Difference between revisions of "Multi-layered vault settlement"
(→Brick: elaboration) |
(Small grammar fixes) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SettlementType}} | {{SettlementType}} | ||
| + | [[File:Mezquita on Mars.jpg|thumb|400x400px|An early evolution of a multiple dome settlement. With only one layer of steel domes and with a thick regolith covering.]] | ||
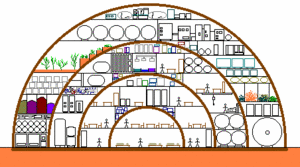
A '''multi-layered vault settlement''' is a [[building]], consisting of several shells. Each shell serves a different purpose: The central shell is the best protected part of the settlement, best useful for living rooms. The outermost shell contains store rooms, [[greenhouse]]s, machinery, etc. It can be dome or barrel shaped. | A '''multi-layered vault settlement''' is a [[building]], consisting of several shells. Each shell serves a different purpose: The central shell is the best protected part of the settlement, best useful for living rooms. The outermost shell contains store rooms, [[greenhouse]]s, machinery, etc. It can be dome or barrel shaped. | ||
[[Image:MultiLayeredDomeSettlement.gif|thumb|right|300px|Principle of a Multi-layered Vault Settlement]] | [[Image:MultiLayeredDomeSettlement.gif|thumb|right|300px|Principle of a Multi-layered Vault Settlement]] | ||
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
| − | Rectangular column, beam and girder design with | + | Rectangular column, beam and girder design with steel structural members as used on Earth would not be appropriate on Mars for any structure intended for human habitation. On Mars the first need for a habitation is that it be a pressure vessel to hold in enough air pressure for human survival, so cylindrical and spherical buildings would be built. |
| + | |||
| + | One option is to dig a semicircular cross section ditch and build a cylindrical building in the ditch with its axis horizontal. Structural tension members would wrap around the entire building; roof, wall and floor to hold air pressure in. Tensile reinforcement would also run lengthwise through the outer wall from end to end. Another option for brick construction is to have a flat slab floor semi cylindrical roof structure and enough fill material over the roof so that the weight of the fill holds in the air pressure in the building below without the need for tensile strength in the walls of the structure. About 30 feet of brick and fill would be required to provide the necessary pressure. The inner surface of the pressure vessel must be lined with a gas-impermeable layer. | ||
Buildings would be made to their design size when first built. There would be no particular advantage to building a new layer of habitation above a previous building because the previous pressure vessel would be wasted and a new outer pressure retaining layer would be required. | Buildings would be made to their design size when first built. There would be no particular advantage to building a new layer of habitation above a previous building because the previous pressure vessel would be wasted and a new outer pressure retaining layer would be required. | ||
==Material== | ==Material== | ||
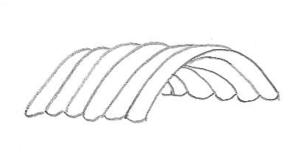
| + | ===Plastics=== | ||
| + | [[Image:FoamDome.png|thumb|left|300px|Arrangement of plastic foil hoses filled with PUR foam]] | ||
| + | A combination of inflatable hose arcs and a filling with polyurethane [[foam]] allows the construction of huge buildings without big machines. Such a [[foam dome]] is probably the first big building in a Martian settlement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The dome is started with one arc, made from a hose that is pumped up with air, thus erected. The hose has, for example, a diameter of 50 cm and a length of 100 m, so the arc spans | ||
| + | about 60 m. Then the hose is filled with PUR foam, which hardens after a short while. A series of arcs is erected, touching each other, creating a tunnel with 60 m width and, for example, 100 m length, resulting in a building with 6000 m2 floor space. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When all arcs are erected and hardened and the side walls are closed with smaller arcs, the surface is finished with an extra layer of PUR foam. This layer glues all arcs together and fills all gaps. It is reinforced with plastic or glass fibers, possibly with several layers. Finally the building is covered with a layer of regolith. | ||
| + | |||
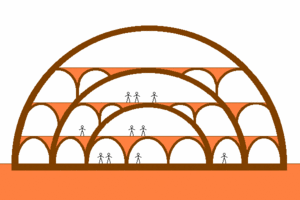
===Brick=== | ===Brick=== | ||
[[Image:MultiLayeredDomeBrick.gif|thumb|right|300px|Multi-layered Vault Settlement made from Bricks with steel reinforcement in the outer layer. Only the above ground half of structure is shown]] | [[Image:MultiLayeredDomeBrick.gif|thumb|right|300px|Multi-layered Vault Settlement made from Bricks with steel reinforcement in the outer layer. Only the above ground half of structure is shown]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 36: | ||
==Layers== | ==Layers== | ||
===Innermost layer=== | ===Innermost layer=== | ||
| − | * Sleeping rooms | + | |
| − | * Living rooms | + | *Sleeping rooms |
| + | *Living rooms | ||
===Middle layer=== | ===Middle layer=== | ||
| − | * Working rooms | + | |
| − | * Vital machinery | + | *Working rooms |
| + | *Vital machinery | ||
===Outermost layer=== | ===Outermost layer=== | ||
| − | * Storage of material and inventories | + | |
| + | *Storage of material and inventories | ||
==Open issues== | ==Open issues== | ||
| + | |||
*What is better for radiation shielding and protection against meteorites: A brick vault or a steel vault? | *What is better for radiation shielding and protection against meteorites: A brick vault or a steel vault? | ||
{{SettlementIndex}} | {{SettlementIndex}} | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Construction, Assembly, Maintenance]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Construction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:39, 5 November 2020
|
v · d · eSettlement Types | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
A multi-layered vault settlement is a building, consisting of several shells. Each shell serves a different purpose: The central shell is the best protected part of the settlement, best useful for living rooms. The outermost shell contains store rooms, greenhouses, machinery, etc. It can be dome or barrel shaped.
Contents
Properties
Rectangular column, beam and girder design with steel structural members as used on Earth would not be appropriate on Mars for any structure intended for human habitation. On Mars the first need for a habitation is that it be a pressure vessel to hold in enough air pressure for human survival, so cylindrical and spherical buildings would be built.
One option is to dig a semicircular cross section ditch and build a cylindrical building in the ditch with its axis horizontal. Structural tension members would wrap around the entire building; roof, wall and floor to hold air pressure in. Tensile reinforcement would also run lengthwise through the outer wall from end to end. Another option for brick construction is to have a flat slab floor semi cylindrical roof structure and enough fill material over the roof so that the weight of the fill holds in the air pressure in the building below without the need for tensile strength in the walls of the structure. About 30 feet of brick and fill would be required to provide the necessary pressure. The inner surface of the pressure vessel must be lined with a gas-impermeable layer.
Buildings would be made to their design size when first built. There would be no particular advantage to building a new layer of habitation above a previous building because the previous pressure vessel would be wasted and a new outer pressure retaining layer would be required.
Material
Plastics
A combination of inflatable hose arcs and a filling with polyurethane foam allows the construction of huge buildings without big machines. Such a foam dome is probably the first big building in a Martian settlement.
The dome is started with one arc, made from a hose that is pumped up with air, thus erected. The hose has, for example, a diameter of 50 cm and a length of 100 m, so the arc spans about 60 m. Then the hose is filled with PUR foam, which hardens after a short while. A series of arcs is erected, touching each other, creating a tunnel with 60 m width and, for example, 100 m length, resulting in a building with 6000 m2 floor space.
When all arcs are erected and hardened and the side walls are closed with smaller arcs, the surface is finished with an extra layer of PUR foam. This layer glues all arcs together and fills all gaps. It is reinforced with plastic or glass fibers, possibly with several layers. Finally the building is covered with a layer of regolith.
Brick
Bricks from sintered regolith allow the construction of vaults without any further material if the building is for unpressurized storage. Gravity alone stabilizes the building. Neither reinforcement nor grout is necessary. However, for people to inhabit a structure on Mars it needs to retain atmospheric pressure.
Specialized bricks (e.g. arch segments) can be made for every vault radius and for special shapes. Advantage: The strength of a brick vault can be optimized. Disadvantage: The effort for manufacturing a great variety of bricks is high. A brick dome on Mars will require steel, fiberglass, or some other structural reinforcement strong in tension to hold in air pressure. It will be most economical to continue the tension members below ground level to form a fully spherical building with the hemispherical dome showing on top and the inverted dome section for a basement and sub basement.
Universal bricks allow different vault radius and shapes with only one sort of brick. Advantage: The manufacturing can be automated easily. Disadvantage: The strength of the masonry depends on the connection between the bricks. It is inevitably weaker than a vault from specialized bricks, for the pressure does not act perpendicular at the surface of each brick in most cases. The requirement for reinforcement material in the outermost wall to retain air pressure is the same as for other brick.
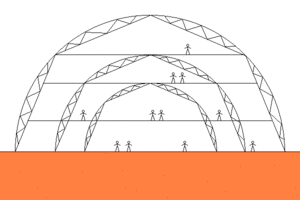
Steel
Steel allows the construction of a great variety of vault shapes. Since steel provides great strength even with thin girders, such vaults provide optimal space inside. Disadvantages: Steel is probably more expensive to produce than bricks.
Layers
Innermost layer
- Sleeping rooms
- Living rooms
Middle layer
- Working rooms
- Vital machinery
Outermost layer
- Storage of material and inventories
Open issues
- What is better for radiation shielding and protection against meteorites: A brick vault or a steel vault?
| Concepts: | Greenhouse · Settlements · Locations · General |
| Hazards: | Space Weather · Climate · General |
| Technology: | Hi-Tech · Lo-Tech · Energy · Spaceflight science · Communication · General |
| Human Considerations: | Economics · Health · Governance · Trade · Law · Social |