Difference between revisions of "Methanol"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:Methanol Lewis.svg|thumb|200x200px|Methanol molecule]] | ||
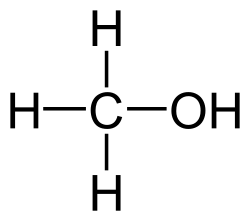
'''Methanol''', [[carbon|C]][[hydrogen|H]]<sub>3</sub>[[oxygen|O]]H, is the simplest [[alcohol]]. It is commonly used as a building block for other chemicals, such as [[formaldehyde]], [[acetic acid]], and [[dimethyl ether]]. Like [[ethanol]] and other alcohols, methanol is toxic and highly flammable. | '''Methanol''', [[carbon|C]][[hydrogen|H]]<sub>3</sub>[[oxygen|O]]H, is the simplest [[alcohol]]. It is commonly used as a building block for other chemicals, such as [[formaldehyde]], [[acetic acid]], and [[dimethyl ether]]. Like [[ethanol]] and other alcohols, methanol is toxic and highly flammable. | ||
Methanol is a liquid [[carbohydrate]], thus capable of [[energy storage|storing large amounts of energy]]. In a [[settlement]] on [[Mars]] it has the potential to play a central part of [[energy]] management. Additionally, it can be used as a resource for making other carbohydrates, to feed [[Biological_reactors|methanotrophs]] or to produce [[synthetic materials]]. | Methanol is a liquid [[carbohydrate]], thus capable of [[energy storage|storing large amounts of energy]]. In a [[settlement]] on [[Mars]] it has the potential to play a central part of [[energy]] management. Additionally, it can be used as a resource for making other carbohydrates, to feed [[Biological_reactors|methanotrophs]] or to produce [[synthetic materials]]. | ||
| − | == | + | ==[[In-situ resource utilization|In Situ Production]]== |
| − | Methanol can be produced from CO and H<sub>2</sub> ([[Syngas]]) | + | Methanol can be produced on Mars from CO and H<sub>2</sub> ([[Syngas]]) |
CO and H<sub>2</sub> can be produced from [[methane]] and [[water]]: | CO and H<sub>2</sub> can be produced from [[methane]] and [[water]]: | ||
| + | |||
:CH<sub>4</sub> + H<sub>2</sub>O → CO + 3 H<sub>2</sub> | :CH<sub>4</sub> + H<sub>2</sub>O → CO + 3 H<sub>2</sub> | ||
CO can also be produced from CO<sub>2</sub> via high temperature electrolysis in a [[Atmospheric_processing|MOXIE]] or chemically using the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bosch_reaction Bosch reaction]: | CO can also be produced from CO<sub>2</sub> via high temperature electrolysis in a [[Atmospheric_processing|MOXIE]] or chemically using the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bosch_reaction Bosch reaction]: | ||
| + | |||
:CO<sub>2</sub> + H<sub>2</sub> → H<sub>2</sub>O + CO | :CO<sub>2</sub> + H<sub>2</sub> → H<sub>2</sub>O + CO | ||
H<sub>2</sub> is obtained from the splitting of [[water]]: | H<sub>2</sub> is obtained from the splitting of [[water]]: | ||
| + | |||
:2H<sub>2</sub>O → 2H<sub>2</sub> + O<sub>2</sub> | :2H<sub>2</sub>O → 2H<sub>2</sub> + O<sub>2</sub> | ||
Synthesis of methanol: | Synthesis of methanol: | ||
| − | |||
| + | :CO + 2 H<sub>2</sub> → CH<sub>3</sub>OH (Copper-based catalyst<ref>https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-099424-6.00012-0</ref> at 200–300°C and 3.5–10 MPa, ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Uses == | ||
| + | Methanol can be used to produce a large number of hydrocarbons and other chemicals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When combined with [[methane]] it is a possible precursor for aromatic hydrocarbons such as [[ethane]] and [[toluene]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
[[category:Materials]] | [[category:Materials]] | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 09:27, 26 May 2021
Methanol, CH3OH, is the simplest alcohol. It is commonly used as a building block for other chemicals, such as formaldehyde, acetic acid, and dimethyl ether. Like ethanol and other alcohols, methanol is toxic and highly flammable.
Methanol is a liquid carbohydrate, thus capable of storing large amounts of energy. In a settlement on Mars it has the potential to play a central part of energy management. Additionally, it can be used as a resource for making other carbohydrates, to feed methanotrophs or to produce synthetic materials.
In Situ Production
Methanol can be produced on Mars from CO and H2 (Syngas)
CO and H2 can be produced from methane and water:
- CH4 + H2O → CO + 3 H2
CO can also be produced from CO2 via high temperature electrolysis in a MOXIE or chemically using the Bosch reaction:
- CO2 + H2 → H2O + CO
H2 is obtained from the splitting of water:
- 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
Synthesis of methanol:
- CO + 2 H2 → CH3OH (Copper-based catalyst[1] at 200–300°C and 3.5–10 MPa, )
Uses
Methanol can be used to produce a large number of hydrocarbons and other chemicals.
When combined with methane it is a possible precursor for aromatic hydrocarbons such as ethane and toluene.