellas Basin|Hellas]] basin, a impact crater 2300 km in diameter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The Hellas quadrangle covers the area from 30° to 65° south latitude and 240° to 300° west longitude (120-60 E ). When an asteroid slammed into Mars to create a big hole that makes up some of this quadrange, many unbelievable events were caused—it was worse than any science fiction movie. Within the Hellas quadrangle lies the classic features Hellas Planitia and Promethei Terra. Many interesting and mysterious features have been discovered in the Hellas quadrangle, including the giant river valleys Dao Vallis, Niger Vallis, Harmakhis, and Reull Vallis—all of which may have contributed water to a lake in the Hellas basin in the distant past.<ref>Carr | first=Michael H. | publisher=Cambridge University Press | isbn= 978-0-521-87201-0 | title= The Surface of Mars |date=2006 |</ref> <ref> Moore | first1= J | last2= Wilhelms | first2= Don E. | title= Hellas as a possible site of ancient ice-covered lakes on Mars | journal= Icarus | volume= 154 | issue= 2 |pages= 258–276 | date= 2001 | doi = 10.1006/icar.2001.6736 | </ref> <ref>Cabrol, N. and E. Grim (eds). 2010. Lakes on Mars</ref> Many places in the Hellas quadrangle show signs that the ground is full of ice, especially with glacier-like flow features. | ||
| + | ==Hellas Basin== | ||
| + | The Hellas quadrangle contains part of the Hellas Basin, the largest known impact crater on the surface of Mars and the second largest in the solar system. The depth of the crater is 7152 m<ref>http://www-star.stanford.edu/projects/mgs/sum/s0403210230.html Martian Weather Observation] https://web.archive.org/web/20080531235046</ref> (23,000ft) below the standard topographic [[datum (geodesy)|datum]] of Mars. The basin is located in the southern highlands of Mars and is thought to have been formed about 3.9 billion years ago, during a period that geologists call the Late Heavy Bombardment. This was period of much greater asteroid impacts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Results of asteroid collision== | ||
| + | The physics of this great event boggles the mind. Studies suggest that when an impact created the Hellas Basin, the entire surface of Mars was heated hundreds of degrees, 70 meters of molted rock fell on the planet, and an atmosphere of gaseous rock was formed. Think about hot, molted rock falling to a depth of a 21 story building. On Earth that would cover all homes and most buildings. This rock atmosphere was 10 times as thick as the Earth's atmosphere. In a few days, the rock would have condensed out and covered the whole planet with an additional 10 m of molten rock.<ref>Carr | first=Michael H. | publisher=Cambridge University Press | isbn= 978-0-521-87201-0 | title= The Surface of Mars |date=2006 |</ref> When all this rock cooled all the planet would be covered with rock that was as deep as a 24 story building is tall. And this is not made up folks—the proof is the big hole called the Hellas Basin. Imagine if such a thing happened on the Earth. | ||
| + | ==Strange surfaces—Origin Unknown== | ||
| + | In the Northwest portion of Hellas Planitia is a strange type of surface called complex banded terrain or taffy-pull terrain. Its process of formation is still largely unknown, although it appears to be due to erosion of hard and soft sediment along with ductile deformation. Ductile deformation results from layers undergoing strain.<ref>http://hirise.lpl.arizonai.edu/P/sP_008559_1405</ref> | ||
| + | ==Giant Lake== | ||
| + | Early in the planet's history, it is believed that a giant lake existed in the Hellas Basin.<ref>Voelker, M., et al. 2016. DISTRIBUTION AND EVOLUTION OF LACUSTRINE AND FLUVIAL FEATURES IN HELLASPLANITIA, MARS, BASED ON PRELIMINARY RESULTS OF GRID-MAPPING. 47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2016) 1228.pdf.</ref> Possible shorelines have been discovered. These are evident in alternating benches and scarps visible in Mars orbiting camera narrow-angle images. In addition, Mars orbiting laser altimeter (MOLA) data show that the contacts of these sedimentary units mark contours of constant elevation for thousands of km, and in one case all around the basin. Channels, believed to be formed by water, enter into the basin. The Hellas drainage basin may be almost one-fifth that of the entire northern plains. A lake in Hellas in today's Martian climate would form a thick ice at the top that would eventually sublimate away. That is the ice would turn directly from a solid to a gas. This is similar to how dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) behaves on Earth.<ref> Moore, J; Wilhelms, Don E. (2001). "Hellas as a possible site of ancient ice-covered lakes on Mars". Icarus. 154 (2): 258–276.</ref> Glacial features ( moraines, drumlins, and eskers) have been found that may have been formed when the water froze.<ref> Carr, Michael H. (2006). The Surface of Mars. Cambridge University Press. p. [page needed]. ISBN 978-0-521-87201-0.</ref> <ref>Kargel |first1= J. |first2= R. |last2=Strom |date= 1991 |title= Terrestrial glacial eskers: analogs for martian sinuous ridges | journal= LPSC | volume=XXII | pages= 683–684 |</ref> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | Image:Hellas basin topo.jpg|Hellas Basin Area topography. Crater depth is 7152 m<ref name="stanhellas"/> (23,000 ft) below the standard topographic [[datum (geodesy)|datum]] of Mars. | ||
| + | Image:False color of Hellas Planitia.jpeg|Hellas Basin with graph showing the great depth of the crater. It is the deepest crater on Mars and has the highest surface pressure: 1155 [[pascal (Pa)]]<ref name="stanhellas"/> (11.55 millibar, 0.17 psi, or 0.01 atm). | ||
| + | Image:Twisted Ground in Hellas.jpg|Twisted Ground in Hellas, as seen by HiRISE This is one more example of how difficult it would be to walk on Mars. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==How climate change caused ice-rich features== | ||
| + | Many features on Mars, including ones in Hellas quadrangle, are believed to contain large amounts of ice. The Hellas region displays many strange and beautiful landscapes. Most do not have their counterparts on the Earth. Researchers have struggled to explain these features and other. Mars holds many mysteries. However, after so much coverage by satellites with increasing better cameras, we have made major strides in understanding the mysteries of the Red Planet. Some aspects of the planet are still debated. Many things we do have some understanding of their natures, but some details have yet to be worked out. | ||
| + | Most of the strangeness of the Hellas region relates to climate change. Indeed, most of the whole planet’s surface appearance is driven by drastic and frequent climate changes. These changes are due to basic physics. Seasons on the planets, including the Earth, are caused of a planet's rotational axis. Because the Earth has a moon of considerable mass, the Earth’s axis does not change much from its usual 23.5 degrees. However, Mars lacks a large moon; consequently its tilt has even been greater than 80 degrees. Note that its tilt at 25 degrees is almost the same as ours. <ref>Touma | first1 = J. | last2 = Wisdom | first2 = J. | year = 1993 | title = The Chaotic Obliquity of Mars | url = | journal = Science | volume = 259 | issue = 5099| pages = 1294–1297 | doi=10.1126/science.259.5099.1294 | pmid=17732249|</ref> <ref> Laskar | first1 = J. | last2 = Correia | first2 = A. | last3 = Gastineau | first3 = M. | last4 = Joutel | first4 = F. | last5 = Levrard | first5 = B. | last6 = Robutel | first6 = P. | year = 2004 | title = Long term evolution and chaotic diffusion of the insolation quantities of Mars | url =https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00000860/file/Ma_2004.laskar_prep.pdf | journal = Icarus | volume = 170 | issue = 2| pages = 343–364 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2004.04.005 | </ref> | ||
| + | Studies have shown that when the tilt of Mars reaches 45 degrees from its current 25 degrees, ice is no longer stable at the poles. As a result, it will disappear.<ref>Head | first2 = J. | last3 = Marchant | first3 = D. | last4 = Kowalewski | first4 = D. | year = 2008 | title = Identification of sublimation-type thermal contraction crack polygons at the proposed NASA Phoenix landing site: Implications for substrate properties and climate-driven morphological evolution | url = | journal = Geophys. Res. Lett. | volume = 35| issue = 4| pages = L04202 | doi = 10.1029/2007GL032813 | </ref> Furthermore, at this high tilt, stores of solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) sublimate, thereby increasing the atmospheric pressure. This increased pressure allows more dust to be held in the atmosphere. With more dust, more ice will freeze onto the dust. Eventually, moisture in the atmosphere will fall as snow or as ice frozen onto dust grains. Calculations suggest this material will concentrate in the mid-latitudes. And Hellas is in the mid-latitudes of the southern hemisphere.<ref> Levy | first1 = J. | last2 = Head | first2 = J. | last3 = Marchant | first3 = D. | year = 2009 | title = Thermal contraction crack polygons on Mars: Classification, distribution, and climate implications from HiRISE observations | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 114| issue = E1| pages = E01007 |</ref> <ref>Hauber, E., D. Reiss, M. Ulrich, F. Preusker, F. Trauthan, M. Zanetti, H. Hiesinger, R. Jaumann, L. Johansson, A. Johnsson, S. Van Gaselt, M. Olvmo. 2011. Landscape evolution in Martian mid-latitude regions: insights from analogous periglacial landforms in Svalbard. In: Balme, M., A. Bargery, C. Gallagher, S. Guta (eds). Martian Geomorphology. Geological Society, London. Special Publications: 356. 111-131</ref> Using decades of date from orbiting satellites together with general principles about weather and climate, researchers have developed theories or models that explain why Mars looks like it does. They call these models or theories general circulation models. These theories predict accumulations of ice-rich dust (which becomes mantle) in the same areas where ice-rich features are found.<ref>Laskar, J.; Correia, A.; Gastineau, M.; Joutel, F.; Levrard, B.; Robutel, P. (2004). "Long term evolution and chaotic diffusion of the insolation quantities of Mars" (PDF). Icarus. 170 (2): 343–364.</ref> | ||
| + | When the tilt begins to return to lower values, the ice sublimates (turns directly to a gas) and leaves behind a lag of dust.<ref>Mellon | first1 = M. | last2 = Jakosky | first2 = B. | year = 1995 | title = The distribution and behavior of Martian ground ice during past and present epochs | url = https://semanticscholar.org/paper/815bfd93bdb19325e03e08556d145fa470112e4e| journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 100 | issue = E6| pages = 11781–11799 |</ref> <ref> Schorghofer | first1 = N | year = 2007 | title = Dynamics of ice ages on Mars | url = | journal = Nature | volume = 449 | issue = 7159| pages = 192–194 |</ref> This lag deposit caps the underlying material so with each cycle of high tilt levels, some ice-rich mantle remains behind.<ref>Madeleine, J., F. Forget, J. Head, B. Levrard, F. Montmessin. 2007. Exploring the northern mid-latitude glaciation with a general circulation model. In: Seventh International Conference on Mars. Abstract 3096.</ref | ||
| + | After many, many cycles of mantle accumulation some places, especially the Hellas region, accumulate very thick deposits of mantle, technically called latitude dependent mantle (because its occurrence depends on the latitude). Some parts of the mantle may have changed into solid ice in a manner analogous to how snow turns into ice in our Earth’s glaciers. The following pictures show expressions of this mantle in the Hellas region. | ||
| + | [[File:Niger Vallis hirise.JPG|thumb|[[Niger Vallis]] with features typical of this latitude, as seen by HiRISE. Chevron patterns result from movement of ice-rich material. Click on image to see chevron pattern and mantle]] | ||
| + | The image at the right shows a good view of this smooth mantle around [[Niger Vallis]], as observed with HiRISE. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | 45070 1440mantlelayers.jpg|Smooth mantle with layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 46270 1445mantle.jpg|Close view of mantle, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 048063 1395crater.jpg|Crater showing how thick mantle is in place, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | 48063 1395mantle.jpg|Close view of the edge of mantle, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | What happens next is that cracks appear in the surface. Stress is suggested to initiate a fracture process that produces cracks. Cracks expose more surfaces, and consequently more ice can escape into the planet's thin atmosphere. Conditions on Mars are such that the process of called sublimation dominates in this process ice will change directly into a gas—rather than melting into a liquid first. Dry ice behaves in a similar fashion on the Earth. On Mars sublimation has been observed when the Phoenix lander uncovered chunks of ice that disappeared in a few days.<ref name=Press>http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/phoenix/news/phoenix-20080619.html Bright Chunks at ''Phoenix'' Lander's Mars Site Must Have Been Ice – Official NASA press release (19.06.2008)</ref> <ref >"nasa.gov">http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/phoenix/news/phoenix-20080619.html</ref> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | Image:Ice sublimating in the Dodo-Goldilocks trench.gif|Die-sized clumps of bright material in the enlarged "Dodo-Goldilocks" trench vanished over the course of four days, implying that they were composed of ice which [[Sublimation (chemistry)|sublimated]] following exposure.<ref name="nasa.gov"/><ref>Smith, P., et al. 2009. H<sub>2</sub>O at the Phoenix Landing Site. Science: 325, 58-61.</ref> | ||
| + | Image:Evaporating ice on Mars Phoenix lander image.jpg|Color versions of the photos showing ice sublimation, with the lower left corner of the trench enlarged in the insets in the upper right of the images. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition, HiRISE has seen fresh craters with ice at the bottom. After a time, HiRISE saw the ice deposit disappear.<ref>Byrne, S. et al. 2009. Distribution of Mid-Latitude Ground Ice on Mars from New Impact Craters: 329.1674-1676</ref> | ||
| + | Eventually, small cracks become large canyons or troughs in the mantle. Small cracks often contain small pits and chains of pits.<ref>Morgenstern, A., et al. 2007</ref> <ref name="Baker, D. 2015">Baker, D., J. Head. 2015. Extensive Middle Amazonian mantling of debris aprons and plains in Deuteronilus Mensae, Mars: Implication for the record of mid-latitude glaciation. Icarus: 260, 269-288.</ref> When parts of this many meters deep mantle start to have cracks, sublimation takes over and many strange landscapes are created. HiRISE has imaged many of these scenes. Pictures below show many of these exotically beautiful forms. | ||
| + | Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from Polar Regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate period’s water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water returns to the ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor condenses on the particles, and then they fall down to the ground due to the additional weight of the water coating. This material that falls, along with snow lands in certain places on Mars. A great deal lands in the Hellas region. It appears as a smooth covering. Due to its great age, the Martian surface is very irregular, but where mantle has accumulated it is smooth. When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulates the remaining ice.<ref> author=MLA NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory |date=December 18, 2003 | title= Mars May Be Emerging From An Ice Age |work= ScienceDaily |accessdate=February 19, 2009 |url= https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2003</ref> | ||
| + | ==Lobate debris aprons (LDA)== | ||
| + | One very important feature common in east Hellas are piles of material surrounding cliffs. The formation is called a lobate debris apron (LDA). Recently, research with the Shallow Radar on the [[Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter]] has provided strong evidence that the LDAs are glaciers that are covered with a thin layer of rocks.<ref> Head | first1= JW | last2= Neukum | first2= G | last3= Jaumann | first3= R | last4= Hiesinger | first4= H | last5= Hauber | first5= E | last6= Carr | first6= M | last7= Masson | first7= P | last8= Foing | first8= B | last9= Hoffmann | first9= H | last10= Kreslavsky | first10= M. | last11= Werner | first11= S. | last12= Milkovich | first12= S. | last13= Van Gasselt | first13= S. | last14= Co-Investigator Team | first14= The Hrsc | title= Tropical to mid-latitude snow and ice accumulation, flow and glaciation on Mars | journal= Nature | volume= 434 | issue= 7031 |pages= 346–350 | date= 2005 | pmid = 15772652 | doi= 10.1038/nature03359 |</ref> <ref>http://news.brown.edu/pressreleases/2008/04/martian-glaciers</ref> <ref> Plaut | first1= Jeffrey J. | last2= Safaeinili | first2= Ali | last3= Holt | first3= John W. | last4= Phillips | first4= Roger J. | last5= Head | first5= James W. | last6= Seu | first6= Roberto | last7= Putzig | first7= Nathaniel E. | last8= Frigeri | first8= Alessandro | title= Radar Evidence for Ice in Lobate Debris Aprons in the Mid-Northern Latitudes of Mars | journal=Geophysical Research Letters | volume= 36 | issue= 2 | pages= n/a | date= 2009 |</ref> <ref>http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2008/pdf/2290.pdf | </ref> <ref>Radar Sounding Evidence for Ice within Lobate Debris Aprons near Hellas Basin, Mid-Southern Latitudes of Mars |http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2008/pdf/2441.pdf | journal = Lunar and Planetary Science |volume=XXXIX | issue = 1391 | pages = 2441 |date=2008 |last1= Holt | first=J.W.| last2 = Safaeinili | first2 = A. | last3 = Plaut | first3 = J. J. | last4 = Young | first4 = D. A. | last5 = Head | first5 = J. W. | last6 = Phillips | first6 = R. J. | last7 = Campbell | first7 = B. A. | last8 = Carter | first8 = L. M. | last9 = Gim | first9 = Y. | last10 = Seu | </ref> Large amounts of water ice are believed to be in the LDAs. Available evidence strongly suggests that the eastern part of Hellas accumulated snow in the past. When the tilt (obliquity) of Mars increases the southern ice cap releases large amounts of water vapor. Climate models predict that when this occurs, water vapor condenses and falls where LDAs are located. The tilt of the earth changes little because our relatively large moon keeps it stable. The two tiny Martian moons do not stabilize their planet, so the rotational axis of Mars undergoes large variations.<ref> Holt | first1 = J. W. | last2 = Safaeinili | first2 = A. | last3 = Plaut | first3 = J. J. | last4 = Head | first4 = J. W. | last5 = Phillips | first5 = R. J. | last6 = Seu | first6 = R. | last7 = Kempf | first7 = S. D. | last8 = Choudhary | first8 = P. | last9 = Young | first9 = D. A. | last10 = Putzig | first10 = N. E. | last11 = Biccari | first11 = D. | last12 = Gim | first12 = Y. | title = Radar Sounding Evidence for Buried Glaciers in the Southern Mid-Latitudes of Mars | journal = Science | volume = 322 | issue = 5905 | pages = 1235–8 | date = 2008 | pmid = 19023078 | doi = 10.1126/science.1164246 | </ref> Lobate debris aprons may be a major source of water for future Mars colonists. Their major advantage over other sources of Martian water are that they can easily mapped from orbit and they are closer to the equator, where manned missions are more likely to land. | ||
| + | ==Lineated Valley Fill (LVF)== | ||
| + | On the floors of some channels are features called lineated floor deposits or lineated valley fill. They are ridged and grooved materials that seem to deflect around obstacles. They are believed to be ice-rich. Some glaciers on the Earth show such features. Lineated floor deposits may be related to lobate debris aprons, which have been proven to contain large amounts of ice. Reull Vallis, as pictured below, displays these deposits.<ref>https://web.archive.org/web/20100617191548/http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20021022a |</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | Image:Reull Vallis.JPG|Drainage features in [[Reull Vallis]], as seen by THEMIS. Click on image to see relationship of Reull Vallis to other features. | ||
| + | File:Reull Vallis lineated deposits.jpg|Reull Vallis with lineated floor deposits, as seen by THEMIS. Click on image to see relationship to other features. | ||
| + | ESP 052138 1435lvf.jpg|Lineated valley fill, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:ESP 055421 1395reullvallis.jpg|Reull Vallis floor showing lineated valley fill at the top and hollows near bottom, as seen by HiRISE under [[HiWish program]] | ||
| + | File:55421 1395lvfclose.jpg|Close, color view of lineated valley fill, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | Image:Reull Vallisl layers.JPG|Layers in [[Reull Vallis]], as seen by THEMIS. | ||
| + | Image:Fretted terrain near ReullVallis.jpg|[[Fretted terrain]] near Reull Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. | ||
| + | Image:Close-up of Fretted Terrain near Reull Vallis.JPG|Close-up of Fretted Terrain near Reull Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. This area would be a challenge to walk across. | ||
| + | Image:Layers in Monument Valley.jpg|Layers in Monument Valley. These are accepted as being formed, at least in part, by water deposition. Since Mars contains similar layers, water remains as a major cause of layering on Mars. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Upper Plains Unit== | ||
| + | Some places the mantle has piled up quite deeply. The remains of a 50-100 meter thick mantling, called the upper plains unit, has been discovered in the mid-latitudes of Mars. It was first investigated in the Deuteronilus Mensae region, but it occurs in other places as well. The remnants sometimes consist of sets of dipping layers in craters and along mesas.<ref>Carr, M. 2001. Mars Global Surveyor observations of Martian fretted terrain. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 106. Issue E10</ref> Sets of dipping layers may be of various sizes and shapes—some look like stepped Aztec pyramids from Central America. The Upper plains unit can have several different appearances. | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 050793 1365pyramids.jpg|Tilted layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 50793 1365layers.jpg|Tilted layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 50793 1365layers2.jpg|Tilted layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | Image:ESP_024868pyramid.jpg|Layered feature probably formed by the erosion of the upper plains unit, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. | ||
| + | P1010377redrocksfall.jpg|Layered feature in Red Rocks Park, Colorado. This has a different origin than ones on Mars, but it has a similar shape. Features in Red Rocks region were caused by uplift of mountains. | ||
| + | Image:ESP 028692 1395pyramidcropped.jpg|Layered feature that is probably the remains of a once widespread unit that fell from the sky, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 034509 1450pyramidshellas.jpg|Layered feature, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 034072 1435pyramidhellas.jpg|Layered feature in crater, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 045321 1415pyramid.jpg|Layered feature in crater, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 046283 1435pyramid.jpg|Layers in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:ESP 054485 1430craterpyramid.jpg|Layered feature in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | File:ESP 054775 1400craterpyramid.jpg|Layered feature in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:54775 1400pyramidcolor.jpg|Close, color view of layered feature in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Different colors are due to different minerals. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 019778 1385pyramid.jpg|Layered structure in crater that is probably what is left of a layered unit that once covered a much larger area. Material for this unit fell from the sky as ice-coated dust. The picture was taken by HiRISE, under the HiWish program. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This unit also degrades into a feature named brain terrain; it looks like the human brain. Brain terrain is a region of maze-like ridges 3–5 meters high. Some ridges may consist of an ice core, so they may be sources of water for future colonists. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 048011 1370upperunit.jpg|Wide view of upper plains unit breaking down into brain terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | 48011 1370upperunit.jpg|Close view of upper plains unit breaking down into brain terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program As ice leaves the ground, the ground collapses and winds blow the remaining dust away. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 028336 1395pyramidhellas.jpg|Small, layered structure, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program Picture also shows brain terrain forming. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some regions of the upper plains unit display large fractures and troughs with raised rims; such regions are called ribbed upper plains. Fractures are believed to have started with small cracks from stresses. Stress is suggested to initiate the fracture process since ribbed upper plains are common when debris aprons come together or near the edge of debris aprons—such sites would generate compressional stresses. Cracks expose more surfaces, and consequently more ice in the material sublimates into the planet's thin atmosphere. Eventually, small cracks become large canyons or troughs.<ref>Morgenstern, A., et al. 2007</ref> <ref name="Baker, D. 2015">Baker, D., J. Head. 2015. Extensive Middle Amazonian mantling of debris aprons and plains in Deuteronilus Mensae, Mars: Implication for the record of mid-latitude glaciation. Icarus: 260, 269-288.</ref> | ||
| + | The upper plains unit is probably just a very thick pile of mantle.to have fallen from the sky. It drapes various surfaces and as is the case for other mantle deposits, it has layers, is fine-grained, and is ice-rich. It is widespread; it does not seem to have a point source. The surface appearance of some regions of Mars is due to how this unit has degraded. | ||
| + | ==Origin of Dao Vallis== | ||
| + | [[File:Dao Vallis.JPG|thumb|[[Dao Vallis]], as seen by [[THEMIS]]. Click on image to see relationship of Dao Vallis to other nearby features]] | ||
| + | Dao Vallis begins near a large volcano, called Hadriaca Patera, so it is thought to have received water when hot magma melted huge amounts of ice in the frozen ground.<ref>Carr, Michael H. (2006). The Surface of Mars. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-87201-0.</ref> The partially circular depressions on the left side of the channel in the adjacent image suggests that groundwater sapping also contributed water.<ref>http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20020807a</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Dust devil tracks== | ||
| + | [[File:Secchi Crater Floor.JPG|thumb|[[Secchi Crater]] Floor, as seen by [[HiRISE]]. Click on image to see dust devil tracks and a pedestal crater]] | ||
| + | Many areas on Mars, including the Hellas quadrangle, experience the passage of giant dust devils. A thin coating of fine bright dust covers most of the Martian surface. When a dust devil goes by it blows away the coating and exposes the underlying dark surface. Dust devils have been seen from the ground and from orbiting spacecraft. They have even blown the dust off of the solar panels of the two Mars Exploration Rovers (Spirit and Opportunity), thereby greatly extending their lives.<ref>http://marsrovers.jpl.nasa.gov/gallery/press/spirit/20070412a.html</ref> The twin Rovers were designed to last for 3 months, instead they have lasted far longer; Opportunity lasted more than 14 years. The pattern of dust devil tracks have been shown to change every few months.<ref name="mars.jpl.nasa.gov">https://web.archive.org/web/20111028015730/http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/spotlight/kenEdgett.html |</ref> A study that combined data from the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and the Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) found that some large dust devils on Mars have a diameter of 700 meters and last at least 26 minutes.<ref>Reiss | first1 = D. |display-authors=etal | year = 2011 | title = Multitemporal observations of identical active dust devils on Mars with High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 215 | issue = 1| pages = 358–369 |</ref> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | Wikiwallacedevils.jpg|[[Dust devil tracks]] on floor of Wallace Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) | ||
| + | ESP 049304 1215streaks.jpg|Dust devil tracks, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program | ||
| + | File:57044 1325colordevilsboulders.jpg|Dust devil tracks and boulders, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program | ||
| + | File:ESP 057533 1445devilswide.jpg|Wide view of dust devil tracks, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program | ||
| + | File:ESP 057533 1445devilscolor.jpg|Close color view of dust devil tracks, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program | ||
| + | File:57533 1445widedevil.jpg|Close color view of dust devil tracks, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program | ||
| + | File:57876 1285streakspatterned.jpg|Close color view of dust devil tracks, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program patterned ground is visible in the background. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Pedestal Craters== | ||
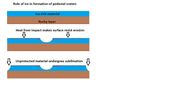
| + | Pedestal craters form when the ejecta from impacts protect the underlying material from erosion. As a result of this process, craters appear perched above their surroundings. | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 047615 1275pedestal.jpg|Pedestal crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | Image:Pedestal crater3.jpg|Pedestal craters form when the ejecta from impacts protect the underlying material from erosion. As a result of this process, craters appear perched above their surroundings. | ||
| + | Image:Pedestaldrawingcolor2.jpg|Drawing shows a later idea of how some pedestal craters form. In this way of thinking, an impacting projectile goes into an ice-rich layer—but no further. Heat and wind from the impact hardens the surface against erosion. This hardening can be accomplished by the melting of ice which produces a salt/mineral solution thereby cementing the surface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:ESP 055449 1175pedestals.jpg|Pedestal craters, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Glacial Features== | ||
| + | Glaciers, loosely defined as patches of currently or recently flowing ice, are thought to be present across large but restricted areas of the modern Martian surface, and are inferred to have been more widely distributed at times in the past.<ref>"Carr">"The Surface of Mars" Series: Cambridge Planetary Science (No. 6) {{ISBN|978-0-511-26688-1 Michael H. Carr, United States Geological Survey, Menlo Park</ref> <ref>"Kieffer, Hugh H. Mars|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NoDvAAAAMAAJ|accessdate=March 7, 2011|date=1992|publisher=University of Arizona Press|isbn=978-0-8165-1257-7</ref> Lobate convex features on the surface known as '''viscous flow features''' and lobate debris aprons are now almost unanimously regarded as true glaciers.<ref>Milliken | first1 = R. E. | last2 = Mustard | first2 = J. F. | last3 = Goldsby | first3 = D. L. | year = 2003 | title = Viscous flow features on the surface of Mars: Observations from high-resolution Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) images | url = https://semanticscholar.org/paper/a822f14644d2294b948e101be2f294ac33b57ec3| journal = Journal of Geophysical Research | volume = 108 | issue = E6| page = 5057 | doi=10.1029/2002je002005 |</ref> <ref name>Squyres | first1 = S.W. | last2 = Carr | first2 = M.H. | year = 1986 | title = Geomorphic evidence for the distribution of ground ice on Mars | url = | journal = Science | volume = 213 | issue = 4735| pages = 249–253 | doi = 10.1126/science.231.4735.249 | pmid = 17769645 |</ref> <ref>Head | first1 = J.W. | last2 = Marchant | first2 = D.R. | last3 = Dickson | first3 = J.L. | last4 = Kress | first4 = A.M. | year = 2010 | title = Criteria for the recognition of debris-covered glacier and valley glacier landsystem deposits | url = | journal = Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. | volume = 294 | issue = | pages = 306–320 | doi=10.1016/j.epsl.2009.06.041 | </ref> <ref>Holt | first1 = J.W. |display-authors=etal | year = 2008 | title = Radar sounding evidence for buried glaciers in the southern mid-latitudes of Mars | url = | journal = Science | volume = 322 | issue = 5905| pages = 1235–1238 |</ref> <ref>Morgan | first1 = G.A. | last2 = Head | first2 = J.W. | last3 = Marchant | first3 = D.R. | year = 2009 | title = Lineated valley fill (LVF) and lobate debris aprons (LDA) in the Deuteronilus Mensae northern dichotomy boundary region, Mars: Constraints on the extent, age and episodicity of Amazonian glacial events | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 202 | issue = 1| pages = 22–38 | </ref> <ref>Plaut | first1 = J.J. | last2 = Safaeinili | first2 = A. | last3 = Holt | first3 = J.W. | last4 = Phillips | first4 = R.J. | last5 = Head | first5 = J.W. | last6 = Sue | first6 = R. | last7 = Putzig | first7 = A. | year = 2009 | title = Frigeri Radar evidence for ice in lobate debris aprons in the mid-northern latitudes of Mars | url = https://semanticscholar.org/paper/f6b94761e6a276ce6894374ae9bea88fdc3e5e19| journal = Geophys. Res. Lett. | volume = 36 | issue = 2| page = L02203 | </ref> <ref>Baker | first1 = D.M.H. | last2 = Head | first2 = J.W. | last3 = Marchant | first3 = D.R. | year = 2010 | title = Flow patterns of lobate debris aprons and lineated valley fill north of Ismeniae Fossae, Mars: Evidence for extensive mid-latitude glaciation in the Late Amazonian | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 207 | issue = 1| pages = 186–209 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2009.11.017 | </ref> <ref>Arfstrom | first1 = J. | year = 2005 | title = Terrestrial analogs and interrelationships | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 174 | issue = 2| pages = 321–335 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2004.05.026 | </ref> | ||
| + | A climate model, reported in the journal Science in 2006, found that large amounts of ice should accumulate in the Hellas region, in the same places where glaciers are observed. Water is transported from the south polar area to northern Hellas and falls as precipitation.<ref>Forget, F., et al. 2006. Formation of Glaciers on Mars by Atmospheric Precipitation at High Obliquity. Science: 311, 368-371.</ref> | ||
| + | The following pictures show many features that are probably glaciers—that is they are mostly ice and move downhill—like rivers—but much slower. | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 051151 1445flow.jpg|Flows, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 051151 1445closecolor.jpg|Close, color view of flow, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 051162 1460flows.jpg|Flows, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:ESP 054973 1405tongue.jpg|Flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 051162 1460flowclosecolor.jpg|Close, color view of flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Patterned ground is visible in the photo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 051175 1430flow.jpg|Flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Flows, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:ESP 055065 1405flow.jpg|Flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:ESP 055091 1405flow.jpg|Flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 049527 1420tongue.jpg|Flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 49527 1420tongueclose.jpg|Close view of snout of flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program [[Polygonal patterned ground]] is visible. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 049949 1420tongues.jpg|Wide view of tongue-shaped glaciers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 49949 1420polygons.jpg|Close view of tongue-shaped glaciers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Polygons are visible. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Image:Gully Flow Features.JPG|Surface features that show downhill movement, as seen by HiRISE. | ||
| + | Image:CTX image of Cirque near Hellas.JPG|CTX context image of Hellas Planitia showing location of next two images. | ||
| + | Image:Glacial features in Hellas.JPG|Surface in Hellas quadrangle, as seen by HiRISE, under the [[HiWish program]]. | ||
| + | Image:Glacial Cirque in Hellas.JPG|Possible Glacial Cirque in [[Hellas Planitia]], as seen by HiRISE, under the HiWish program. Lines are probably due to downhill movement. | ||
| + | Wikielephantglacier.jpg|Romer Lake's Elephant Foot Glacier in the Earth's Arctic, as seen by Landsat 8. This picture shows several glaciers that have the same shape as many features on Mars that are believed to also be glaciers. | ||
| + | ESP 045505 1400flow.jpg|Flow feature that was probably a glacier, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 046270 1445flowridges.jpg|Flow ridges, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program Ridges probably formed at the end of old glacier. | ||
| + | Image:ESP_020319flowcontext.jpg|Context for the next image of the end of a flow feature or glacier. Location is Hellas quadrangle. | ||
| + | Image:ESP_020319flowsclose-up.jpg|Close-up of the area in the box in the previous image. This may be called by some the terminal moraine of a glacier. For scale, the box shows the approximate size of a football field. Image taken with HiRISE under the HiWish program. Location is Hellas quadrangle. | ||
| + | Image:20543 gap in crater rim.jpg|Material Flowing through a crater rim, as seen by HiRISE, under the HiWish program. Lateral moraines are labeled. | ||
| + | Image:ESP020886 with tongue shaped glacier.jpg|Glaciers, as seen by HiRISE, under HiWish program. Glacier on left is thin because it has lost much of its ice. Glacier on the right, on the other hand, is thick; it still contains a lot of ice that is under a thin layer of dirt and rock. | ||
| + | Image:Tongue23141.jpg|Tongue-shaped glacier, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program. Ice may exist in the glacier, even today, beneath an insulating layer of dirt. | ||
| + | Image:Tongue23141close.jpg|Close-up of tongue-shaped glacier, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program Resolution is about 1 meter, so one can see objects a few meters across in this image. Ice may exist in the glacier, even today, beneath an insulating layer of dirt. | ||
| + | ESP 045070 1440tongues.jpg|Tongue-shaped glaciers indicated with arrows, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | 45070 1440glacialsnout.jpg|Close view of snout of glacier, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program High center polygons are visible. Box shows size of football field. | ||
| + | 45070 1440polygons.jpg|Close view of high center polygons near glacier, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | 45070 1440polygonsclose.jpg|Close view of high center polygons near glacier, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | 45070 1440polygonscloseshadows.jpg|Close view of high center polygons near glacier, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program Box shows size of football field. | ||
| + | 45070 1440polygonshadows.jpg|Close view of high center polygons near glacier, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 051017 1420glacier.jpg|Tongue-shaped glacier, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 047193 1440tongues.jpg|Wide view of tongue-shaped flows, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | 47193 1440tonguesclose.jpg|Close view of tongue-shaped flows, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | 47193 1440polygons.jpg|Close view of tongue-shaped flows and polygonal terrain (which is labeled), as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | 47193 1440polygonsclose2.jpg|Close view of polygonal terrain near tongue-shaped flows, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | 48854 1455grooves.jpg|Grooves caused by movement of glacier, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 048854 1455polygonsclosecolor.jpg|Close, color view of polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Polygons are common in ice-rich ground. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Channels== | ||
| + | Today, it is generally accepted that water once flowed in river valleys on Mars.<ref>Baker | first1 = V. |display-authors=etal | year = 2015 | title = Fluvial geomorphology on Earth-like planetary surfaces: a review | url = | journal = Geomorphology | volume = 245 | issue = | pages = 149–182 | doi=10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.05.002|</ref> <ref>Carr, M. 1996. in Water on Mars. Oxford Univ. Press.</ref> Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early seventies with the [[Mariner 9]] orbiter.<ref>Baker, V. 1982. The Channels of Mars. Univ. of Tex. Press, Austin, TX</ref> <ref>Baker | first1 = V. | last2 = Strom | first2 = R. | last3 = Gulick | first3 = V. | last4 = Kargel | first4 = J. | last5 = Komatsu | first5 = G. | last6 = Kale | first6 = V. | year = 1991 | title = Ancient oceans, ice sheets and the hydrological cycle on Mars | url = | journal = Nature | volume = 352 | issue = 6336| pages = 589–594 | doi=10.1038/352589a0 | </ref> <ref>Carr | first1 = M | year = 1979 | title = Formation of Martian flood features by release of water from confined aquifers | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 84 | issue = | pages = 2995–300 | doi=10.1029/jb084ib06p02995 |</ref> <ref>Komar | first1 = P | year = 1979 | title = Comparisons of the hydraulics of water flows in Martian outflow channels with flows of similar scale on Earth | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 37 | issue = 1| pages = 156–181 | doi=10.1016/0019-1035(79)90123-4 |</ref> Indeed, a study published in June 2017, calculated that the volume of water needed to carve all the channels on Mars was even larger than the proposed ocean that the planet may have had. <ref>http://spaceref.com/mars/how-much-water-was-needed-to-carve-valleys-on-mars.html</ref> <ref>Luo, W., et al. 2017. New Martian valley network volume estimate consistent with ancient ocean and warm and wet climate. Nature Communications 8. Article number: 15766 (2017). </ref> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | Image:Mad Vallis.JPG|[[Mad Vallis]], as seen by HiRISE. Picture on right is an enlargement of part of the other picture. | ||
| + | ESP 039902 1455channel.jpg|Channels, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. | ||
| + | ESP 041972 1490channel.jpg|Streamlined shape in old river valley, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. The streamlined shape is evidence of running water. | ||
| + | ESP 045492 1430channel.jpg|Channel, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 045492 1430channeltop.jpg|Channel, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 047997 1415channels.jpg|Channels, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 048196 1460meteorite.jpg|Wide view of small channels, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 48196 1460channels.jpg|Close view of channels, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 048855 1450channels.jpg|Channel network, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 050886 1475valley.jpg|Valley, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 052494 1395meanders.jpg|Channel, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Arrows indicate evidence of a meander. | ||
| + | File:55091 1405mantlechannels.jpg|Close view of small channels that seem to originate in a mantle layer, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 050964 1410channel.jpg|Channels, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Layers== | ||
| + | Many places on Mars show rocks arranged in layers. Rock can form layers in a variety of ways. Volcanoes, wind, or water can produce layers.<ref>http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu?PSP_008437_1750 |title=HiRISE | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment |publisher=Hirise.lpl.arizona.edu?psp_008437_1750 |</ref> A detailed discussion of layering with many Martian examples can be found in Sedimentary Geology of Mars.<ref>Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.). 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM.</ref> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 051110 1465layers.jpg|Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 51110 1465layerswide.jpg|Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 51110 1465layersblocks.jpg|Close views of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Boulders are also visible in the image. | ||
| + | ESP 045507 1470layers.jpg|Wide view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 045507 1470layeredcrater.jpg|Close view of layered deposit in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 45507 1470layers.jpg|Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 45507 1470layerswhite.jpg|Layered formation, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 45507 1470layerswhiteclose.jpg|Close view of layers from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 46139 1375layers.jpg|Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 047154 1410layers.jpg|Wide view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 47154 1410gullyclose.jpg|Channel of a gully indicated with arrows Picture enlarged from previous image | ||
| + | 47154 1410layersclose.jpg|Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 048144 1475layers.jpg|Wide view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 48144 1475layers.jpg|Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 48144 1475layerscubes.jpg|Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Some of the layers are breaking up into large blocks | ||
| + | 48144 1475cubes.jpg|Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Some of the layers are breaking up into large blocks | ||
| + | 48605 1485layers.jpg|Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 048882 1490lighttoned.jpg|Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Some layers are light-toned which means that they may have been associated with water. | ||
| + | 48882 1490layers.jpg|Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Some layers are light-toned which means that they may have been associated with water. | ||
| + | ESP 048882 1490layersclosecolor.jpg|Close view of light-toned materials, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Light-toned materials have been associated with water. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | File:ESP 054763 1500layers.jpg|Wide view of light and dark toned layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:54763 1500layers.jpg|Close view of light and dark toned layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:54763 1500layers2.jpg|Close view of light and dark toned layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:54763 1500layerscolor.jpg|Close, color view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program The different colors represent different minerals. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | File:ESP 055053 1485layers.jpg|Wide view of light and dark toned layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:55053 1485layersclosecolor.jpg|Close, color view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program The different colors represent different minerals. | ||
| + | File:55053 1485layersclosecolor2.jpg|Close, color view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | File:ESP 055581 1470layers.jpg|Wide view of layers in mounds, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:55581 1470layered mounds.jpg|Close view of layers in mound, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Honeycomb terrain== | ||
| + | Honeycomb terrain is strangely beautiful. It presents with relatively flat-lying “cells” that appear to have concentric layers or bands, similar to a honeycomb. This "honeycomb" terrain was first discovered in the northwestern part of Hellas.<ref>Bernhardt | first1 = H. |display-authors=etal | year = 2016 | title = The honeycomb terrain on the Hellas basin floor, mars: a case for salt or ice diapirism: hellas honeycombs as salt/ice diapirs | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 121 | issue = 4| pages = 714–738 | doi=10.1002/2016je005007| </ref> Although several ideas have been put forth, the exact geologic process responsible for creating these features remains unresolved.<ref>http://www.uahirise.org/ESP_049330_1425</ref> Some calculations indicate that this formation may have been caused by ice moving up through the ground in this region. The ice layer would have been between 100 m and 1 km thick.<ref>Weiss, D., J. Head. 2017. HYDROLOGY OF THE HELLAS BASIN AND THE EARLY MARS CLIMATE: WAS THE HONEYCOMB TERRAIN FORMED BY SALT OR ICE DIAPIRISM? Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII. 1060.pdf</ref> <ref>Weiss | first1 = D. | last2 = Head | first2 = J. | year = 2017 | title = Salt or ice diapirism origin for the honeycomb terrain in Hellas basin, Mars?: Implications for the early martian climate | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 284 | issue = | pages = 249–263 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2016.11.016 | </ref> <ref>Bernhardt | first1 = H. |display-authors=etal | year = 2016 | title = The honeycomb terrain on the Hellas basin floor, mars: a case for salt or ice diapirism: hellas honeycombs as salt/ice diapirs | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 121 | issue = 4| pages = 714–738 | doi=10.1002/2016je005007| </ref> When one substance moves up through another denser substance, it is called a “diapir.” So, it seems that large masses of ice have pushed up layers of rock into domes that were eroded. After erosion removed the top of the layered domes, circular features remained. | ||
| + | Diapirs are thought to be responsible for features on Neptune's moon Triton, Jupiter's moon Europa, Saturn's moon Enceladus, and Uranus's moon Miranda.<ref>Cassini Imaging Central Laboratory for Operations, [http://ciclops.org/view/5156/Enceladus_Rev_80_Flyby Enceladus Rev 80 Flyby: Aug 11 '08]. Retrieved 2008-08-15.</ref> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 048130 1380honeycomb.jpg|Concentric bands and layers that has been called "honeycomb terrain" Picture was taken by HiRISE under the HiWish program. | ||
| + | ESP 045348 1415rings.jpg|Circular layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 046139 1375ridgeslayers.jpg|layers and ridges that form strange patterns, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 46139 1375ridges.jpg|Close view of ridges forming strange patterns, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 049330 1425honeycomb.jpg|Honeycomb terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 049330 1425honeycombcolor.jpg|Close, color view of honeycomb terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | 49330 1425honeycombcubes.jpg|Close view of honeycomb terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | 49330 1425honeycombcubesclose.jpg|Close view of honeycomb terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program This enlargement shows material breaking up into blocks. Arrow indicates a cube-shaped block. | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:ESP 057110 1365ridges.jpg|Ridges, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:ESP 057110 1365ridgescircles.jpg|Close view of concentric and parallel ridges, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:ESP 057111 1455ridges.jpg|Wide view of ridge network, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:ESP 057111 1455ridges3.jpg|Close view of ridge network, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:57111 1455ridgenetwork.jpg|Close view of ridge network, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Gullies== | ||
| + | Gullies occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Gullies are believed to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. Moreover, they lie on top of sand dunes which themselves are considered to be quite young. Usually, each gully has an alcove, channel, and apron.<ref>Edgett |first1= K. |last2= Malin |first2= M. C. |last3= Williams |first3= R. M. E. |last4= Davis |first4= S. D. |date= 2003 |title= Polar-and middle-latitude martian gullies: A view from MGS MOC after 2 Mars years in the mapping orbit |journal= Lunar Planet. Sci. |volume=34 |at=p. 1038, Abstract 1038 | url=http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2003/pdf/1038.pdf |</ref> <ref>Dickson | first1 = J | last2 = Head | first2 = J | last3 = Kreslavsky | first3 = M | title = Martian gullies in the southern mid-latitudes of Mars: Evidence for climate-controlled formation of young fluvial features based upon local and global topography | doi = 10.1016/j.icarus.2006.11.020 | </ref> <ref>http://www.planetary.brown.edu/pdfs/3138.pdf | date = 2007 | pages = 315–323 | volume = 188 | issue = 2 | journal = Icarus | </ref> | ||
| + | For years, many believed that gullies were formed by running water, but further observations demonstrate that they may be formed by dry ice. Recent studies describe using the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on MRO to examine gullies at 356 sites, starting in 2006. Thirty-eight of the sites showed active gully formation. Before-and-after images demonstrated the timing of this activity coincided with seasonal carbon dioxide frost and temperatures that would not have allowed for liquid water. When dry ice frost changes to a gas, it may lubricate dry material to flow especially on steep slopes.<ref>http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2014-226</ref> <ref>http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/ESP_032078_1420</ref><ref>http://www.space.com/26534-mars-gullies-dry-ice.html</ref> In some years frost, perhaps as thick as 1 meter, triggers avalanches. This frost contains mostly dry ice, but also has tiny amounts of water ice.<ref>http://spaceref.com/mars/frosty-gullies-on-mars.html</ref> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 048881 1415gullies.jpg|Gullies in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | 48881 1415polygons.jpg|Close view of gullies in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Polygons are visible in this close view. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 049185 1350gullieslayers.jpg|Wide view of layers and gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Arrows point to small gullies. | ||
| + | 49185 1350gully.jpg|Close view of small gully, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:ESP 057044 1325gullies.jpg|Wide view of gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:57044 1325colorgullies.jpg|Close, color view of gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:57044 1325curvedgullies.jpg|Close view of gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Curves in channels are evidence that these gullies were not created by landslides. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Polygons== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some surfaces on Mars display polygons. These may be of different sizes. Polygons are an example of patterned ground. '''Polygonal, patterned ground''' is quite common in some regions of Mars.<ref>Kostama | first1 = V.-P. | last2 = Kreslavsky | first2 = M. | last3 = Head | first3 = J. | year = 2006 | title = Recent high-latitude icy mantle in the northern plains of Mars: Characteristics and ages of emplacement | url = | journal = Geophys. Res. Lett. | volume = 33 | issue = 11| page = L11201 | doi = 10.1029/2006GL025946 |</ref> <ref>Malin | first1 = M. | last2 = Edgett | first2 = K. | year = 2001 | title = Mars Global Surveyor Mars Orbiter Camera: Interplanetary cruise through primary mission | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 106 | issue = E10| pages = 23429–23540 | doi=10.1029/2000je001455 | </ref> <ref>Milliken | first1 = R. |display-authors=etal | year = 2003 | title = Viscous flow features on the surface of Mars: Observations from high-resolution Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) images | url = https://semanticscholar.org/paper/a822f14644d2294b948e101be2f294ac33b57ec3| journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 108 | issue = | page = |</ref> <ref>Mangold | first1 = N | year = 2005 | title = High latitude patterned grounds on Mars: Classification, distribution and climatic control | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 174 | issue = 2| pages = 336–359 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2004.07.030 |</ref> <ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Kreslavsky | first1 = M. | last2 = Head | first2 = J. | year = 2000 | title = Kilometer-scale roughness on Mars: Results from MOLA data analysis | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 105 | issue = E11| pages = 26695–26712 | doi=10.1029/2000je001259 |</ref> <ref>Seibert | first1 = N. | last2 = Kargel | first2 = J. | year = 2001 | title = Small-scale martian polygonal terrain: Implications for liquid surface water | url = | journal = Geophys. Res. Lett. | volume = 28 | issue = 5| pages = 899–902 | doi=10.1029/2000gl012093 |</ref> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | 49185 1350polygons.jpg|Group of polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:040310 1475flagstones.jpg|Patterned ground in Hellas, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program The rectangle shows the size of a football field. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 049660 1200polygons.jpg|Wide view of polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Parts of this image are enlarged in following images. | ||
| + | 49660 1200polygonswide.jpg|Polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 49660 1200polygonsrockscraters.jpg|Close view of polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Arrow point to boulders that sit inside of small craters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 49660 1200polygonspits.jpg|Close view of polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | 49660 1200polygonsrockscratersclose.jpg|Close view of polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Exposed ice sheets== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thick deposits of ice were found by a team of researchers using instruments on board the [[Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter]] (MRO).<ref>Dundas, E., et al. 2018. Exposed subsurface ice sheets in the martian mid-latitudes. Science. 359. 199.</ref> The team of scientists found eight eroding slopes that showed exposed water ice sheets as thick as 100 meters. Seven of the locations were in the southern hemisphere. Much evidence of buried ice under the ground on vast regions of Mars has already been found by past studies, but this study found that the ice was only covered by a layer of about 1 or 2 meters thick of Martian soil.<ref>https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7038 Steep Slopes on Mars Reveal Structure of Buried Ice]. NASA Press Release. 11 January 2018.</ref> <ref>http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2018/01/ice-cliffs-spotted-mars Ice cliffs spotted on Mars. ''Science News''. Paul Voosen. 11 January 2018.</ref> <ref>https://www.slideshare.net/sacani/exposed-subsurface-ice-sheets-in-the-martian-midlatitudes</ref> Shane Byrne of the University of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, Tucson, one of the co-authors remarked that future colonists of the Red Planet would be able to gather up ice with just a bucket and shovel.<ref>http://spaceref.com/mars/steep-slopes-on-mars-reveal-structure-of-buried-ice.html</ref> | ||
| + | The layered ice is exposed in triangular shaped depressions. They are unique in that one wall is very steep and faces the pole. Confirmation that water-ice makes up the layers came from the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) on board the [[Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter]] (MRO). Spectra gathered by CRISM showed strong signals of water.<ref>Colin M. Dundas, et al. ''Science'', 12 January 2018. Vol. 359, Issue 6372, pp. 199-201. </ref> These layers are especially prominent in depressions in Hellas quadrangle as shown in the enlarged views below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | PIA22078 hireswideview.jpg|Wide view of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE The colored strip shows the part of the image that can be seen in color. The wall at the top of the depression contains pure ice. This wall faces the south pole. Location is Hellas quadrangle.<ref>Supplementary Materials Exposed subsurface ice sheets in the Martian mid-latitudes Colin M. Dundas, Ali M. Bramson, Lujendra Ojha, James J. Wray, Michael T. Mellon, Shane Byrne, Alfred S. McEwen, Nathaniel E. Putzig, Donna Viola, Sarah Sutton, Erin Clark, John W. Holt</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | PIA22077 hirescloseblue.jpg|Close, color view of wall containing ice from previous image, as seen by HiRISE | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | ESP 050345 1230icelayersangles.jpg|Wide view of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE The wall which faces the south pole contains ice in distinct layers that are visible in next image. Location is Hellas quadrangle.<ref>Supplementary Materials Exposed subsurface ice sheets in the Martian mid-latitudes Colin M. Dundas, Ali M. Bramson, Lujendra Ojha, James J. Wray, Michael T. Mellon, Shane Byrne, Alfred S. McEwen, Nathaniel E. Putzig, Donna Viola, Sarah Sutton, Erin Clark, John W. Holt</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 50345 1230icelayersangular.jpg|Close view of wall of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE layers are visible in the wall. The lower layers are tilted, while layers near the surface are more or less horizontal. Such an arrangement of layers is called an "angular unconformity."<ref>Supplementary Materials Exposed subsurface ice sheets in the Martian mid-latitudes Colin M. Dundas, Ali M. Bramson, Lujendra Ojha, James J. Wray, Michael T. Mellon, Shane Byrne, Alfred S. McEwen, Nathaniel E. Putzig, Donna Viola, Sarah Sutton, Erin Clark, John W. Holt</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 050477 1220icelayers.jpg|Wide view of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE The wall which faces the south pole contains ice in distinct layers that are visible in next image. Location is Hellas quadrangle.<ref>Supplementary Materials Exposed subsurface ice sheets in the Martian mid-latitudes Colin M. Dundas, Ali M. Bramson, Lujendra Ojha, James J. Wray, Michael T. Mellon, Shane Byrne, Alfred S. McEwen, Nathaniel E. Putzig, Donna Viola, Sarah Sutton, Erin Clark, John W. Holt</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 50477 1230icelayersangular.jpg|Close view of wall of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE layers are visible in the wall. The lower layers are tilted, while layers near the surface are more or less horizontal. Such an arrangement of layers is called an "angular unconformity." | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Besides being of great value to future explorers, these ice layers could help us better understand the climate history of Mars. They provide a record of the past. The large variations in the tilt of the planet cause dramatic climate variations. Mars does not possess a large moon to keep its tilt stable. Today, ice is concentrated at the poles, with a greater tilt, more ice will exist at mid-latitudes. | ||
| + | These climate changes may be able to be measured with study of these layers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These triangular depressions are similar to those in scalloped terrain. However scalloped terrain, displays a gentle equator-facing slope and is rounded. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Scalloped topography== | ||
| + | Scalloped topography is common in the mid-latitudes of Mars, between 45° and 60° north and south. In the region around Hellas it is found in locations called Peneus Patera and Amphitrites Paterae<ref> Lefort | first1 = A. | last2 = Russell | first2 = P. | last3 = Thomas | first3 = N. | year = 2009 | title = Scalloped terrains in the Peneus and Amphitrites Paterae region of Mars as observed by HiRISE | journal = Icarus | volume = 205| issue = 1 | pages = 259–268| doi = 10.1016/j.icarus.2009.06.005 |</ref> <ref>Zanetti, M., Hiesinger,H., Reiss, D., Hauber, E. and Neukum, G. 2009. http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2009/pdf/2178.pdf "Scalloped Depression Development on Malea Planum and the Southern Wall of the Hellas Basin, Mars", 40th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, abstract 2178</ref> in the southern hemisphere. It consists of shallow, rimless depressions with scalloped edges, commonly referred to as "scalloped depressions" or simply "scallops". Scalloped depressions can be isolated or clustered and sometimes seem to coalesce. A typical scalloped depression displays a gentle equator-facing slope and a steeper pole-facing scarp.<ref>http://www.uahirise.org/ESP_038821_1235</ref> Scalloped depressions are believed to form from the removal of subsurface material, possibly interstitial ice, by sublimation (direct transition of a material from the solid to the gas phase with no intermediate liquid stage). This process may still be happening at present.<ref>http://hiroc.lpl.arizona.edu/images/PSP/diafotizo.php?ID=PSP_002296_1215|title=Scalloped Topography in Peneus Patera Crater|publisher=HiRISE Operations Center|date=2007-02-28|accessdate=2014-11-24}}</ref> This topography may be of great importance for future colonization of Mars because it may point to deposits of pure ice.<ref>Dundas | first1 = C. | last2 = Bryrne | first2 = S. | last3 = McEwen | first3 = A. | year = 2015 | title = Modeling the development of martian sublimation thermokarst landforms | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 262 | issue = | pages = 154–169 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2015.07.033 |</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | Image:Scalop formation.jpg|Stages in scalop formation, as seen by HiRISE. These formations probably form from the sublimation of ground rich in pure water ice many meters in depth.<ref name="ReferenceC">Dundas, C., S. Bryrne, A. McEwen. 2015. Modeling the development of martian sublimation thermokarst landforms. Icarus: 262, 154-169.</ref> | ||
| + | ESP 049304 1215scallops.jpg|Scalloped terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program [[Dust devil tracks]] are also visible. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Additional Images in Hellas quadrangle== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | Image:Hellas quantangle.JPG|Hellas quadrangle map showing two large river valleys that slope left, toward the floor of the crater. | ||
| + | ESP 046376 1425hollows.jpg|Field of hollows, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 46376 1425surface.jpg|Surface features, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | File:55421 1395ribbed.jpg|Hollows on floor of Reull Vallis, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | Image:Banded terrain in Hellas.JPG|Banded or taffy-pull terrain in Hellas, as seen by [[Mars Global Surveyor]]. Origin is unknown at present. | ||
| + | Image:Centauri Montes detail.jpg|[[Centauri Montes]], as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 500 meters long. The original enlargement of the image at the left is full of rich detail on all parts of the picture. | ||
| + | Image:Ausonia Mensa.JPG|[[Ausonia Mensa]], as seen by [[Mars Global Surveyor|MGS]], under the [[MOC Public Targeting Program]]. This eroded mensa has many channels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Image:Scalop formation.jpg|Stages in scalop formation, as seen by HiRISE. These formations probably form from the sublimation of ground rich in pure water ice many meters in depth.<ref name="ReferenceC"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 043554 1440dike.jpg|Possible dike and troughs, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program The arrows point to the possible dike along the left edge of picture. Straight features are rare in nature; they are often due to dikes and joints. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 045571 1375strange.jpg|Odd shapes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program part of this image is enlarged in next image. | ||
| + | 45571 1375cracks.jpg|Ridges forming from cracks, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Box in upper left shows size of football field. | ||
| + | ESP 047168 1395dunes.jpg|Dunes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 047180 1375brains.jpg|Wide view of brain terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 47180 1375brainscross.jpg|Close, side view of brain terrain from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | 48196 1460meteoriteclose.jpg|Out of place rock, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program The arrow points to a large rock that is definitely out of place. It may be a meteorite or it may have been tossed here by a nearby impact. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 48196 1460meteoriteclosest.jpg|Close view of out of place rock, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program It may be a meteorite or it may have been tossed here by a nearby impact. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Mars Atlas]] | [[Category:Mars Atlas]] | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 5 March 2020
| MC-28 | Hellas | 30–65° S | 60–120° E | Quadrangles | Atlas |
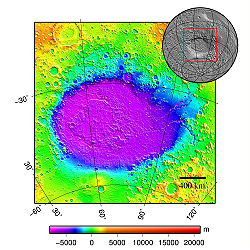
The most famous feature of this area is the Hellas basin, a impact crater 2300 km in diameter.
The Hellas quadrangle covers the area from 30° to 65° south latitude and 240° to 300° west longitude (120-60 E ). When an asteroid slammed into Mars to create a big hole that makes up some of this quadrange, many unbelievable events were caused—it was worse than any science fiction movie. Within the Hellas quadrangle lies the classic features Hellas Planitia and Promethei Terra. Many interesting and mysterious features have been discovered in the Hellas quadrangle, including the giant river valleys Dao Vallis, Niger Vallis, Harmakhis, and Reull Vallis—all of which may have contributed water to a lake in the Hellas basin in the distant past.[1] [2] [3] Many places in the Hellas quadrangle show signs that the ground is full of ice, especially with glacier-like flow features.
Contents
- 1 Hellas Basin
- 2 Results of asteroid collision
- 3 Strange surfaces—Origin Unknown
- 4 Giant Lake
- 5 How climate change caused ice-rich features
- 6 Lobate debris aprons (LDA)
- 7 Lineated Valley Fill (LVF)
- 8 Upper Plains Unit
- 9 Origin of Dao Vallis
- 10 Dust devil tracks
- 11 Pedestal Craters
- 12 Glacial Features
- 13 Channels
- 14 Layers
- 15 Honeycomb terrain
- 16 Gullies
- 17 Polygons
- 18 Exposed ice sheets
- 19 Scalloped topography=
Hellas Basin
The Hellas quadrangle contains part of the Hellas Basin, the largest known impact crater on the surface of Mars and the second largest in the solar system. The depth of the crater is 7152 m[4] (23,000ft) below the standard topographic datum of Mars. The basin is located in the southern highlands of Mars and is thought to have been formed about 3.9 billion years ago, during a period that geologists call the Late Heavy Bombardment. This was period of much greater asteroid impacts.
Results of asteroid collision
The physics of this great event boggles the mind. Studies suggest that when an impact created the Hellas Basin, the entire surface of Mars was heated hundreds of degrees, 70 meters of molted rock fell on the planet, and an atmosphere of gaseous rock was formed. Think about hot, molted rock falling to a depth of a 21 story building. On Earth that would cover all homes and most buildings. This rock atmosphere was 10 times as thick as the Earth's atmosphere. In a few days, the rock would have condensed out and covered the whole planet with an additional 10 m of molten rock.[5] When all this rock cooled all the planet would be covered with rock that was as deep as a 24 story building is tall. And this is not made up folks—the proof is the big hole called the Hellas Basin. Imagine if such a thing happened on the Earth.
Strange surfaces—Origin Unknown
In the Northwest portion of Hellas Planitia is a strange type of surface called complex banded terrain or taffy-pull terrain. Its process of formation is still largely unknown, although it appears to be due to erosion of hard and soft sediment along with ductile deformation. Ductile deformation results from layers undergoing strain.[6]
Giant Lake
Early in the planet's history, it is believed that a giant lake existed in the Hellas Basin.[7] Possible shorelines have been discovered. These are evident in alternating benches and scarps visible in Mars orbiting camera narrow-angle images. In addition, Mars orbiting laser altimeter (MOLA) data show that the contacts of these sedimentary units mark contours of constant elevation for thousands of km, and in one case all around the basin. Channels, believed to be formed by water, enter into the basin. The Hellas drainage basin may be almost one-fifth that of the entire northern plains. A lake in Hellas in today's Martian climate would form a thick ice at the top that would eventually sublimate away. That is the ice would turn directly from a solid to a gas. This is similar to how dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) behaves on Earth.[8] Glacial features ( moraines, drumlins, and eskers) have been found that may have been formed when the water froze.[9] [10]
Hellas Basin with graph showing the great depth of the crater. It is the deepest crater on Mars and has the highest surface pressure: 1155 pascal (Pa)[11] (11.55 millibar, 0.17 psi, or 0.01 atm).
How climate change caused ice-rich features
Many features on Mars, including ones in Hellas quadrangle, are believed to contain large amounts of ice. The Hellas region displays many strange and beautiful landscapes. Most do not have their counterparts on the Earth. Researchers have struggled to explain these features and other. Mars holds many mysteries. However, after so much coverage by satellites with increasing better cameras, we have made major strides in understanding the mysteries of the Red Planet. Some aspects of the planet are still debated. Many things we do have some understanding of their natures, but some details have yet to be worked out.
Most of the strangeness of the Hellas region relates to climate change. Indeed, most of the whole planet’s surface appearance is driven by drastic and frequent climate changes. These changes are due to basic physics. Seasons on the planets, including the Earth, are caused of a planet's rotational axis. Because the Earth has a moon of considerable mass, the Earth’s axis does not change much from its usual 23.5 degrees. However, Mars lacks a large moon; consequently its tilt has even been greater than 80 degrees. Note that its tilt at 25 degrees is almost the same as ours. [12] [13]
Studies have shown that when the tilt of Mars reaches 45 degrees from its current 25 degrees, ice is no longer stable at the poles. As a result, it will disappear.[14] Furthermore, at this high tilt, stores of solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) sublimate, thereby increasing the atmospheric pressure. This increased pressure allows more dust to be held in the atmosphere. With more dust, more ice will freeze onto the dust. Eventually, moisture in the atmosphere will fall as snow or as ice frozen onto dust grains. Calculations suggest this material will concentrate in the mid-latitudes. And Hellas is in the mid-latitudes of the southern hemisphere.[15] [16] Using decades of date from orbiting satellites together with general principles about weather and climate, researchers have developed theories or models that explain why Mars looks like it does. They call these models or theories general circulation models. These theories predict accumulations of ice-rich dust (which becomes mantle) in the same areas where ice-rich features are found.[17]
When the tilt begins to return to lower values, the ice sublimates (turns directly to a gas) and leaves behind a lag of dust.[18] [19] This lag deposit caps the underlying material so with each cycle of high tilt levels, some ice-rich mantle remains behind.Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag [20]
Die-sized clumps of bright material in the enlarged "Dodo-Goldilocks" trench vanished over the course of four days, implying that they were composed of ice which sublimated following exposure.[21][22]
In addition, HiRISE has seen fresh craters with ice at the bottom. After a time, HiRISE saw the ice deposit disappear.[23]
Eventually, small cracks become large canyons or troughs in the mantle. Small cracks often contain small pits and chains of pits.[24] [25] When parts of this many meters deep mantle start to have cracks, sublimation takes over and many strange landscapes are created. HiRISE has imaged many of these scenes. Pictures below show many of these exotically beautiful forms. Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from Polar Regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate period’s water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water returns to the ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor condenses on the particles, and then they fall down to the ground due to the additional weight of the water coating. This material that falls, along with snow lands in certain places on Mars. A great deal lands in the Hellas region. It appears as a smooth covering. Due to its great age, the Martian surface is very irregular, but where mantle has accumulated it is smooth. When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulates the remaining ice.[26]
Lobate debris aprons (LDA)
One very important feature common in east Hellas are piles of material surrounding cliffs. The formation is called a lobate debris apron (LDA). Recently, research with the Shallow Radar on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has provided strong evidence that the LDAs are glaciers that are covered with a thin layer of rocks.[27] [28] [29] [30] [31] Large amounts of water ice are believed to be in the LDAs. Available evidence strongly suggests that the eastern part of Hellas accumulated snow in the past. When the tilt (obliquity) of Mars increases the southern ice cap releases large amounts of water vapor. Climate models predict that when this occurs, water vapor condenses and falls where LDAs are located. The tilt of the earth changes little because our relatively large moon keeps it stable. The two tiny Martian moons do not stabilize their planet, so the rotational axis of Mars undergoes large variations.[32] Lobate debris aprons may be a major source of water for future Mars colonists. Their major advantage over other sources of Martian water are that they can easily mapped from orbit and they are closer to the equator, where manned missions are more likely to land.
Lineated Valley Fill (LVF)
On the floors of some channels are features called lineated floor deposits or lineated valley fill. They are ridged and grooved materials that seem to deflect around obstacles. They are believed to be ice-rich. Some glaciers on the Earth show such features. Lineated floor deposits may be related to lobate debris aprons, which have been proven to contain large amounts of ice. Reull Vallis, as pictured below, displays these deposits.[33]
Drainage features in Reull Vallis, as seen by THEMIS. Click on image to see relationship of Reull Vallis to other features.
Reull Vallis floor showing lineated valley fill at the top and hollows near bottom, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Layers in Reull Vallis, as seen by THEMIS.
Fretted terrain near Reull Vallis, as seen by HiRISE.
Upper Plains Unit
Some places the mantle has piled up quite deeply. The remains of a 50-100 meter thick mantling, called the upper plains unit, has been discovered in the mid-latitudes of Mars. It was first investigated in the Deuteronilus Mensae region, but it occurs in other places as well. The remnants sometimes consist of sets of dipping layers in craters and along mesas.[34] Sets of dipping layers may be of various sizes and shapes—some look like stepped Aztec pyramids from Central America. The Upper plains unit can have several different appearances.
This unit also degrades into a feature named brain terrain; it looks like the human brain. Brain terrain is a region of maze-like ridges 3–5 meters high. Some ridges may consist of an ice core, so they may be sources of water for future colonists.
Some regions of the upper plains unit display large fractures and troughs with raised rims; such regions are called ribbed upper plains. Fractures are believed to have started with small cracks from stresses. Stress is suggested to initiate the fracture process since ribbed upper plains are common when debris aprons come together or near the edge of debris aprons—such sites would generate compressional stresses. Cracks expose more surfaces, and consequently more ice in the material sublimates into the planet's thin atmosphere. Eventually, small cracks become large canyons or troughs.[35] [25] The upper plains unit is probably just a very thick pile of mantle.to have fallen from the sky. It drapes various surfaces and as is the case for other mantle deposits, it has layers, is fine-grained, and is ice-rich. It is widespread; it does not seem to have a point source. The surface appearance of some regions of Mars is due to how this unit has degraded.
Origin of Dao Vallis

Dao Vallis begins near a large volcano, called Hadriaca Patera, so it is thought to have received water when hot magma melted huge amounts of ice in the frozen ground.[36] The partially circular depressions on the left side of the channel in the adjacent image suggests that groundwater sapping also contributed water.[37]
Dust devil tracks

Many areas on Mars, including the Hellas quadrangle, experience the passage of giant dust devils. A thin coating of fine bright dust covers most of the Martian surface. When a dust devil goes by it blows away the coating and exposes the underlying dark surface. Dust devils have been seen from the ground and from orbiting spacecraft. They have even blown the dust off of the solar panels of the two Mars Exploration Rovers (Spirit and Opportunity), thereby greatly extending their lives.[38] The twin Rovers were designed to last for 3 months, instead they have lasted far longer; Opportunity lasted more than 14 years. The pattern of dust devil tracks have been shown to change every few months.[39] A study that combined data from the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and the Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) found that some large dust devils on Mars have a diameter of 700 meters and last at least 26 minutes.[40]
Dust devil tracks on floor of Wallace Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter)
Pedestal Craters
Pedestal craters form when the ejecta from impacts protect the underlying material from erosion. As a result of this process, craters appear perched above their surroundings.
Drawing shows a later idea of how some pedestal craters form. In this way of thinking, an impacting projectile goes into an ice-rich layer—but no further. Heat and wind from the impact hardens the surface against erosion. This hardening can be accomplished by the melting of ice which produces a salt/mineral solution thereby cementing the surface.
Glacial Features
Glaciers, loosely defined as patches of currently or recently flowing ice, are thought to be present across large but restricted areas of the modern Martian surface, and are inferred to have been more widely distributed at times in the past.[41] [42] Lobate convex features on the surface known as viscous flow features and lobate debris aprons are now almost unanimously regarded as true glaciers.[43] [44] [45] [46] [47] [48] [49] [50] A climate model, reported in the journal Science in 2006, found that large amounts of ice should accumulate in the Hellas region, in the same places where glaciers are observed. Water is transported from the south polar area to northern Hellas and falls as precipitation.[51] The following pictures show many features that are probably glaciers—that is they are mostly ice and move downhill—like rivers—but much slower.
Close view of snout of flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Polygonal patterned ground is visible.
- Gully Flow Features.JPG
Surface features that show downhill movement, as seen by HiRISE.
Surface in Hellas quadrangle, as seen by HiRISE, under the HiWish program.
Possible Glacial Cirque in Hellas Planitia, as seen by HiRISE, under the HiWish program. Lines are probably due to downhill movement.
Channels
Today, it is generally accepted that water once flowed in river valleys on Mars.[52] [53] Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early seventies with the Mariner 9 orbiter.[54] [55] [56] [57] Indeed, a study published in June 2017, calculated that the volume of water needed to carve all the channels on Mars was even larger than the proposed ocean that the planet may have had. [58] [59]
Mad Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. Picture on right is an enlargement of part of the other picture.
Layers
Many places on Mars show rocks arranged in layers. Rock can form layers in a variety of ways. Volcanoes, wind, or water can produce layers.[60] A detailed discussion of layering with many Martian examples can be found in Sedimentary Geology of Mars.[61]
Honeycomb terrain
Honeycomb terrain is strangely beautiful. It presents with relatively flat-lying “cells” that appear to have concentric layers or bands, similar to a honeycomb. This "honeycomb" terrain was first discovered in the northwestern part of Hellas.[62] Although several ideas have been put forth, the exact geologic process responsible for creating these features remains unresolved.[63] Some calculations indicate that this formation may have been caused by ice moving up through the ground in this region. The ice layer would have been between 100 m and 1 km thick.[64] [65] [66] When one substance moves up through another denser substance, it is called a “diapir.” So, it seems that large masses of ice have pushed up layers of rock into domes that were eroded. After erosion removed the top of the layered domes, circular features remained. Diapirs are thought to be responsible for features on Neptune's moon Triton, Jupiter's moon Europa, Saturn's moon Enceladus, and Uranus's moon Miranda.[67]
Gullies
Gullies occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Gullies are believed to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. Moreover, they lie on top of sand dunes which themselves are considered to be quite young. Usually, each gully has an alcove, channel, and apron.[68] [69] [70] For years, many believed that gullies were formed by running water, but further observations demonstrate that they may be formed by dry ice. Recent studies describe using the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on MRO to examine gullies at 356 sites, starting in 2006. Thirty-eight of the sites showed active gully formation. Before-and-after images demonstrated the timing of this activity coincided with seasonal carbon dioxide frost and temperatures that would not have allowed for liquid water. When dry ice frost changes to a gas, it may lubricate dry material to flow especially on steep slopes.[71] [72][73] In some years frost, perhaps as thick as 1 meter, triggers avalanches. This frost contains mostly dry ice, but also has tiny amounts of water ice.[74]
Polygons
Some surfaces on Mars display polygons. These may be of different sizes. Polygons are an example of patterned ground. Polygonal, patterned ground is quite common in some regions of Mars.[75] [76] [77] [78] [79] [80]
Exposed ice sheets
Thick deposits of ice were found by a team of researchers using instruments on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).[81] The team of scientists found eight eroding slopes that showed exposed water ice sheets as thick as 100 meters. Seven of the locations were in the southern hemisphere. Much evidence of buried ice under the ground on vast regions of Mars has already been found by past studies, but this study found that the ice was only covered by a layer of about 1 or 2 meters thick of Martian soil.[82] [83] [84] Shane Byrne of the University of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, Tucson, one of the co-authors remarked that future colonists of the Red Planet would be able to gather up ice with just a bucket and shovel.[85] The layered ice is exposed in triangular shaped depressions. They are unique in that one wall is very steep and faces the pole. Confirmation that water-ice makes up the layers came from the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Spectra gathered by CRISM showed strong signals of water.[86] These layers are especially prominent in depressions in Hellas quadrangle as shown in the enlarged views below.
Wide view of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE The colored strip shows the part of the image that can be seen in color. The wall at the top of the depression contains pure ice. This wall faces the south pole. Location is Hellas quadrangle.[87]
Wide view of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE The wall which faces the south pole contains ice in distinct layers that are visible in next image. Location is Hellas quadrangle.[88]
Close view of wall of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE layers are visible in the wall. The lower layers are tilted, while layers near the surface are more or less horizontal. Such an arrangement of layers is called an "angular unconformity."[89]
Wide view of triangular depression, as seen by HiRISE The wall which faces the south pole contains ice in distinct layers that are visible in next image. Location is Hellas quadrangle.[90]
Besides being of great value to future explorers, these ice layers could help us better understand the climate history of Mars. They provide a record of the past. The large variations in the tilt of the planet cause dramatic climate variations. Mars does not possess a large moon to keep its tilt stable. Today, ice is concentrated at the poles, with a greater tilt, more ice will exist at mid-latitudes. These climate changes may be able to be measured with study of these layers.
These triangular depressions are similar to those in scalloped terrain. However scalloped terrain, displays a gentle equator-facing slope and is rounded.
Scalloped topography=
Scalloped topography is common in the mid-latitudes of Mars, between 45° and 60° north and south. In the region around Hellas it is found in locations called Peneus Patera and Amphitrites Paterae[91] [92] in the southern hemisphere. It consists of shallow, rimless depressions with scalloped edges, commonly referred to as "scalloped depressions" or simply "scallops". Scalloped depressions can be isolated or clustered and sometimes seem to coalesce. A typical scalloped depression displays a gentle equator-facing slope and a steeper pole-facing scarp.[93] Scalloped depressions are believed to form from the removal of subsurface material, possibly interstitial ice, by sublimation (direct transition of a material from the solid to the gas phase with no intermediate liquid stage). This process may still be happening at present.[94] This topography may be of great importance for future colonization of Mars because it may point to deposits of pure ice.[95]
Stages in scalop formation, as seen by HiRISE. These formations probably form from the sublimation of ground rich in pure water ice many meters in depth.[96]
Scalloped terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HIWish program Dust devil tracks are also visible.
Additional Images in Hellas quadrangle
Banded or taffy-pull terrain in Hellas, as seen by Mars Global Surveyor. Origin is unknown at present.
Centauri Montes, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 500 meters long. The original enlargement of the image at the left is full of rich detail on all parts of the picture.
Ausonia Mensa, as seen by MGS, under the MOC Public Targeting Program. This eroded mensa has many channels.
Stages in scalop formation, as seen by HiRISE. These formations probably form from the sublimation of ground rich in pure water ice many meters in depth.[96]
- ↑ Carr | first=Michael H. | publisher=Cambridge University Press | isbn= 978-0-521-87201-0 | title= The Surface of Mars |date=2006 |
- ↑ Moore | first1= J | last2= Wilhelms | first2= Don E. | title= Hellas as a possible site of ancient ice-covered lakes on Mars | journal= Icarus | volume= 154 | issue= 2 |pages= 258–276 | date= 2001 | doi = 10.1006/icar.2001.6736 |
- ↑ Cabrol, N. and E. Grim (eds). 2010. Lakes on Mars
- ↑ http://www-star.stanford.edu/projects/mgs/sum/s0403210230.html Martian Weather Observation] https://web.archive.org/web/20080531235046
- ↑ Carr | first=Michael H. | publisher=Cambridge University Press | isbn= 978-0-521-87201-0 | title= The Surface of Mars |date=2006 |
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizonai.edu/P/sP_008559_1405
- ↑ Voelker, M., et al. 2016. DISTRIBUTION AND EVOLUTION OF LACUSTRINE AND FLUVIAL FEATURES IN HELLASPLANITIA, MARS, BASED ON PRELIMINARY RESULTS OF GRID-MAPPING. 47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2016) 1228.pdf.
- ↑ Moore, J; Wilhelms, Don E. (2001). "Hellas as a possible site of ancient ice-covered lakes on Mars". Icarus. 154 (2): 258–276.
- ↑ Carr, Michael H. (2006). The Surface of Mars. Cambridge University Press. p. [page needed]. ISBN 978-0-521-87201-0.
- ↑ Kargel |first1= J. |first2= R. |last2=Strom |date= 1991 |title= Terrestrial glacial eskers: analogs for martian sinuous ridges | journal= LPSC | volume=XXII | pages= 683–684 |
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedstanhellas - ↑ Touma | first1 = J. | last2 = Wisdom | first2 = J. | year = 1993 | title = The Chaotic Obliquity of Mars | url = | journal = Science | volume = 259 | issue = 5099| pages = 1294–1297 | doi=10.1126/science.259.5099.1294 | pmid=17732249|
- ↑ Laskar | first1 = J. | last2 = Correia | first2 = A. | last3 = Gastineau | first3 = M. | last4 = Joutel | first4 = F. | last5 = Levrard | first5 = B. | last6 = Robutel | first6 = P. | year = 2004 | title = Long term evolution and chaotic diffusion of the insolation quantities of Mars | url =https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00000860/file/Ma_2004.laskar_prep.pdf | journal = Icarus | volume = 170 | issue = 2| pages = 343–364 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2004.04.005 |
- ↑ Head | first2 = J. | last3 = Marchant | first3 = D. | last4 = Kowalewski | first4 = D. | year = 2008 | title = Identification of sublimation-type thermal contraction crack polygons at the proposed NASA Phoenix landing site: Implications for substrate properties and climate-driven morphological evolution | url = | journal = Geophys. Res. Lett. | volume = 35| issue = 4| pages = L04202 | doi = 10.1029/2007GL032813 |
- ↑ Levy | first1 = J. | last2 = Head | first2 = J. | last3 = Marchant | first3 = D. | year = 2009 | title = Thermal contraction crack polygons on Mars: Classification, distribution, and climate implications from HiRISE observations | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 114| issue = E1| pages = E01007 |
- ↑ Hauber, E., D. Reiss, M. Ulrich, F. Preusker, F. Trauthan, M. Zanetti, H. Hiesinger, R. Jaumann, L. Johansson, A. Johnsson, S. Van Gaselt, M. Olvmo. 2011. Landscape evolution in Martian mid-latitude regions: insights from analogous periglacial landforms in Svalbard. In: Balme, M., A. Bargery, C. Gallagher, S. Guta (eds). Martian Geomorphology. Geological Society, London. Special Publications: 356. 111-131
- ↑ Laskar, J.; Correia, A.; Gastineau, M.; Joutel, F.; Levrard, B.; Robutel, P. (2004). "Long term evolution and chaotic diffusion of the insolation quantities of Mars" (PDF). Icarus. 170 (2): 343–364.
- ↑ Mellon | first1 = M. | last2 = Jakosky | first2 = B. | year = 1995 | title = The distribution and behavior of Martian ground ice during past and present epochs | url = https://semanticscholar.org/paper/815bfd93bdb19325e03e08556d145fa470112e4e%7C journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 100 | issue = E6| pages = 11781–11799 |
- ↑ Schorghofer | first1 = N | year = 2007 | title = Dynamics of ice ages on Mars | url = | journal = Nature | volume = 449 | issue = 7159| pages = 192–194 |
- ↑ "nasa.gov">http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/phoenix/news/phoenix-20080619.html
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namednasa.gov - ↑ Smith, P., et al. 2009. H2O at the Phoenix Landing Site. Science: 325, 58-61.
- ↑ Byrne, S. et al. 2009. Distribution of Mid-Latitude Ground Ice on Mars from New Impact Craters: 329.1674-1676
- ↑ Morgenstern, A., et al. 2007
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Baker, D., J. Head. 2015. Extensive Middle Amazonian mantling of debris aprons and plains in Deuteronilus Mensae, Mars: Implication for the record of mid-latitude glaciation. Icarus: 260, 269-288.
- ↑ author=MLA NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory |date=December 18, 2003 | title= Mars May Be Emerging From An Ice Age |work= ScienceDaily |accessdate=February 19, 2009 |url= https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2003
- ↑ Head | first1= JW | last2= Neukum | first2= G | last3= Jaumann | first3= R | last4= Hiesinger | first4= H | last5= Hauber | first5= E | last6= Carr | first6= M | last7= Masson | first7= P | last8= Foing | first8= B | last9= Hoffmann | first9= H | last10= Kreslavsky | first10= M. | last11= Werner | first11= S. | last12= Milkovich | first12= S. | last13= Van Gasselt | first13= S. | last14= Co-Investigator Team | first14= The Hrsc | title= Tropical to mid-latitude snow and ice accumulation, flow and glaciation on Mars | journal= Nature | volume= 434 | issue= 7031 |pages= 346–350 | date= 2005 | pmid = 15772652 | doi= 10.1038/nature03359 |
- ↑ http://news.brown.edu/pressreleases/2008/04/martian-glaciers
- ↑ Plaut | first1= Jeffrey J. | last2= Safaeinili | first2= Ali | last3= Holt | first3= John W. | last4= Phillips | first4= Roger J. | last5= Head | first5= James W. | last6= Seu | first6= Roberto | last7= Putzig | first7= Nathaniel E. | last8= Frigeri | first8= Alessandro | title= Radar Evidence for Ice in Lobate Debris Aprons in the Mid-Northern Latitudes of Mars | journal=Geophysical Research Letters | volume= 36 | issue= 2 | pages= n/a | date= 2009 |
- ↑ http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2008/pdf/2290.pdf |
- ↑ Radar Sounding Evidence for Ice within Lobate Debris Aprons near Hellas Basin, Mid-Southern Latitudes of Mars |http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2008/pdf/2441.pdf | journal = Lunar and Planetary Science |volume=XXXIX | issue = 1391 | pages = 2441 |date=2008 |last1= Holt | first=J.W.| last2 = Safaeinili | first2 = A. | last3 = Plaut | first3 = J. J. | last4 = Young | first4 = D. A. | last5 = Head | first5 = J. W. | last6 = Phillips | first6 = R. J. | last7 = Campbell | first7 = B. A. | last8 = Carter | first8 = L. M. | last9 = Gim | first9 = Y. | last10 = Seu |
- ↑ Holt | first1 = J. W. | last2 = Safaeinili | first2 = A. | last3 = Plaut | first3 = J. J. | last4 = Head | first4 = J. W. | last5 = Phillips | first5 = R. J. | last6 = Seu | first6 = R. | last7 = Kempf | first7 = S. D. | last8 = Choudhary | first8 = P. | last9 = Young | first9 = D. A. | last10 = Putzig | first10 = N. E. | last11 = Biccari | first11 = D. | last12 = Gim | first12 = Y. | title = Radar Sounding Evidence for Buried Glaciers in the Southern Mid-Latitudes of Mars | journal = Science | volume = 322 | issue = 5905 | pages = 1235–8 | date = 2008 | pmid = 19023078 | doi = 10.1126/science.1164246 |
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20100617191548/http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20021022a |
- ↑ Carr, M. 2001. Mars Global Surveyor observations of Martian fretted terrain. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 106. Issue E10
- ↑ Morgenstern, A., et al. 2007
- ↑ Carr, Michael H. (2006). The Surface of Mars. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-87201-0.
- ↑ http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20020807a
- ↑ http://marsrovers.jpl.nasa.gov/gallery/press/spirit/20070412a.html
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20111028015730/http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/spotlight/kenEdgett.html |
- ↑ Reiss | first1 = D. |display-authors=etal | year = 2011 | title = Multitemporal observations of identical active dust devils on Mars with High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 215 | issue = 1| pages = 358–369 |
- ↑ "Carr">"The Surface of Mars" Series: Cambridge Planetary Science (No. 6) {{ISBN|978-0-511-26688-1 Michael H. Carr, United States Geological Survey, Menlo Park
- ↑ "Kieffer, Hugh H. Mars|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NoDvAAAAMAAJ%7Caccessdate=March 7, 2011|date=1992|publisher=University of Arizona Press|isbn=978-0-8165-1257-7
- ↑ Milliken | first1 = R. E. | last2 = Mustard | first2 = J. F. | last3 = Goldsby | first3 = D. L. | year = 2003 | title = Viscous flow features on the surface of Mars: Observations from high-resolution Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) images | url = https://semanticscholar.org/paper/a822f14644d2294b948e101be2f294ac33b57ec3%7C journal = Journal of Geophysical Research | volume = 108 | issue = E6| page = 5057 | doi=10.1029/2002je002005 |
- ↑ Squyres | first1 = S.W. | last2 = Carr | first2 = M.H. | year = 1986 | title = Geomorphic evidence for the distribution of ground ice on Mars | url = | journal = Science | volume = 213 | issue = 4735| pages = 249–253 | doi = 10.1126/science.231.4735.249 | pmid = 17769645 |
- ↑ Head | first1 = J.W. | last2 = Marchant | first2 = D.R. | last3 = Dickson | first3 = J.L. | last4 = Kress | first4 = A.M. | year = 2010 | title = Criteria for the recognition of debris-covered glacier and valley glacier landsystem deposits | url = | journal = Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. | volume = 294 | issue = | pages = 306–320 | doi=10.1016/j.epsl.2009.06.041 |
- ↑ Holt | first1 = J.W. |display-authors=etal | year = 2008 | title = Radar sounding evidence for buried glaciers in the southern mid-latitudes of Mars | url = | journal = Science | volume = 322 | issue = 5905| pages = 1235–1238 |
- ↑ Morgan | first1 = G.A. | last2 = Head | first2 = J.W. | last3 = Marchant | first3 = D.R. | year = 2009 | title = Lineated valley fill (LVF) and lobate debris aprons (LDA) in the Deuteronilus Mensae northern dichotomy boundary region, Mars: Constraints on the extent, age and episodicity of Amazonian glacial events | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 202 | issue = 1| pages = 22–38 |
- ↑ Plaut | first1 = J.J. | last2 = Safaeinili | first2 = A. | last3 = Holt | first3 = J.W. | last4 = Phillips | first4 = R.J. | last5 = Head | first5 = J.W. | last6 = Sue | first6 = R. | last7 = Putzig | first7 = A. | year = 2009 | title = Frigeri Radar evidence for ice in lobate debris aprons in the mid-northern latitudes of Mars | url = https://semanticscholar.org/paper/f6b94761e6a276ce6894374ae9bea88fdc3e5e19%7C journal = Geophys. Res. Lett. | volume = 36 | issue = 2| page = L02203 |
- ↑ Baker | first1 = D.M.H. | last2 = Head | first2 = J.W. | last3 = Marchant | first3 = D.R. | year = 2010 | title = Flow patterns of lobate debris aprons and lineated valley fill north of Ismeniae Fossae, Mars: Evidence for extensive mid-latitude glaciation in the Late Amazonian | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 207 | issue = 1| pages = 186–209 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2009.11.017 |
- ↑ Arfstrom | first1 = J. | year = 2005 | title = Terrestrial analogs and interrelationships | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 174 | issue = 2| pages = 321–335 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2004.05.026 |
- ↑ Forget, F., et al. 2006. Formation of Glaciers on Mars by Atmospheric Precipitation at High Obliquity. Science: 311, 368-371.
- ↑ Baker | first1 = V. |display-authors=etal | year = 2015 | title = Fluvial geomorphology on Earth-like planetary surfaces: a review | url = | journal = Geomorphology | volume = 245 | issue = | pages = 149–182 | doi=10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.05.002|
- ↑ Carr, M. 1996. in Water on Mars. Oxford Univ. Press.
- ↑ Baker, V. 1982. The Channels of Mars. Univ. of Tex. Press, Austin, TX
- ↑ Baker | first1 = V. | last2 = Strom | first2 = R. | last3 = Gulick | first3 = V. | last4 = Kargel | first4 = J. | last5 = Komatsu | first5 = G. | last6 = Kale | first6 = V. | year = 1991 | title = Ancient oceans, ice sheets and the hydrological cycle on Mars | url = | journal = Nature | volume = 352 | issue = 6336| pages = 589–594 | doi=10.1038/352589a0 |
- ↑ Carr | first1 = M | year = 1979 | title = Formation of Martian flood features by release of water from confined aquifers | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 84 | issue = | pages = 2995–300 | doi=10.1029/jb084ib06p02995 |
- ↑ Komar | first1 = P | year = 1979 | title = Comparisons of the hydraulics of water flows in Martian outflow channels with flows of similar scale on Earth | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 37 | issue = 1| pages = 156–181 | doi=10.1016/0019-1035(79)90123-4 |
- ↑ http://spaceref.com/mars/how-much-water-was-needed-to-carve-valleys-on-mars.html
- ↑ Luo, W., et al. 2017. New Martian valley network volume estimate consistent with ancient ocean and warm and wet climate. Nature Communications 8. Article number: 15766 (2017).
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu?PSP_008437_1750 |title=HiRISE | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment |publisher=Hirise.lpl.arizona.edu?psp_008437_1750 |
- ↑ Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.). 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM.
- ↑ Bernhardt | first1 = H. |display-authors=etal | year = 2016 | title = The honeycomb terrain on the Hellas basin floor, mars: a case for salt or ice diapirism: hellas honeycombs as salt/ice diapirs | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 121 | issue = 4| pages = 714–738 | doi=10.1002/2016je005007|
- ↑ http://www.uahirise.org/ESP_049330_1425
- ↑ Weiss, D., J. Head. 2017. HYDROLOGY OF THE HELLAS BASIN AND THE EARLY MARS CLIMATE: WAS THE HONEYCOMB TERRAIN FORMED BY SALT OR ICE DIAPIRISM? Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII. 1060.pdf
- ↑ Weiss | first1 = D. | last2 = Head | first2 = J. | year = 2017 | title = Salt or ice diapirism origin for the honeycomb terrain in Hellas basin, Mars?: Implications for the early martian climate | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 284 | issue = | pages = 249–263 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2016.11.016 |
- ↑ Bernhardt | first1 = H. |display-authors=etal | year = 2016 | title = The honeycomb terrain on the Hellas basin floor, mars: a case for salt or ice diapirism: hellas honeycombs as salt/ice diapirs | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 121 | issue = 4| pages = 714–738 | doi=10.1002/2016je005007|
- ↑ Cassini Imaging Central Laboratory for Operations, Enceladus Rev 80 Flyby: Aug 11 '08. Retrieved 2008-08-15.
- ↑ Edgett |first1= K. |last2= Malin |first2= M. C. |last3= Williams |first3= R. M. E. |last4= Davis |first4= S. D. |date= 2003 |title= Polar-and middle-latitude martian gullies: A view from MGS MOC after 2 Mars years in the mapping orbit |journal= Lunar Planet. Sci. |volume=34 |at=p. 1038, Abstract 1038 | url=http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2003/pdf/1038.pdf |
- ↑ Dickson | first1 = J | last2 = Head | first2 = J | last3 = Kreslavsky | first3 = M | title = Martian gullies in the southern mid-latitudes of Mars: Evidence for climate-controlled formation of young fluvial features based upon local and global topography | doi = 10.1016/j.icarus.2006.11.020 |
- ↑ http://www.planetary.brown.edu/pdfs/3138.pdf | date = 2007 | pages = 315–323 | volume = 188 | issue = 2 | journal = Icarus |
- ↑ http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2014-226
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/ESP_032078_1420
- ↑ http://www.space.com/26534-mars-gullies-dry-ice.html
- ↑ http://spaceref.com/mars/frosty-gullies-on-mars.html
- ↑ Kostama | first1 = V.-P. | last2 = Kreslavsky | first2 = M. | last3 = Head | first3 = J. | year = 2006 | title = Recent high-latitude icy mantle in the northern plains of Mars: Characteristics and ages of emplacement | url = | journal = Geophys. Res. Lett. | volume = 33 | issue = 11| page = L11201 | doi = 10.1029/2006GL025946 |
- ↑ Malin | first1 = M. | last2 = Edgett | first2 = K. | year = 2001 | title = Mars Global Surveyor Mars Orbiter Camera: Interplanetary cruise through primary mission | url = | journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 106 | issue = E10| pages = 23429–23540 | doi=10.1029/2000je001455 |
- ↑ Milliken | first1 = R. |display-authors=etal | year = 2003 | title = Viscous flow features on the surface of Mars: Observations from high-resolution Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) images | url = https://semanticscholar.org/paper/a822f14644d2294b948e101be2f294ac33b57ec3%7C journal = J. Geophys. Res. | volume = 108 | issue = | page = |
- ↑ Mangold | first1 = N | year = 2005 | title = High latitude patterned grounds on Mars: Classification, distribution and climatic control | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 174 | issue = 2| pages = 336–359 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2004.07.030 |
- ↑ "Scalloped Topography in Peneus Patera Crater" (2007-02-28). Icarus 205 (1): 259–268. HiRISE Operations Center. doi:. Retrieved on 2014-11-24.
- ↑ Dundas | first1 = C. | last2 = Bryrne | first2 = S. | last3 = McEwen | first3 = A. | year = 2015 | title = Modeling the development of martian sublimation thermokarst landforms | url = | journal = Icarus | volume = 262 | issue = | pages = 154–169 | doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2015.07.033 |
- ↑ 96.0 96.1 Dundas, C., S. Bryrne, A. McEwen. 2015. Modeling the development of martian sublimation thermokarst landforms. Icarus: 262, 154-169.