InSight Mission
NASA’s Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) made a soft landing as planned on November 26, 2018. It is the first space robotic explorer to study the inside of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. It set down at exactly 2:52:59 p.m. EST. We found out about the landing by way of two small experimental Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats. They were launched on the same rocket as InSight and relayed information from the lander. [1] The launch took place with an Atlas V-401 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California on May 5, 2018 7:05 a.m. ET. It’s main instruments are a seismometer (SEIS), a heat probe, and a radio science instrument (RISE).[2]
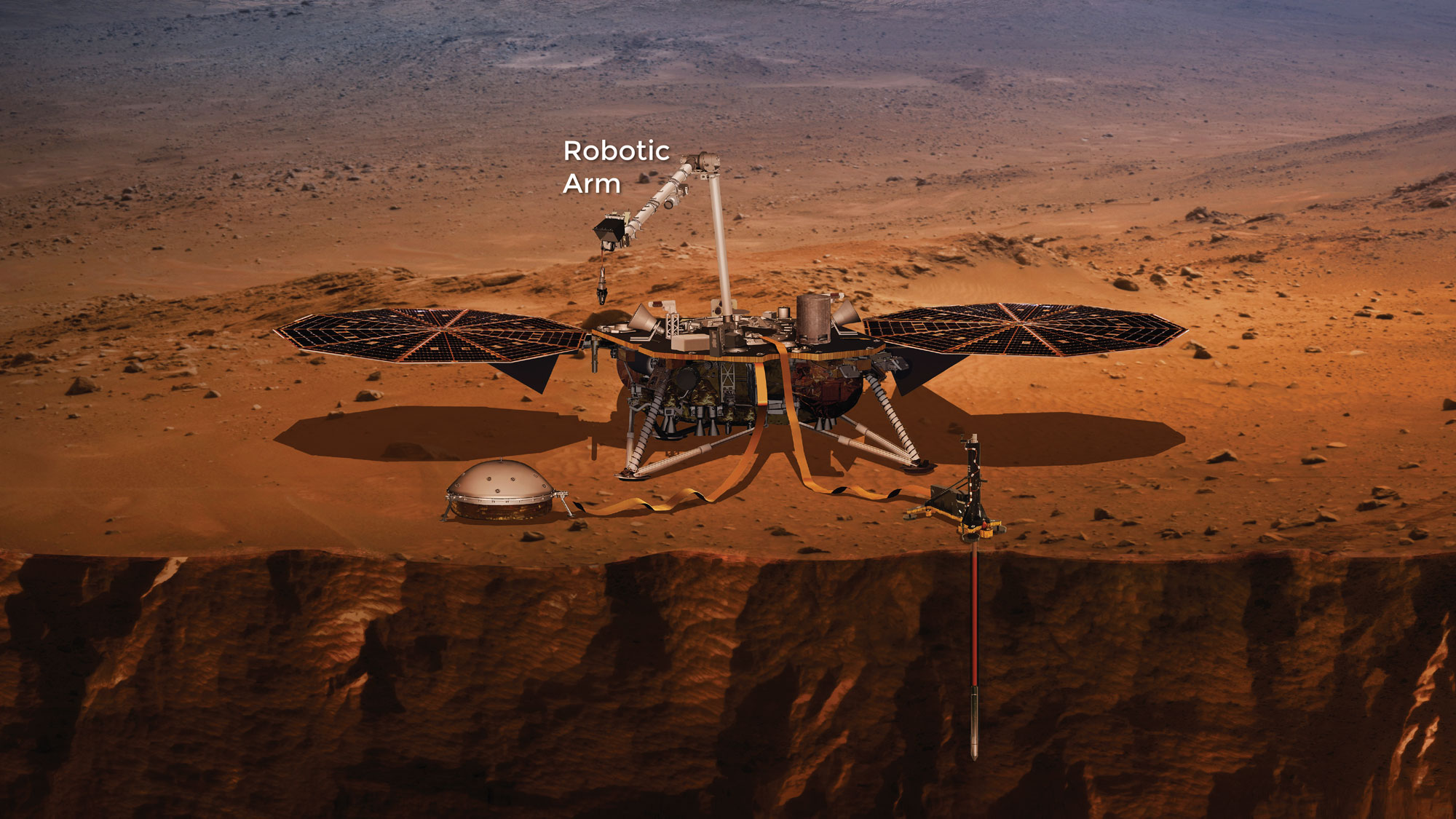
Artist’s conception of Insight lander sitting on Mars with instruments deployed
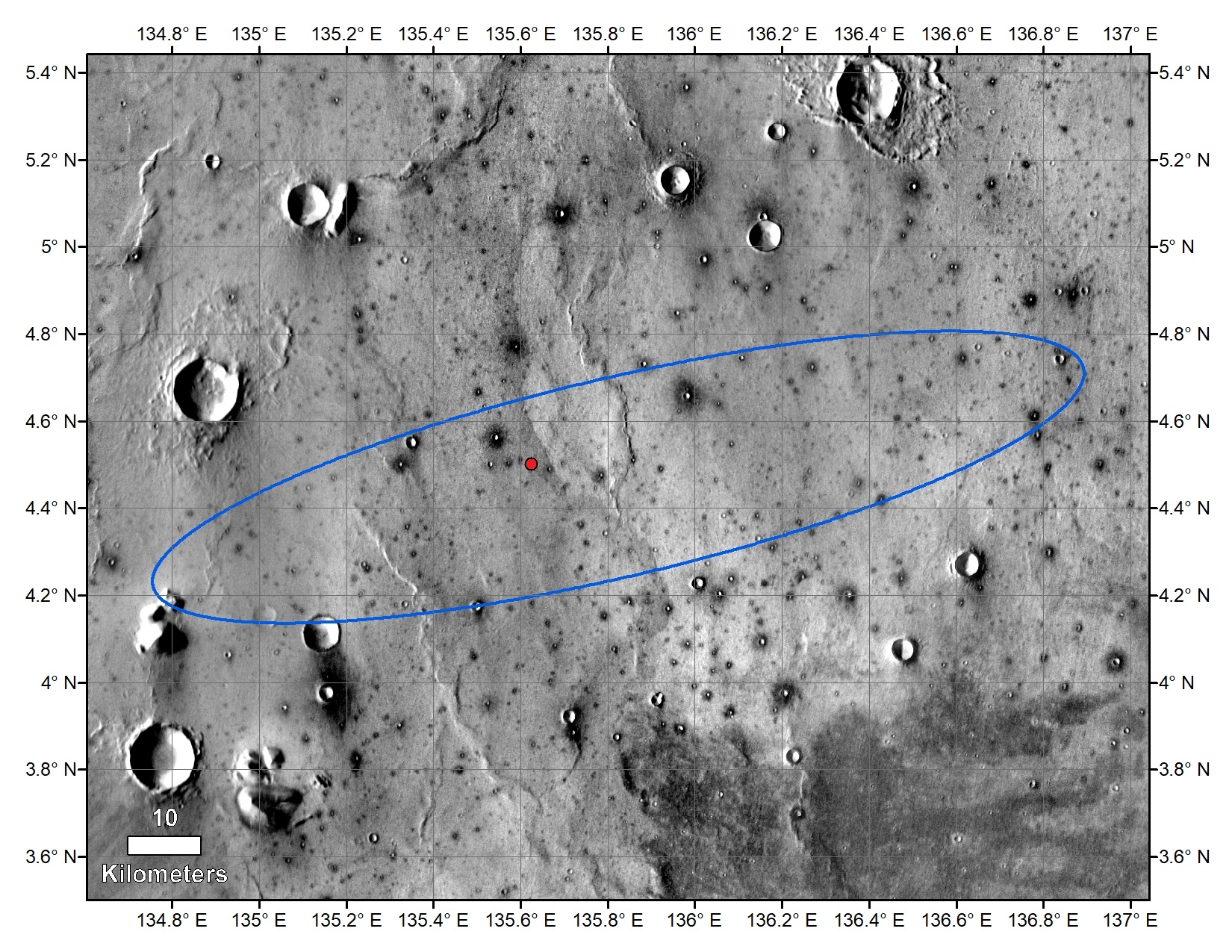
The red dot shows where InSight landed. It landed just about in the center of its landing ellipse. The location is in the Elysium quadrangle at about 4.5 N and 135.6 E (224.4 W).
Contents
Spacecraft
InSight weighs 794 pounds (360 kilograms). It is 19 feet 8 inches (6 meters) with solar panels deployed ("wingspan"), and its deck is 5 feet 1 inch (1.56 meters) in diameter.[3]
Mission Activities
December 19, 2018, InSight's seismometer was set onto the ground directly in front of the lander, about as far away as the arm can reach ---- 5.367 feet. Principal Investigator Bruce Banerdt, stated "The seismometer is the highest-priority instrument on InSight: We need it in order to complete about three-quarters of our science objectives." The seismometer allows scientists to peer into the Martian interior by studying ground motion — also known as marsquakes. Each marsquake acts as a kind of flashbulb that illuminates the structure of the planet's interior. By studying how seismic waves pass through the layers of the planet, scientists can deduce the depth and composition of these layers.[4]
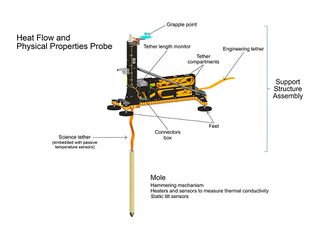
On February 13, 2019, NASA announced that the InSight lander has placed its second instrument on the Martian surface. New images confirm that the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package, or HP3, was successfully deployed on Feb. 12 about 3 feet (1 meter) from InSight's seismometer. HP3 measures heat moving through Mars' subsurface.
Equipped with a self-hammering spike, mole, the instrument will burrow up to 16 feet (5 meters) below the surface, deeper than any previous mission to the Red Planet. This compares to, the Viking 1 lander which went down 8.6 inches (22 centimeters). While the Phoenix lander dug down 7 inches (18 centimeters).
HP3 looks a bit like an automobile jack but with a vertical metal tube up front to hold the 16-inch-long (40-centimeter-long) mole. A tether connects HP3's support structure to the lander, while a tether attached to the top of the mole features heat sensors to measure the temperature of the Martian subsurface. Meanwhile, heat sensors in the mole itself will measure the soil's thermal conductivity, that is how easily heat moves through the subsurface.
The mole will stop every 19 inches (50 centimeters) to take a thermal conductivity measurement of the soil. Because hammering creates friction and releases heat, the mole is first allowed to cool down for a good two days. Then it will be heated up by about 50 degrees Fahrenheit (10 degrees Celsius) over 24 hours. Temperature sensors within the mole measure how rapidly this happens, which tells scientists the conductivity of the soil. If the mole encounters a large rock before reaching at least 10 feet (3 meters) down, the team will need a full Martian year (two Earth years) to filter noise out of their data. This is one reason the team carefully selected a landing site with few rocks and why it spent weeks picking where to place the instrument.[5]
Mission Discoveries
InSight's seismometer recorded its first marsquake on April 6, 2019, and its largest seismic signal to date at 7:23 p.m. PDT (10:23 EDT) on May 22, 2019. That last event is believed to be a marsquake of magnitude 3.0.[6] [7]
References
- ↑ https://mars.nasa.gov/news/8392/nasa-insight-lander-arrives-on-martian-surface/?site=insight
- ↑ https://mars.nasa.gov/insight/spacecraft/instruments/summary/
- ↑ https://mars.nasa.gov/insight/spacecraft/about-the-lander/
- ↑ https://mars.nasa.gov/news/8402/nasas-insight-places-first-instrument-on-mars/?site=insight
- ↑ https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7335&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily-20190213-4
- ↑ https://outlook.live.com/mail/inbox/id/AQMkADAwATExAGNiNy00YzQ1LTM4MjMtMDACLTAwCgBGAAADdsmEa%2FgtIEmBK%2FX8yb671wcAkr%2FaXi2mwEKimhNbcs0ITQAAAgEMAAAAkr%2FaXi2mwEKimhNbcs0ITQACxRb2xwAAAA%3D%3D
- ↑ https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=7383&utm_source=iContact&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=nasajpl&utm_content=daily-20190605-1
See Also
Recommended reading
- Kieffer, H., et al. (eds) 1992. Mars. The University of Arizona Press. Tucson
- JPL Mission to Mars InSight