Difference between revisions of "Carbon dioxide"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| − | CO2 will be extracted [[In-situ resource utilization|in-situ]] by [[atmospheric processing]] | + | CO2 will be extracted [[In-situ resource utilization|in-situ]] by [[atmospheric processing]] using compression and cooling. |
==Settlement atmosphere== | ==Settlement atmosphere== | ||
Revision as of 09:04, 18 April 2019
Carbon dioxide[1] (chemical formula: CO2) is a chemical substance that occupies about 96 % of Mars's atmosphere.
Molar Mass of 12(C)+32(O2)=44
Biological significance
The metabolism of human beings, animals and various microbes depends on the oxidation of carbohydrates, resulting in carbon dioxide and water exhalation. Plants use the carbon from carbon dioxide to produce carbohydrates and release the oxygen back to the atmosphere, completing the cycle.
- The reaction is: CO2(carbon dioxide) + 2H2O (water) + photons (light energy) → C(n)H2O(m) (carbohydrate) + O2(oxygen)+ H2O (water)[2]
Production
CO2 will be extracted in-situ by atmospheric processing using compression and cooling.
Settlement atmosphere
Carbon dioxide is required in the settlement atmosphere for plant metabolism. Standard concentration on Earth is increasing, so the value is a moving target. However, a concentration between 300ppm (0,03%) and 1000ppm (0,1%) is considered acceptable[3]. Nuclear submarines have varying carbon monoxide levels that can reach 9000 ppm in normal operations.
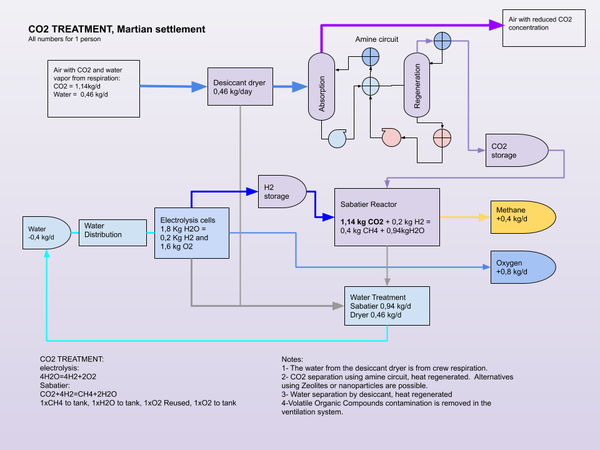
The Sabatier process can be used in place of photosynthesis to complete the atmospheric part of the carbon cycle. Synthesis of carbohydrates from methane would be required to complete the carbon metabolic cycle without the use of plants. Or food can be supplied from Earth or Mars for a partial cycle, where Methane from the Sabatier process can be stored for use as a propellant.
Uses
- Photosynthesis by plants in greenhouses to create carbohydrates for plant metabolism.
- Synthetic materials, hydrocarbons using the Fischer Tropsch reaction process.
- Propellant production. Methane (CH4) and Oxygen (O2), through ISRU using the Sabatier process. The hydrogen comes from Electrolysis of water or is brought from Earth.
- Carbon using the Bosch reaction process. The Bosch reaction consumes hydrogen to produce carbon and water. The hydrogen can come from electrolysis of water.