Difference between revisions of "InSight Mission"
(tried to create new article with info, ref, images, links) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
NASA’s Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport ( InSight) made a soft landing as planned on November 26, 2018. It is the first space robotic explorer to study the inside of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. It set down at exactly 2:52:59 p.m. EST. We found out about the landing by way of two small experimental Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats. They were launched on the same rocket as InSight and relayed information from the lander. <ref> https://mars.nasa.gov/news/8392/nasa-insight-lander-arrives-on-martian-surface/?site=insight</ref> | NASA’s Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport ( InSight) made a soft landing as planned on November 26, 2018. It is the first space robotic explorer to study the inside of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. It set down at exactly 2:52:59 p.m. EST. We found out about the landing by way of two small experimental Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats. They were launched on the same rocket as InSight and relayed information from the lander. <ref> https://mars.nasa.gov/news/8392/nasa-insight-lander-arrives-on-martian-surface/?site=insight</ref> | ||
The launch took place with an Atlas V-401 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California on May 5, 2018 7:05 a.m. ET. It’s main instruments are seismometer (SEIS), a heat probe, and a radio science instrument (RISE).<ref> https://mars.nasa.gov/insight/spacecraft/instruments/summary/</ref> | The launch took place with an Atlas V-401 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California on May 5, 2018 7:05 a.m. ET. It’s main instruments are seismometer (SEIS), a heat probe, and a radio science instrument (RISE).<ref> https://mars.nasa.gov/insight/spacecraft/instruments/summary/</ref> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File: File:Insightlander.jpg |600pxr|Insight lander]] | ||
Artist’s conception of Insight lander sitting on Mars with instruments deployed | Artist’s conception of Insight lander sitting on Mars with instruments deployed | ||
Revision as of 16:10, 15 December 2018
NASA’s Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport ( InSight) made a soft landing as planned on November 26, 2018. It is the first space robotic explorer to study the inside of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. It set down at exactly 2:52:59 p.m. EST. We found out about the landing by way of two small experimental Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats. They were launched on the same rocket as InSight and relayed information from the lander. [1] The launch took place with an Atlas V-401 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California on May 5, 2018 7:05 a.m. ET. It’s main instruments are seismometer (SEIS), a heat probe, and a radio science instrument (RISE).[2]
Insight lander Artist’s conception of Insight lander sitting on Mars with instruments deployed
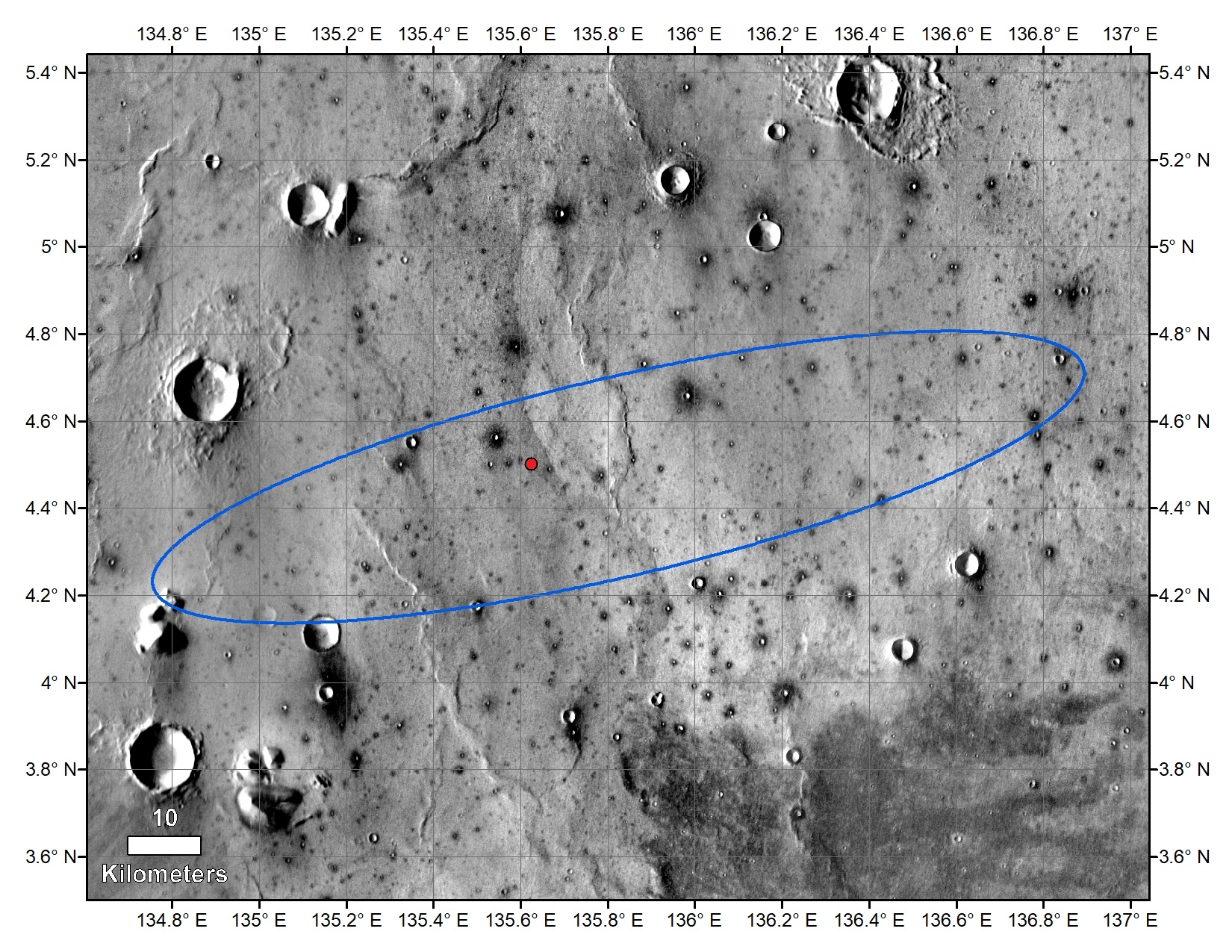
The red dot shows where InSight landed. It landed just about in the center of its landing ellipse.
Spacecraft
InSight weighs 794 pounds (360 kilograms). It is 19 feet 8 inches (6 meters) with solar panels deployed ("wingspan") and its deck is 5 feet 1 inch (1.56 meters) in diameter.[3]
[[File:ESP 058005 1845-lander-full-res.jpg |right|thumb|320px|InSight sitting on the surface, as seen by HiRISE
References
See Also
Recommended reading
- Kieffer, H., et al. (eds) 1992. Mars. The University of Arizona Press. Tucson
- JPL Mission to Mars InSight
External links
- [[1]
- Mission Control Live: NASA InSight Mars Landing
- How NASA's Next Mars Mission Will Take the Red Planet's Pulse | Decoder