Difference between revisions of "Elysium quadrangle"
(→Volcanoes: added picture possibilites for this section) |
(→Volcanoes: added a new section that I will edit) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
File:ESP 054891 2040lavarafts.jpg|Lava rafts, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | File:ESP 054891 2040lavarafts.jpg|Lava rafts, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Rootless cone]]s== | ||
| + | |||
| + | So-called "Rootless cones" are caused by explosions of lava with ground ice under the flow.<ref>Keszthelyi, L. et al. 2010. Hydrovolcanic features on Mars: Preliminary observations from the first Mars year of HiRISE. Icarus: 205, 211-229. imaging</ref><ref name="psrd.hawaii.edu">http://www.psrd.hawaii.edu/June01/lavaIceMars.html</ref><ref>Lanagan, P., A. McEwen, L. Keszthelyi, and T. Thordarson. 2001. Rootless cones on Mars indicating the presence of shallow equatorial ground ice in recent times, Geophysical Research Letters: 28, 2365-2368.</ref> The ice melts and turns into a vapor that expands in an explosion that produces a cone or ring. Features like these are found in Iceland, when lavas cover water-saturated substrates.<ref>S. Fagents1, A., P. Lanagan, R. Greeley. 2002. Rootless cones on Mars: a consequence of lava-ground ice interaction. Geological Society, Londo. Special Publications: 202, 295-317.</ref> <ref name="psrd.hawaii.edu"/> <ref>Jaeger, W., L. Keszthelyi, A. McEwen, C. Dundas, P. Russell, and the HiRISE team. 2007. EARLY HiRISE OBSERVATIONS OF RING/MOUND LANDFORMS IN ATHABASCA VALLES, MARS. Lunar and Planetary Science XXXVIII 1955.pdf.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery class="center" widths="190px" heights="180px" > | ||
| + | |||
| + | ESP 052267 2065rootlesscones.jpg|Wide view of field of rootless cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 52267 2065rootlessconesclose.jpg|Close view of field of rootless cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | |||
| + | Image:Rootless Cones.jpg|Rootless Cones, as seen by HiRISE. The chains of rings are interpreted to be caused by crust moving over a source of steam. The steam was produced by lava interacting with water ice. | ||
| + | ESP 037643 2060cones.jpg|Rootless Cones, as seen by HiRISE under [[HiWish program]] These group of rings or cones are believed to be caused by lava flowing over water ice or ground containing water ice. The ice quickly changes to steam which blows out a ring or cone. | ||
| + | Wikiesp37643 2060cones.jpg|Rootless Cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. These group of rings or cones are believed to be caused by lava flowing over water ice or ground containing water ice. The ice quickly changes to steam which blows out a ring or cone. Here the kink in the chain may have been caused by the lava changing direction. | ||
| + | Wikiesp37643 2060coneslong.jpg|Rootless Cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. These group of rings or cones are believed to be caused by lava flowing over water ice or ground containing water ice. The ice quickly changes to steam which blows out a ring or cone. Here the kink in the chain may have been caused by the lava changing direction. Some of the forms do not have the shape of rings or cones because maybe the lava moved too quickly; thereby not allowing a complete cone shape to form. | ||
| + | ESP 040162 2065conesrings.jpg|Cones and possible maars, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 045384 2065lavaice.jpg|Wide view of field of rootless cones in Phlegra region, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 45384 2065cones.jpg|Close view of rootless cones with tails that suggest lava was moving toward the Southwest over ice-rich ground, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 45384 2065conesclose.jpg|Close view of cones with the size of a football field shown, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 045464 2175cones.jpg|Close view of cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 045819 2085lavacones.jpg|Cones and surface of lava, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | 45819 2085cones.jpg|Cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program | ||
| + | ESP 045885 2070cones.jpg|Cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program These cones probably formed when hot lava flowed over ice-rich ground. | ||
| + | 45885 2070cones.jpg|Close view of cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program These cones probably formed when hot lava flowed over ice-rich ground. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 28 February 2020
| MC-15 | Elysium | 0–30° N | 135–180° E | Quadrangles | Atlas |
This quadrangle was named after Elysium, a place of reward (Heaven), according to Homer in the Odyssey.[1]
The Elysium quadrangle covers the area between 180° to 225° west longitude and 0° to 30° north latitude on Mars. A small part of the Medusae Fossae Formation lies in this quadrangle. Eddie, Lockyer, and Tombaugh are the largest craters in the Elysium quadrangle. Elysium Mons and Albor Tholus are large volcanoes in this quadrangle. Just outside the boundaries of Elysium quadrangle sits another large volcano called Hecates. There are possible giant river valleys in this area. Athabasca Valles may be one of the youngest on the planet. A large lake may once have existed in the south near Lethe Valles and Athabasca Valles.[2]
The InSight lander touched down in the southern part of this quadrangle in 2018 and is now gathering data especially on Marsquakes.
Volcanoes
The area near the volcanoes of Elysium is covered with lava flows. On close examination, some flows can even be seen to approach and then stop when reaching higher ground. (See pictures below for examples) The top of a lava flow often cools quickly , forming a hard crust, but it still moves under the crust. Such movement breaks up the top layer making it very rough.[3] Such rough flow is called aa lava. The lava flows here are of the aa variety.
Some places in the Elysium quadrangle are young geological. Some researchers call them Platy-Ridged-Polygonized terrain. The surface of this terrain has been suggested to be pack ice, basalt lava, or muddy flows. HiRISE images show the heights of the surface ridges to be usually less than 2 meters. This is far less than what is expected from lava flows. In addition the high resolution photos of HiRISE indicates that the surface appears to flow. This would not occur with pack ice. So, the researchers concluded that muddy flows cover the surface.[4] For a while, many believed the surface was made of ice flows, which it resembles.
Lava flow in Elysium. There are many lava flows in Elysium. In this one, the lava flowed toward the upper right. Image taken by Mars Global Surveyor, under the MOC Public Targeting Program.
Lava flow, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Dark slope streaks are also visible
Lava flows in Elysium as seen by HiRISE. Upper part of image shows lava that solidified on the top then crumpled as lava still moved.
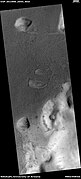
Rootless cones
So-called "Rootless cones" are caused by explosions of lava with ground ice under the flow.[5][6][7] The ice melts and turns into a vapor that expands in an explosion that produces a cone or ring. Features like these are found in Iceland, when lavas cover water-saturated substrates.[8] [6] [9]
Rootless Cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program These group of rings or cones are believed to be caused by lava flowing over water ice or ground containing water ice. The ice quickly changes to steam which blows out a ring or cone.
Rootless Cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. These group of rings or cones are believed to be caused by lava flowing over water ice or ground containing water ice. The ice quickly changes to steam which blows out a ring or cone. Here the kink in the chain may have been caused by the lava changing direction.
Rootless Cones, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. These group of rings or cones are believed to be caused by lava flowing over water ice or ground containing water ice. The ice quickly changes to steam which blows out a ring or cone. Here the kink in the chain may have been caused by the lava changing direction. Some of the forms do not have the shape of rings or cones because maybe the lava moved too quickly; thereby not allowing a complete cone shape to form.
References
- ↑ Blunck, J. 1982. Mars and its Satellites. Exposition Press. Smithtown, N.Y.
- ↑ "Cabrol, N 2010">Cabrol, N. and E. Grin (eds.). 2010. Lakes on Mars. Elsevier. NY.
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_010744_1840 | title=Southern Margin of Cerberus Palus (PSP_010744_1840) |
- ↑ Yue, Z., et al. 2017. AN INVESTIGATION OF THE HYPOTHESES FOR FORMATION OF THE PLATY-RIDGEDPOLYGONIZED TERRAIN IN ELYSIUM PLANITIA, MARS. Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII (2017). 1770.pdf
- ↑ Keszthelyi, L. et al. 2010. Hydrovolcanic features on Mars: Preliminary observations from the first Mars year of HiRISE. Icarus: 205, 211-229. imaging
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 http://www.psrd.hawaii.edu/June01/lavaIceMars.html
- ↑ Lanagan, P., A. McEwen, L. Keszthelyi, and T. Thordarson. 2001. Rootless cones on Mars indicating the presence of shallow equatorial ground ice in recent times, Geophysical Research Letters: 28, 2365-2368.
- ↑ S. Fagents1, A., P. Lanagan, R. Greeley. 2002. Rootless cones on Mars: a consequence of lava-ground ice interaction. Geological Society, Londo. Special Publications: 202, 295-317.
- ↑ Jaeger, W., L. Keszthelyi, A. McEwen, C. Dundas, P. Russell, and the HiRISE team. 2007. EARLY HiRISE OBSERVATIONS OF RING/MOUND LANDFORMS IN ATHABASCA VALLES, MARS. Lunar and Planetary Science XXXVIII 1955.pdf.