Difference between revisions of "List of ISRU"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
*[[Electrolysis|Water Electrolysis]] (Hydrogen-Oxygen) | *[[Electrolysis|Water Electrolysis]] (Hydrogen-Oxygen) | ||
*[[Glass]] production (SiO2) | *[[Glass]] production (SiO2) | ||
| − | *[[Steeling|Steel]] production | + | *[[Steeling|Steel]] production |
| − | *Atmospheric compression and separation | + | *Atmospheric compression and separation (N2,CO2,O2,Ar) |
| − | *[[Water Infrastructure|Water treatment]] | + | *[[Water Infrastructure|Water treatment]] (Water) |
| − | *[[Carbon dioxide electrolysis]] | + | *[[Carbon dioxide electrolysis]] (CO and hydrocarbons) |
*[[Atmosphere absorption methods]] | *[[Atmosphere absorption methods]] | ||
Revision as of 13:38, 28 December 2019
|
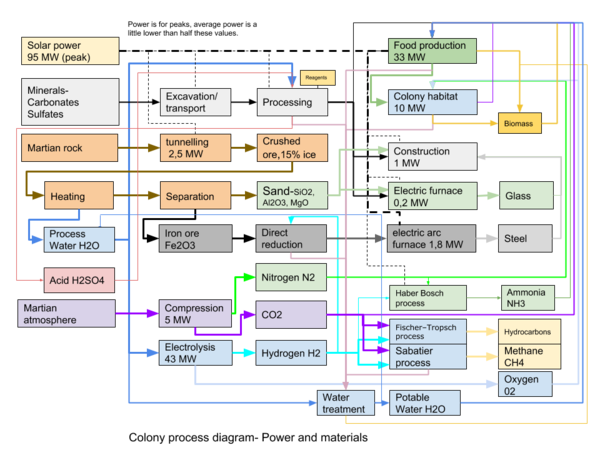
The idea of In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) is essential for a Martian colony. As part of the Mars Direct initiative it aims at the production of propellant material for a Mars return mission. The following issues are specifically considered:
- Sabatier/Water Electrolysis Process (methane fuel, CH4)
- Reverse Water-Gas Shift Reaction
- Fischer-Tropsch Reaction (hydrocarbons)
- Water Electrolysis (Hydrogen-Oxygen)
- Glass production (SiO2)
- Steel production
- Atmospheric compression and separation (N2,CO2,O2,Ar)
- Water treatment (Water)
- Carbon dioxide electrolysis (CO and hydrocarbons)
- Atmosphere absorption methods
ISRU is also part of the NASA base plan() as well as the SpaceX Mars colonisation plans().