Difference between revisions of "Carbon cycle"
(initial version) |
m (bigger picture) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
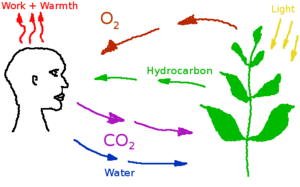
The natural '''Carbon Cycle''' describes the way of energetic interaction of [[plants]] and [[animals]]. | The natural '''Carbon Cycle''' describes the way of energetic interaction of [[plants]] and [[animals]]. | ||
| − | [[Image:carbon_cycle_simplified.png|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:carbon_cycle_simplified.png|thumb|right|300px|The Carbon Cycle (simplified)]] |
The [[CO2]] is consumed by the [[food]] plants. This is part of the carbon cycle, assumed that all food is grown by food plants in the [[colony]]. All [[hydrocarbon]] intake is exhaled as CO2 after digestion and metabolizing. Exactly the same amount of CO2 is inhaled by the food plants and metabolized to hydrocarbons. The carbon is neither created nor destroyed anywhere in the cycle. | The [[CO2]] is consumed by the [[food]] plants. This is part of the carbon cycle, assumed that all food is grown by food plants in the [[colony]]. All [[hydrocarbon]] intake is exhaled as CO2 after digestion and metabolizing. Exactly the same amount of CO2 is inhaled by the food plants and metabolized to hydrocarbons. The carbon is neither created nor destroyed anywhere in the cycle. | ||
Revision as of 12:31, 27 October 2015
The natural Carbon Cycle describes the way of energetic interaction of plants and animals.
The CO2 is consumed by the food plants. This is part of the carbon cycle, assumed that all food is grown by food plants in the colony. All hydrocarbon intake is exhaled as CO2 after digestion and metabolizing. Exactly the same amount of CO2 is inhaled by the food plants and metabolized to hydrocarbons. The carbon is neither created nor destroyed anywhere in the cycle.